Carolin Holtermann
SoS: Analysis of Surface over Semantics in Multilingual Text-To-Image Generation
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) models are increasingly employed by users worldwide. However, prior research has pointed to the high sensitivity of T2I towards particular input languages - when faced with languages other than English (i.e., different surface forms of the same prompt), T2I models often produce culturally stereotypical depictions, prioritizing the surface over the prompt's semantics. Yet a comprehensive analysis of this behavior, which we dub Surface-over-Semantics (SoS), is missing. We present the first analysis of T2I models' SoS tendencies. To this end, we create a set of prompts covering 171 cultural identities, translated into 14 languages, and use it to prompt seven T2I models. To quantify SoS tendencies across models, languages, and cultures, we introduce a novel measure and analyze how the tendencies we identify manifest visually. We show that all but one model exhibit strong surface-level tendency in at least two languages, with this effect intensifying across the layers of T2I text encoders. Moreover, these surface tendencies frequently correlate with stereotypical visual depictions.
TempViz: On the Evaluation of Temporal Knowledge in Text-to-Image Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Time alters the visual appearance of entities in our world, like objects, places, and animals. Thus, for accurately generating contextually-relevant images, knowledge and reasoning about time can be crucial (e.g., for generating a landscape in spring vs. in winter). Yet, although substantial work exists on understanding and improving temporal knowledge in natural language processing, research on how temporal phenomena appear and are handled in text-to-image (T2I) models remains scarce. We address this gap with TempViz, the first data set to holistically evaluate temporal knowledge in image generation, consisting of 7.9k prompts and more than 600 reference images. Using TempViz, we study the capabilities of five T2I models across five temporal knowledge categories. Human evaluation shows that temporal competence is generally weak, with no model exceeding 75% accuracy across categories. Towards larger-scale studies, we also examine automated evaluation methods, comparing several established approaches against human judgments. However, none of these approaches provides a reliable assessment of temporal cues - further indicating the pressing need for future research on temporal knowledge in T2I.
Large Language Models Discriminate Against Speakers of German Dialects
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Dialects represent a significant component of human culture and are found across all regions of the world. In Germany, more than 40% of the population speaks a regional dialect (Adler and Hansen, 2022). However, despite cultural importance, individuals speaking dialects often face negative societal stereotypes. We examine whether such stereotypes are mirrored by large language models (LLMs). We draw on the sociolinguistic literature on dialect perception to analyze traits commonly associated with dialect speakers. Based on these traits, we assess the dialect naming bias and dialect usage bias expressed by LLMs in two tasks: an association task and a decision task. To assess a model's dialect usage bias, we construct a novel evaluation corpus that pairs sentences from seven regional German dialects (e.g., Alemannic and Bavarian) with their standard German counterparts. We find that: (1) in the association task, all evaluated LLMs exhibit significant dialect naming and dialect usage bias against German dialect speakers, reflected in negative adjective associations; (2) all models reproduce these dialect naming and dialect usage biases in their decision making; and (3) contrary to prior work showing minimal bias with explicit demographic mentions, we find that explicitly labeling linguistic demographics--German dialect speakers--amplifies bias more than implicit cues like dialect usage.
Around the World in 24 Hours: Probing LLM Knowledge of Time and Place
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Reasoning over time and space is essential for understanding our world. However, the abilities of language models in this area are largely unexplored as previous work has tested their abilities for logical reasoning in terms of time and space in isolation or only in simple or artificial environments. In this paper, we present the first evaluation of the ability of language models to jointly reason over time and space. To enable our analysis, we create GeoTemp, a dataset of 320k prompts covering 289 cities in 217 countries and 37 time zones. Using GeoTemp, we evaluate eight open chat models of three different model families for different combinations of temporal and geographic knowledge. We find that most models perform well on reasoning tasks involving only temporal knowledge and that overall performance improves with scale. However, performance remains constrained in tasks that require connecting temporal and geographical information. We do not find clear correlations of performance with specific geographic regions. Instead, we find a significant performance increase for location names with low model perplexity, suggesting their repeated occurrence during model training. We further demonstrate that their performance is heavily influenced by prompt formulation - a direct injection of geographical knowledge leads to performance gains, whereas, surprisingly, techniques like chain-of-thought prompting decrease performance on simpler tasks.
GIMMICK -- Globally Inclusive Multimodal Multitask Cultural Knowledge Benchmarking
Feb 19, 2025


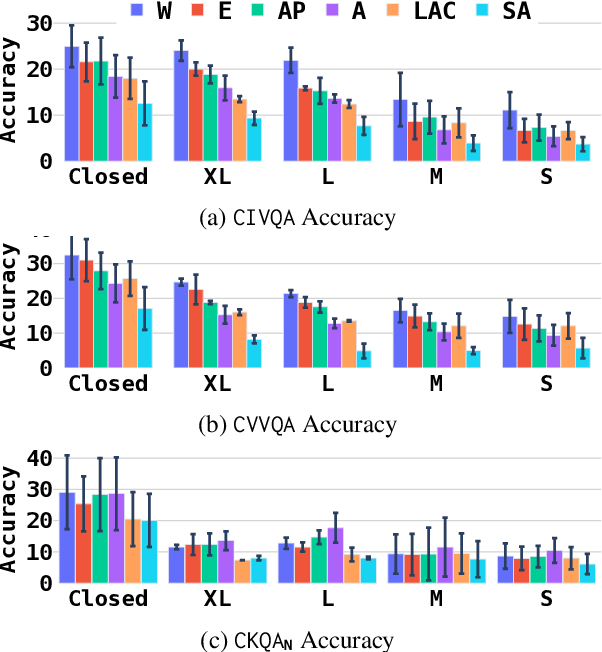
Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have recently gained attention due to their distinctive performance and broad applicability. While it has been previously shown that their efficacy in usage scenarios involving non-Western contexts falls short, existing studies are limited in scope, covering just a narrow range of cultures, focusing exclusively on a small number of cultural aspects, or evaluating a limited selection of models on a single task only. Towards globally inclusive LVLM research, we introduce GIMMICK, an extensive multimodal benchmark designed to assess a broad spectrum of cultural knowledge across 144 countries representing six global macro-regions. GIMMICK comprises six tasks built upon three new datasets that span 728 unique cultural events or facets on which we evaluated 20 LVLMs and 11 LLMs, including five proprietary and 26 open-weight models of all sizes. We systematically examine (1) regional cultural biases, (2) the influence of model size, (3) input modalities, and (4) external cues. Our analyses reveal strong biases toward Western cultures across models and tasks and highlight strong correlations between model size and performance, as well as the effectiveness of multimodal input and external geographic cues. We further find that models have more knowledge of tangible than intangible aspects (e.g., food vs. rituals) and that they excel in recognizing broad cultural origins but struggle with a more nuanced understanding.
Centurio: On Drivers of Multilingual Ability of Large Vision-Language Model
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Most Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to date are trained predominantly on English data, which makes them struggle to understand non-English input and fail to generate output in the desired target language. Existing efforts mitigate these issues by adding multilingual training data, but do so in a largely ad-hoc manner, lacking insight into how different training mixes tip the scale for different groups of languages. In this work, we present a comprehensive investigation into the training strategies for massively multilingual LVLMs. First, we conduct a series of multi-stage experiments spanning 13 downstream vision-language tasks and 43 languages, systematically examining: (1) the number of training languages that can be included without degrading English performance and (2) optimal language distributions of pre-training as well as (3) instruction-tuning data. Further, we (4) investigate how to improve multilingual text-in-image understanding, and introduce a new benchmark for the task. Surprisingly, our analysis reveals that one can (i) include as many as 100 training languages simultaneously (ii) with as little as 25-50\% of non-English data, to greatly improve multilingual performance while retaining strong English performance. We further find that (iii) including non-English OCR data in pre-training and instruction-tuning is paramount for improving multilingual text-in-image understanding. Finally, we put all our findings together and train Centurio, a 100-language LVLM, offering state-of-the-art performance in an evaluation covering 14 tasks and 56 languages.
Why do LLaVA Vision-Language Models Reply to Images in English?
Jul 02, 2024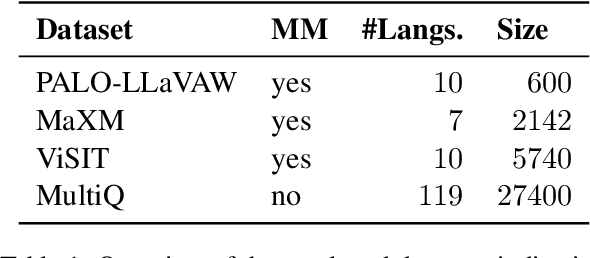
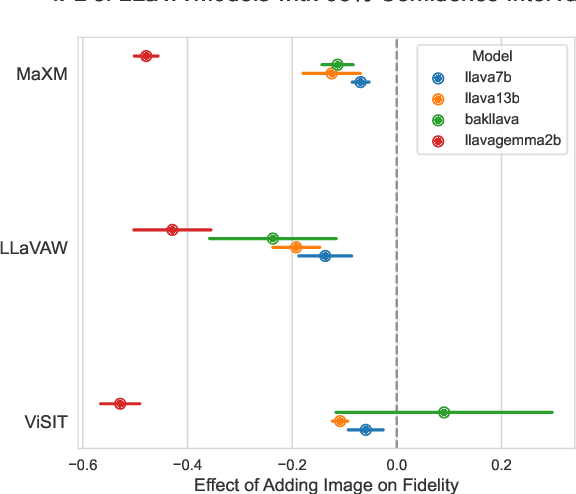
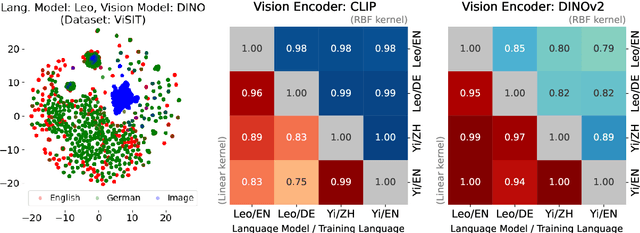
Abstract:We uncover a surprising multilingual bias occurring in a popular class of multimodal vision-language models (VLMs). Including an image in the query to a LLaVA-style VLM significantly increases the likelihood of the model returning an English response, regardless of the language of the query. This paper investigates the causes of this loss with a two-pronged approach that combines extensive ablation of the design space with a mechanistic analysis of the models' internal representations of image and text inputs. Both approaches indicate that the issue stems in the language modelling component of the LLaVA model. Statistically, we find that switching the language backbone for a bilingual language model has the strongest effect on reducing this error. Mechanistically, we provide compelling evidence that visual inputs are not mapped to a similar space as text ones, and that intervening on intermediary attention layers can reduce this bias. Our findings provide important insights to researchers and engineers seeking to understand the crossover between multimodal and multilingual spaces, and contribute to the goal of developing capable and inclusive VLMs for non-English contexts.
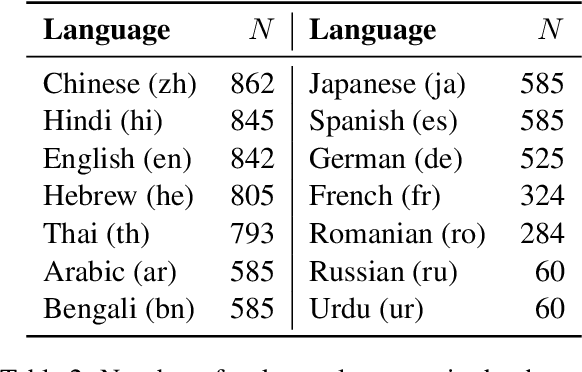
Evaluating the Elementary Multilingual Capabilities of Large Language Models with MultiQ
Mar 06, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) need to serve everyone, including a global majority of non-English speakers. However, most LLMs today, and open LLMs in particular, are often intended for use in just English (e.g. Llama2, Mistral) or a small handful of high-resource languages (e.g. Mixtral, Qwen). Recent research shows that, despite limits in their intended use, people prompt LLMs in many different languages. Therefore, in this paper, we investigate the basic multilingual capabilities of state-of-the-art open LLMs beyond their intended use. For this purpose, we introduce MultiQ, a new silver standard benchmark for basic open-ended question answering with 27.4k test questions across a typologically diverse set of 137 languages. With MultiQ, we evaluate language fidelity, i.e.\ whether models respond in the prompted language, and question answering accuracy. All LLMs we test respond faithfully and/or accurately for at least some languages beyond their intended use. Most models are more accurate when they respond faithfully. However, differences across models are large, and there is a long tail of languages where models are neither accurate nor faithful. We explore differences in tokenization as a potential explanation for our findings, identifying possible correlations that warrant further investigation.
What the Weight?! A Unified Framework for Zero-Shot Knowledge Composition
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:The knowledge encapsulated in a model is the core factor determining its final performance on downstream tasks. Much research in NLP has focused on efficient methods for storing and adapting different types of knowledge, e.g., in dedicated modularized structures, and on how to effectively combine these, e.g., by learning additional parameters. However, given the many possible options, a thorough understanding of the mechanisms involved in these compositions is missing, and hence it remains unclear which strategies to utilize. To address this research gap, we propose a novel framework for zero-shot module composition, which encompasses existing and some novel variations for selecting, weighting, and combining parameter modules under a single unified notion. Focusing on the scenario of domain knowledge and adapter layers, our framework provides a systematic unification of concepts, allowing us to conduct the first comprehensive benchmarking study of various zero-shot knowledge composition strategies. In particular, we test two module combination methods and five selection and weighting strategies for their effectiveness and efficiency in an extensive experimental setup. Our results highlight the efficacy of ensembling but also hint at the power of simple though often-ignored weighting methods. Further in-depth analyses allow us to understand the role of weighting vs. top-k selection, and show that, to a certain extent, the performance of adapter composition can even be predicted.
ScaLearn: Simple and Highly Parameter-Efficient Task Transfer by Learning to Scale
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) has shown considerable practical benefits, particularly when using pre-trained language models (PLMs). While this is commonly achieved by simultaneously learning $n$ tasks under a joint optimization procedure, recent methods such as AdapterFusion structure the problem into two distinct stages: (i) task learning, where knowledge specific to a task is encapsulated within sets of parameters (\eg adapters), and (ii) transfer, where this already learned knowledge is leveraged for a target task. This separation of concerns provides numerous benefits, such as promoting reusability, and addressing cases involving data privacy and societal concerns; on the flip side, current two-stage MTL methods come with the cost of introducing a substantial number of additional parameters. In this work, we address this issue by leveraging the usefulness of linearly scaling the output representations of source adapters for transfer learning. We introduce ScaLearn, a simple and highly parameter-efficient two-stage MTL method that capitalizes on the knowledge of the source tasks by learning a minimal set of scaling parameters that enable effective knowledge transfer to a target task. Our experiments on three benchmarks (GLUE, SuperGLUE, and HumSet) show that our ScaLearn, in addition to facilitating the benefits of two-stage MTL, consistently outperforms strong baselines with only a small number of transfer parameters - roughly 0.35% of those of AdapterFusion. Remarkably, we observe that ScaLearn maintains its strong abilities even when further reducing parameters through uniform scaling and layer-sharing, achieving similarly competitive results with only $8$ transfer parameters for each target task. Our proposed approach thus demonstrates the power of simple scaling as a promise for more efficient task transfer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge