Dana Kianfar
NeuroSteiner: A Graph Transformer for Wirelength Estimation
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:A core objective of physical design is to minimize wirelength (WL) when placing chip components on a canvas. Computing the minimal WL of a placement requires finding rectilinear Steiner minimum trees (RSMTs), an NP-hard problem. We propose NeuroSteiner, a neural model that distills GeoSteiner, an optimal RSMT solver, to navigate the cost--accuracy frontier of WL estimation. NeuroSteiner is trained on synthesized nets labeled by GeoSteiner, alleviating the need to train on real chip designs. Moreover, NeuroSteiner's differentiability allows to place by minimizing WL through gradient descent. On ISPD 2005 and 2019, NeuroSteiner can obtain 0.3% WL error while being 60% faster than GeoSteiner, or 0.2% and 30%.
Bayesian Optimization for Macro Placement
Jul 18, 2022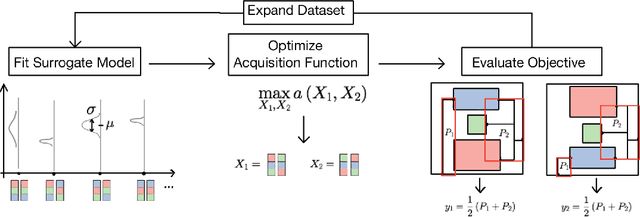
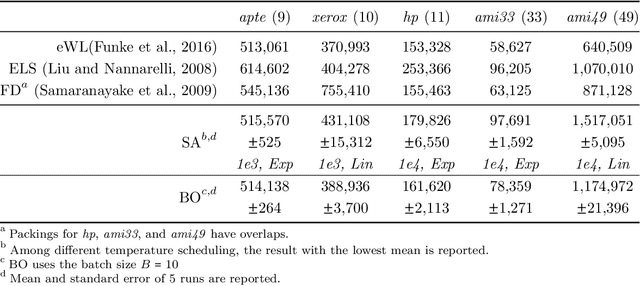
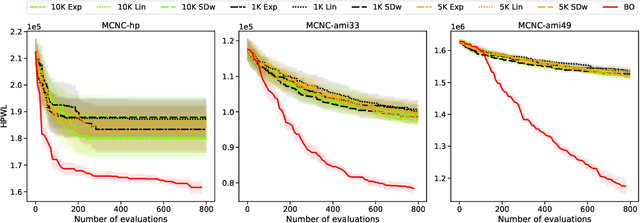
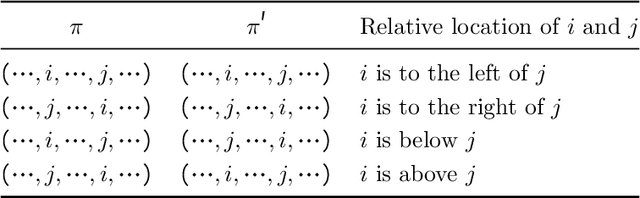
Abstract:Macro placement is the problem of placing memory blocks on a chip canvas. It can be formulated as a combinatorial optimization problem over sequence pairs, a representation which describes the relative positions of macros. Solving this problem is particularly challenging since the objective function is expensive to evaluate. In this paper, we develop a novel approach to macro placement using Bayesian optimization (BO) over sequence pairs. BO is a machine learning technique that uses a probabilistic surrogate model and an acquisition function that balances exploration and exploitation to efficiently optimize a black-box objective function. BO is more sample-efficient than reinforcement learning and therefore can be used with more realistic objectives. Additionally, the ability to learn from data and adapt the algorithm to the objective function makes BO an appealing alternative to other black-box optimization methods such as simulated annealing, which relies on problem-dependent heuristics and parameter-tuning. We benchmark our algorithm on the fixed-outline macro placement problem with the half-perimeter wire length objective and demonstrate competitive performance.
Parallelized Rate-Distortion Optimized Quantization Using Deep Learning
Dec 11, 2020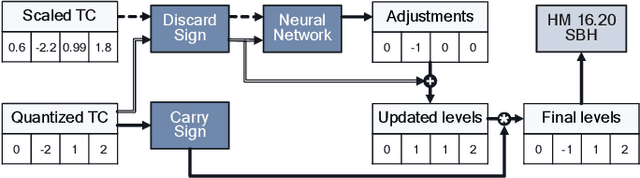
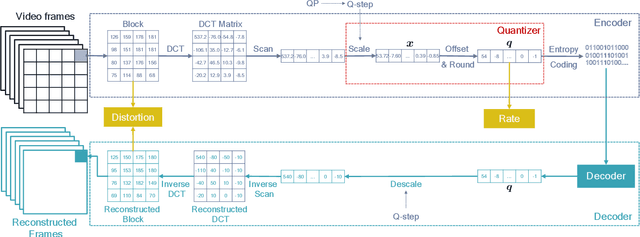
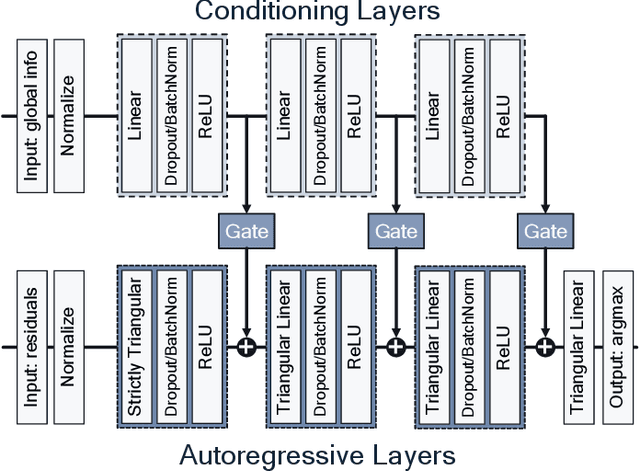
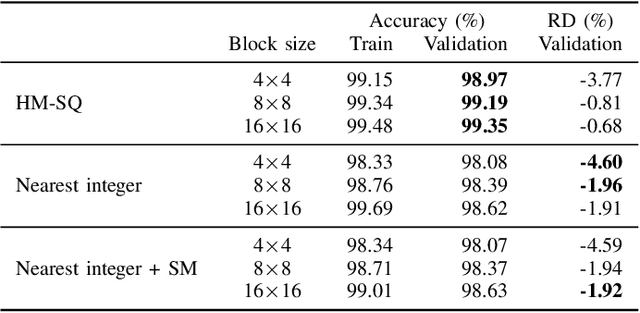
Abstract:Rate-Distortion Optimized Quantization (RDOQ) has played an important role in the coding performance of recent video compression standards such as H.264/AVC, H.265/HEVC, VP9 and AV1. This scheme yields significant reductions in bit-rate at the expense of relatively small increases in distortion. Typically, RDOQ algorithms are prohibitively expensive to implement on real-time hardware encoders due to their sequential nature and their need to frequently obtain entropy coding costs. This work addresses this limitation using a neural network-based approach, which learns to trade-off rate and distortion during offline supervised training. As these networks are based solely on standard arithmetic operations that can be executed on existing neural network hardware, no additional area-on-chip needs to be reserved for dedicated RDOQ circuitry. We train two classes of neural networks, a fully-convolutional network and an auto-regressive network, and evaluate each as a post-quantization step designed to refine cheap quantization schemes such as scalar quantization (SQ). Both network architectures are designed to have a low computational overhead. After training they are integrated into the HM 16.20 implementation of HEVC, and their video coding performance is evaluated on a subset of the H.266/VVC SDR common test sequences. Comparisons are made to RDOQ and SQ implementations in HM 16.20. Our method achieves 1.64% BD-rate savings on luminosity compared to the HM SQ anchor, and on average reaches 45% of the performance of the iterative HM RDOQ algorithm.
Examining Cooperation in Visual Dialog Models
Dec 04, 2017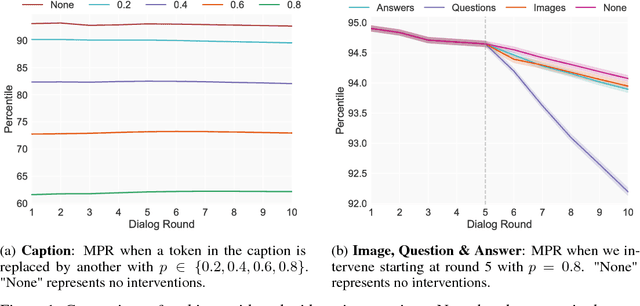
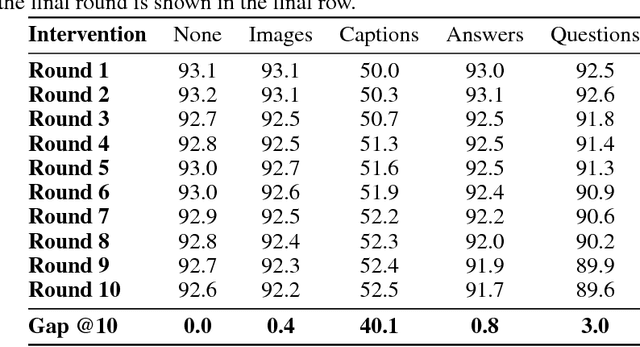
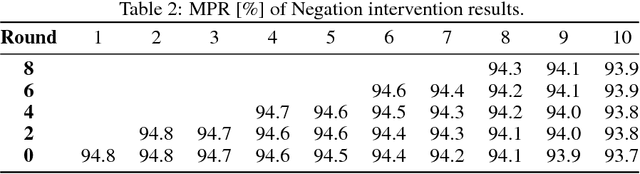

Abstract:In this work we propose a blackbox intervention method for visual dialog models, with the aim of assessing the contribution of individual linguistic or visual components. Concretely, we conduct structured or randomized interventions that aim to impair an individual component of the model, and observe changes in task performance. We reproduce a state-of-the-art visual dialog model and demonstrate that our methodology yields surprising insights, namely that both dialog and image information have minimal contributions to task performance. The intervention method presented here can be applied as a sanity check for the strength and robustness of each component in visual dialog systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge