Navid Rekabsaz
Batched Self-Consistency Improves LLM Relevance Assessment and Ranking
May 18, 2025Abstract:Given some information need, Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used for candidate text relevance assessment, typically using a one-by-one pointwise (PW) strategy where each LLM call evaluates one candidate at a time. Meanwhile, it has been shown that LLM performance can be improved through self-consistency: prompting the LLM to do the same task multiple times (possibly in perturbed ways) and then aggregating the responses. To take advantage of self-consistency, we hypothesize that batched PW strategies, where multiple passages are judged in one LLM call, are better suited than one-by-one PW methods since a larger input context can induce more diverse LLM sampling across self-consistency calls. We first propose several candidate batching strategies to create prompt diversity across self-consistency calls through subset reselection and permutation. We then test our batched PW methods on relevance assessment and ranking tasks against one-by-one PW and listwise LLM ranking baselines with and without self-consistency, using three passage retrieval datasets and GPT-4o, Claude Sonnet 3, and Amazon Nova Pro. We find that batched PW methods outperform all baselines, and show that batching can greatly amplify the positive effects of self-consistency. For instance, on our legal search dataset, GPT-4o one-by-one PW ranking NDCG@10 improves only from 44.9% to 46.8% without self-consistency vs. with 15 self consistency calls, while batched PW ranking improves from 43.8% to 51.3%, respectively.
Unlabeled Debiasing in Downstream Tasks via Class-wise Low Variance Regularization
Sep 29, 2024Abstract:Language models frequently inherit societal biases from their training data. Numerous techniques have been proposed to mitigate these biases during both the pre-training and fine-tuning stages. However, fine-tuning a pre-trained debiased language model on a downstream task can reintroduce biases into the model. Additionally, existing debiasing methods for downstream tasks either (i) require labels of protected attributes (e.g., age, race, or political views) that are often not available or (ii) rely on indicators of bias, which restricts their applicability to gender debiasing since they rely on gender-specific words. To address this, we introduce a novel debiasing regularization technique based on the class-wise variance of embeddings. Crucially, our method does not require attribute labels and targets any attribute, thus addressing the shortcomings of existing debiasing methods. Our experiments on encoder language models and three datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing strong debiasing baselines that rely on target attribute labels while maintaining performance on the target task.
What the Weight?! A Unified Framework for Zero-Shot Knowledge Composition
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:The knowledge encapsulated in a model is the core factor determining its final performance on downstream tasks. Much research in NLP has focused on efficient methods for storing and adapting different types of knowledge, e.g., in dedicated modularized structures, and on how to effectively combine these, e.g., by learning additional parameters. However, given the many possible options, a thorough understanding of the mechanisms involved in these compositions is missing, and hence it remains unclear which strategies to utilize. To address this research gap, we propose a novel framework for zero-shot module composition, which encompasses existing and some novel variations for selecting, weighting, and combining parameter modules under a single unified notion. Focusing on the scenario of domain knowledge and adapter layers, our framework provides a systematic unification of concepts, allowing us to conduct the first comprehensive benchmarking study of various zero-shot knowledge composition strategies. In particular, we test two module combination methods and five selection and weighting strategies for their effectiveness and efficiency in an extensive experimental setup. Our results highlight the efficacy of ensembling but also hint at the power of simple though often-ignored weighting methods. Further in-depth analyses allow us to understand the role of weighting vs. top-k selection, and show that, to a certain extent, the performance of adapter composition can even be predicted.
ScaLearn: Simple and Highly Parameter-Efficient Task Transfer by Learning to Scale
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) has shown considerable practical benefits, particularly when using pre-trained language models (PLMs). While this is commonly achieved by simultaneously learning $n$ tasks under a joint optimization procedure, recent methods such as AdapterFusion structure the problem into two distinct stages: (i) task learning, where knowledge specific to a task is encapsulated within sets of parameters (\eg adapters), and (ii) transfer, where this already learned knowledge is leveraged for a target task. This separation of concerns provides numerous benefits, such as promoting reusability, and addressing cases involving data privacy and societal concerns; on the flip side, current two-stage MTL methods come with the cost of introducing a substantial number of additional parameters. In this work, we address this issue by leveraging the usefulness of linearly scaling the output representations of source adapters for transfer learning. We introduce ScaLearn, a simple and highly parameter-efficient two-stage MTL method that capitalizes on the knowledge of the source tasks by learning a minimal set of scaling parameters that enable effective knowledge transfer to a target task. Our experiments on three benchmarks (GLUE, SuperGLUE, and HumSet) show that our ScaLearn, in addition to facilitating the benefits of two-stage MTL, consistently outperforms strong baselines with only a small number of transfer parameters - roughly 0.35% of those of AdapterFusion. Remarkably, we observe that ScaLearn maintains its strong abilities even when further reducing parameters through uniform scaling and layer-sharing, achieving similarly competitive results with only $8$ transfer parameters for each target task. Our proposed approach thus demonstrates the power of simple scaling as a promise for more efficient task transfer.
Domain Information Control at Inference Time for Acoustic Scene Classification
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Domain shift is considered a challenge in machine learning as it causes significant degradation of model performance. In the Acoustic Scene Classification task (ASC), domain shift is mainly caused by different recording devices. Several studies have already targeted domain generalization to improve the performance of ASC models on unseen domains, such as new devices. Recently, the Controllable Gate Adapter ConGater has been proposed in Natural Language Processing to address the biased training data problem. ConGater allows controlling the debiasing process at inference time. ConGater's main advantage is the continuous and selective debiasing of a trained model, during inference. In this work, we adapt ConGater to the audio spectrogram transformer for an acoustic scene classification task. We show that ConGater can be used to selectively adapt the learned representations to be invariant to device domain shifts such as recording devices. Our analysis shows that ConGater can progressively remove device information from the learned representations and improve the model generalization, especially under domain shift conditions (e.g. unseen devices). We show that information removal can be extended to both device and location domain. Finally, we demonstrate ConGater's ability to enhance specific device performance without further training.
Leveraging Domain Knowledge for Inclusive and Bias-aware Humanitarian Response Entry Classification
May 30, 2023Abstract:Accurate and rapid situation analysis during humanitarian crises is critical to delivering humanitarian aid efficiently and is fundamental to humanitarian imperatives and the Leave No One Behind (LNOB) principle. This data analysis can highly benefit from language processing systems, e.g., by classifying the text data according to a humanitarian ontology. However, approaching this by simply fine-tuning a generic large language model (LLM) involves considerable practical and ethical issues, particularly the lack of effectiveness on data-sparse and complex subdomains, and the encoding of societal biases and unwanted associations. In this work, we aim to provide an effective and ethically-aware system for humanitarian data analysis. We approach this by (1) introducing a novel architecture adjusted to the humanitarian analysis framework, (2) creating and releasing a novel humanitarian-specific LLM called HumBert, and (3) proposing a systematic way to measure and mitigate biases. Our experiments' results show the better performance of our approach on zero-shot and full-training settings in comparison with strong baseline models, while also revealing the existence of biases in the resulting LLMs. Utilizing a targeted counterfactual data augmentation approach, we significantly reduce these biases without compromising performance.
Enhancing the Ranking Context of Dense Retrieval Methods through Reciprocal Nearest Neighbors
May 25, 2023Abstract:Sparse annotation poses persistent challenges to training dense retrieval models, such as the problem of false negatives, i.e. unlabeled relevant documents that are spuriously used as negatives in contrastive learning, distorting the training signal. To alleviate this problem, we introduce evidence-based label smoothing, a computationally efficient method that prevents penalizing the model for assigning high relevance to false negatives. To compute the target relevance distribution over candidate documents within the ranking context of a given query, candidates most similar to the ground truth are assigned a non-zero relevance probability based on the degree of their similarity to the ground-truth document(s). As a relevance estimate we leverage an improved similarity metric based on reciprocal nearest neighbors, which can also be used independently to rerank candidates in post-processing. Through extensive experiments on two large-scale ad hoc text retrieval datasets we demonstrate that both methods can improve the ranking effectiveness of dense retrieval models.
Parameter-efficient Modularised Bias Mitigation via AdapterFusion
Feb 13, 2023Abstract:Large pre-trained language models contain societal biases and carry along these biases to downstream tasks. Current in-processing bias mitigation approaches (like adversarial training) impose debiasing by updating a model's parameters, effectively transferring the model to a new, irreversible debiased state. In this work, we propose a novel approach to develop stand-alone debiasing functionalities separate from the model, which can be integrated into the model on-demand, while keeping the core model untouched. Drawing from the concept of AdapterFusion in multi-task learning, we introduce DAM (Debiasing with Adapter Modules) - a debiasing approach to first encapsulate arbitrary bias mitigation functionalities into separate adapters, and then add them to the model on-demand in order to deliver fairness qualities. We conduct a large set of experiments on three classification tasks with gender, race, and age as protected attributes. Our results show that DAM improves or maintains the effectiveness of bias mitigation, avoids catastrophic forgetting in a multi-attribute scenario, and maintains on-par task performance, while granting parameter-efficiency and easy switching between the original and debiased models.
Leveraging Vision-Language Models for Granular Market Change Prediction
Jan 17, 2023Abstract:Predicting future direction of stock markets using the historical data has been a fundamental component in financial forecasting. This historical data contains the information of a stock in each specific time span, such as the opening, closing, lowest, and highest price. Leveraging this data, the future direction of the market is commonly predicted using various time-series models such as Long-Short Term Memory networks. This work proposes modeling and predicting market movements with a fundamentally new approach, namely by utilizing image and byte-based number representation of the stock data processed with the recently introduced Vision-Language models. We conduct a large set of experiments on the hourly stock data of the German share index and evaluate various architectures on stock price prediction using historical stock data. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the results with various metrics to accurately depict the actual performance of various approaches. Our evaluation results show that our novel approach based on representation of stock data as text (bytes) and image significantly outperforms strong deep learning-based baselines.
HumSet: Dataset of Multilingual Information Extraction and Classification for Humanitarian Crisis Response
Oct 10, 2022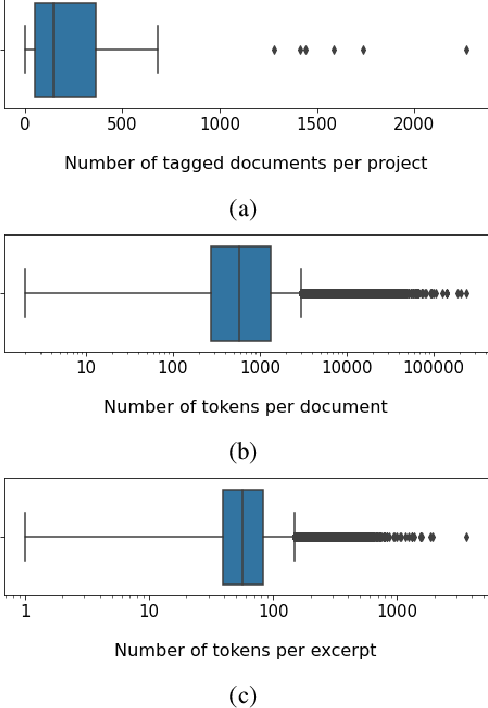
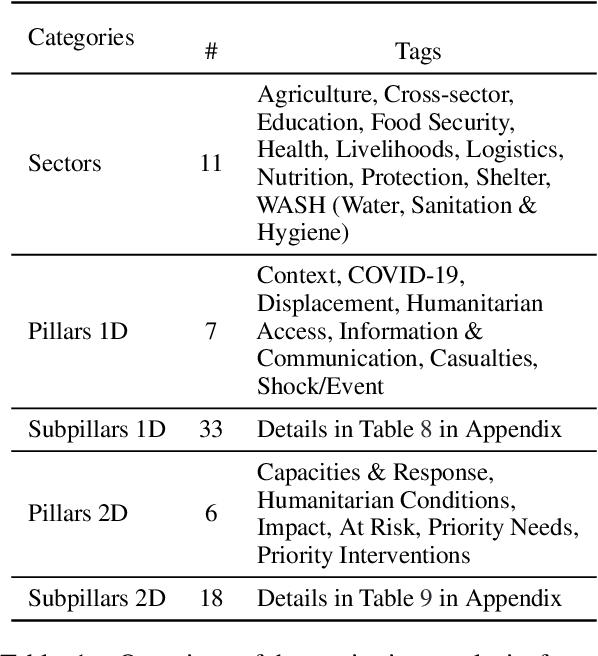
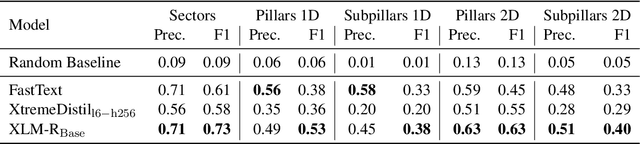
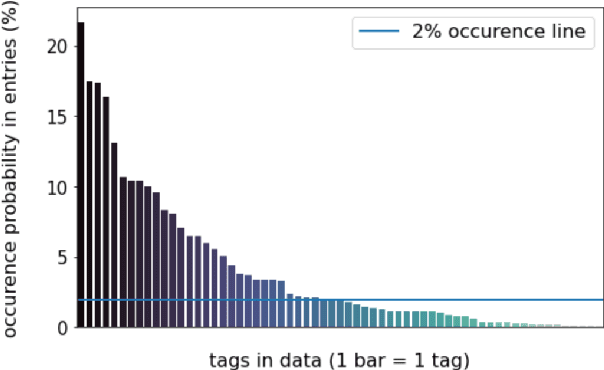
Abstract:Timely and effective response to humanitarian crises requires quick and accurate analysis of large amounts of text data - a process that can highly benefit from expert - assisted NLP systems trained on validated and annotated data in the humanitarian response domain. To enable creation of such NLP systems, we introduce and release HumSet, a novel and rich multilingual dataset of humanitarian response documents annotated by experts in the humanitarian response community. The dataset provides documents in three languages (English, French, Spanish) and covers a variety of humanitarian crises from 2018 to 2021 across the globe. For each document, HumSet provides selected snippets (entries) as well as assigned classes to each entry annotated using common humanitarian information analysis frameworks. HumSet also provides novel and challenging entry extraction and multi-label entry classification tasks. In this paper, we take a first step towards approaching these tasks and conduct a set of experiments on Pre-trained Language Models (PLM) to establish strong baselines for future research in this domain. The dataset is available at The dataset is available at https: //blog.thedeep.io/humset/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge