Antonio G. Marques
BUILD with Precision: Bottom-Up Inference of Linear DAGs
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Learning the structure of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) from observational data is a central problem in causal discovery, statistical signal processing, and machine learning. Under a linear Gaussian structural equation model (SEM) with equal noise variances, the problem is identifiable and we show that the ensemble precision matrix of the observations exhibits a distinctive structure that facilitates DAG recovery. Exploiting this property, we propose BUILD (Bottom-Up Inference of Linear DAGs), a deterministic stepwise algorithm that identifies leaf nodes and their parents, then prunes the leaves by removing incident edges to proceed to the next step, exactly reconstructing the DAG from the true precision matrix. In practice, precision matrices must be estimated from finite data, and ill-conditioning may lead to error accumulation across BUILD steps. As a mitigation strategy, we periodically re-estimate the precision matrix (with less variables as leaves are pruned), trading off runtime for enhanced robustness. Reproducible results on challenging synthetic benchmarks demonstrate that BUILD compares favorably to state-of-the-art DAG learning algorithms, while offering an explicit handle on complexity.
Graph-Aware Diffusion for Signal Generation
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:We study the problem of generating graph signals from unknown distributions defined over given graphs, relevant to domains such as recommender systems or sensor networks. Our approach builds on generative diffusion models, which are well established in vision and graph generation but remain underexplored for graph signals. Existing methods lack generality, either ignoring the graph structure in the forward process or designing graph-aware mechanisms tailored to specific domains. We adopt a forward process that incorporates the graph through the heat equation. Rather than relying on the standard formulation, we consider a time-warped coefficient to mitigate the exponential decay of the drift term, yielding a graph-aware generative diffusion model (GAD). We analyze its forward dynamics, proving convergence to a Gaussian Markov random field with covariance parametrized by the graph Laplacian, and interpret the backward dynamics as a sequence of graph-signal denoising problems. Finally, we demonstrate the advantages of GAD on synthetic data, real traffic speed measurements, and a temperature sensor network.
Precision Neural Networks: Joint Graph And Relational Learning
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:CoVariance Neural Networks (VNNs) perform convolutions on the graph determined by the covariance matrix of the data, which enables expressive and stable covariance-based learning. However, covariance matrices are typically dense, fail to encode conditional independence, and are often precomputed in a task-agnostic way, which may hinder performance. To overcome these limitations, we study Precision Neural Networks (PNNs), i.e., VNNs on the precision matrix -- the inverse covariance. The precision matrix naturally encodes statistical independence, often exhibits sparsity, and preserves the covariance spectral structure. To make precision estimation task-aware, we formulate an optimization problem that jointly learns the network parameters and the precision matrix, and solve it via alternating optimization, by sequentially updating the network weights and the precision estimate. We theoretically bound the distance between the estimated and true precision matrices at each iteration, and demonstrate the effectiveness of joint estimation compared to two-step approaches on synthetic and real-world data.
Graph signal aware decomposition of dynamic networks via latent graphs
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Dynamics on and of networks refer to changes in topology and node-associated signals, respectively and are pervasive in many socio-technological systems, including social, biological, and infrastructure networks. Due to practical constraints, privacy concerns, or malfunctions, we often observe only a fraction of the topological evolution and associated signal, which not only hinders downstream tasks but also restricts our analysis of network evolution. Such aspects could be mitigated by moving our attention at the underlying latent driving factors of the network evolution, which can be naturally uncovered via low-rank tensor decomposition. Tensor-based methods provide a powerful means of uncovering the underlying factors of network evolution through low-rank decompositions. However, the extracted embeddings typically lack a relational structure and are obtained independently from the node signals. This disconnect reduces the interpretability of the embeddings and overlooks the coupling between topology and signals. To address these limitations, we propose a novel two-way decomposition to represent a dynamic graph topology, where the structural evolution is captured by a linear combination of latent graph adjacency matrices reflecting the overall joint evolution of both the topology and the signal. Using spatio-temporal data, we estimate the latent adjacency matrices and their temporal scaling signatures via alternating minimization, and prove that our approach converges to a stationary point. Numerical results show that the proposed method recovers individually and collectively expressive latent graphs, outperforming both standard tensor-based decompositions and signal-based topology identification methods in reconstructing the missing network especially when observations are limited.
Adapting to Heterophilic Graph Data with Structure-Guided Neighbor Discovery
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) often struggle with heterophilic data, where connected nodes may have dissimilar labels, as they typically assume homophily and rely on local message passing. To address this, we propose creating alternative graph structures by linking nodes with similar structural attributes (e.g., role-based or global), thereby fostering higher label homophily on these new graphs. We theoretically prove that GNN performance can be improved by utilizing graphs with fewer false positive edges (connections between nodes of different classes) and that considering multiple graph views increases the likelihood of finding such beneficial structures. Building on these insights, we introduce Structure-Guided GNN (SG-GNN), an architecture that processes the original graph alongside the newly created structural graphs, adaptively learning to weigh their contributions. Extensive experiments on various benchmark datasets, particularly those with heterophilic characteristics, demonstrate that our SG-GNN achieves state-of-the-art or highly competitive performance, highlighting the efficacy of exploiting structural information to guide GNNs.
A Few Moments Please: Scalable Graphon Learning via Moment Matching
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Graphons, as limit objects of dense graph sequences, play a central role in the statistical analysis of network data. However, existing graphon estimation methods often struggle with scalability to large networks and resolution-independent approximation, due to their reliance on estimating latent variables or costly metrics such as the Gromov-Wasserstein distance. In this work, we propose a novel, scalable graphon estimator that directly recovers the graphon via moment matching, leveraging implicit neural representations (INRs). Our approach avoids latent variable modeling by training an INR--mapping coordinates to graphon values--to match empirical subgraph counts (i.e., moments) from observed graphs. This direct estimation mechanism yields a polynomial-time solution and crucially sidesteps the combinatorial complexity of Gromov-Wasserstein optimization. Building on foundational results, we establish a theoretical guarantee: when the observed subgraph motifs sufficiently represent those of the true graphon (a condition met with sufficiently large or numerous graph samples), the estimated graphon achieves a provable upper bound in cut distance from the ground truth. Additionally, we introduce MomentMixup, a data augmentation technique that performs mixup in the moment space to enhance graphon-based learning. Our graphon estimation method achieves strong empirical performance--demonstrating high accuracy on small graphs and superior computational efficiency on large graphs--outperforming state-of-the-art scalable estimators in 75\% of benchmark settings and matching them in the remaining cases. Furthermore, MomentMixup demonstrated improved graph classification accuracy on the majority of our benchmarks.
Graph Guided Diffusion: Unified Guidance for Conditional Graph Generation
May 26, 2025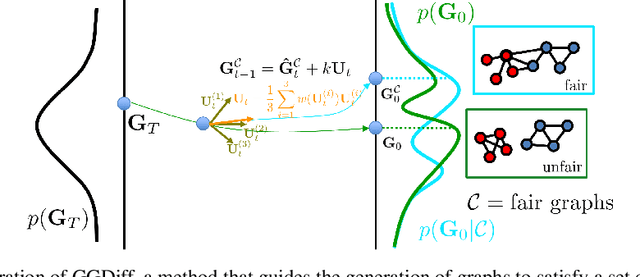
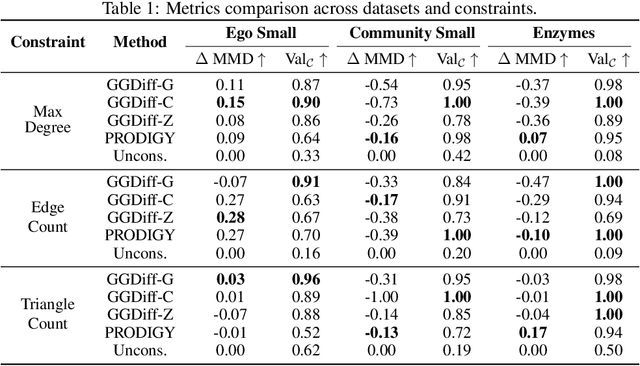
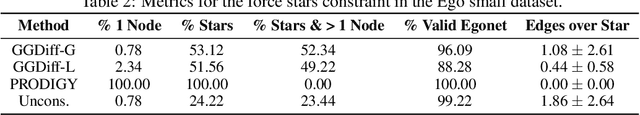
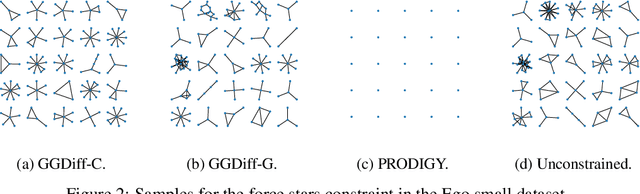
Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as powerful generative models for graph generation, yet their use for conditional graph generation remains a fundamental challenge. In particular, guiding diffusion models on graphs under arbitrary reward signals is difficult: gradient-based methods, while powerful, are often unsuitable due to the discrete and combinatorial nature of graphs, and non-differentiable rewards further complicate gradient-based guidance. We propose Graph Guided Diffusion (GGDiff), a novel guidance framework that interprets conditional diffusion on graphs as a stochastic control problem to address this challenge. GGDiff unifies multiple guidance strategies, including gradient-based guidance (for differentiable rewards), control-based guidance (using control signals from forward reward evaluations), and zero-order approximations (bridging gradient-based and gradient-free optimization). This comprehensive, plug-and-play framework enables zero-shot guidance of pre-trained diffusion models under both differentiable and non-differentiable reward functions, adapting well-established guidance techniques to graph generation--a direction largely unexplored. Our formulation balances computational efficiency, reward alignment, and sample quality, enabling practical conditional generation across diverse reward types. We demonstrate the efficacy of GGDiff in various tasks, including constraints on graph motifs, fairness, and link prediction, achieving superior alignment with target rewards while maintaining diversity and fidelity.
Early Detection of Multidrug Resistance Using Multivariate Time Series Analysis and Interpretable Patient-Similarity Representations
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Background and Objectives: Multidrug Resistance (MDR) is a critical global health issue, causing increased hospital stays, healthcare costs, and mortality. This study proposes an interpretable Machine Learning (ML) framework for MDR prediction, aiming for both accurate inference and enhanced explainability. Methods: Patients are modeled as Multivariate Time Series (MTS), capturing clinical progression and patient-to-patient interactions. Similarity among patients is quantified using MTS-based methods: descriptive statistics, Dynamic Time Warping, and Time Cluster Kernel. These similarity measures serve as inputs for MDR classification via Logistic Regression, Random Forest, and Support Vector Machines, with dimensionality reduction and kernel transformations improving model performance. For explainability, patient similarity networks are constructed from these metrics. Spectral clustering and t-SNE are applied to identify MDR-related subgroups and visualize high-risk clusters, enabling insight into clinically relevant patterns. Results: The framework was validated on ICU Electronic Health Records from the University Hospital of Fuenlabrada, achieving an AUC of 81%. It outperforms baseline ML and deep learning models by leveraging graph-based patient similarity. The approach identifies key risk factors -- prolonged antibiotic use, invasive procedures, co-infections, and extended ICU stays -- and reveals clinically meaningful clusters. Code and results are available at \https://github.com/oscarescuderoarnanz/DM4MTS. Conclusions: Patient similarity representations combined with graph-based analysis provide accurate MDR prediction and interpretable insights. This method supports early detection, risk factor identification, and patient stratification, highlighting the potential of explainable ML in critical care.
Matched Topological Subspace Detector
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Topological spaces, represented by simplicial complexes, capture richer relationships than graphs by modeling interactions not only between nodes but also among higher-order entities, such as edges or triangles. This motivates the representation of information defined in irregular domains as topological signals. By leveraging the spectral dualities of Hodge and Dirac theory, practical topological signals often concentrate in specific spectral subspaces (e.g., gradient or curl). For instance, in a foreign currency exchange network, the exchange flow signals typically satisfy the arbitrage-free condition and hence are curl-free. However, the presence of anomalies can disrupt these conditions, causing the signals to deviate from such subspaces. In this work, we formulate a hypothesis testing framework to detect whether simplicial complex signals lie in specific subspaces in a principled and tractable manner. Concretely, we propose Neyman-Pearson matched topological subspace detectors for signals defined at a single simplicial level (such as edges) or jointly across all levels of a simplicial complex. The (energy-based projection) proposed detectors handle missing values, provide closed-form performance analysis, and effectively capture the unique topological properties of the data. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed topological detectors on various real-world data, including foreign currency exchange networks.
Enhancing Graphical Lasso: A Robust Scheme for Non-Stationary Mean Data
Mar 25, 2025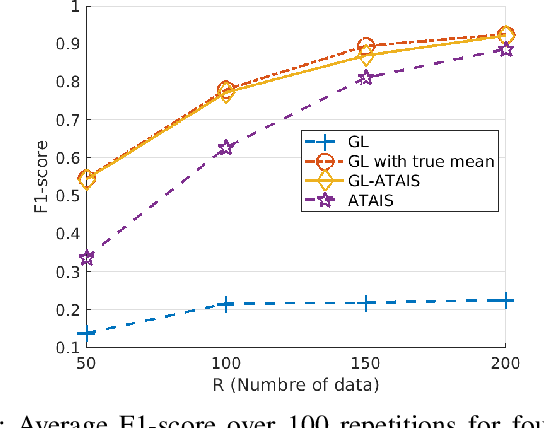
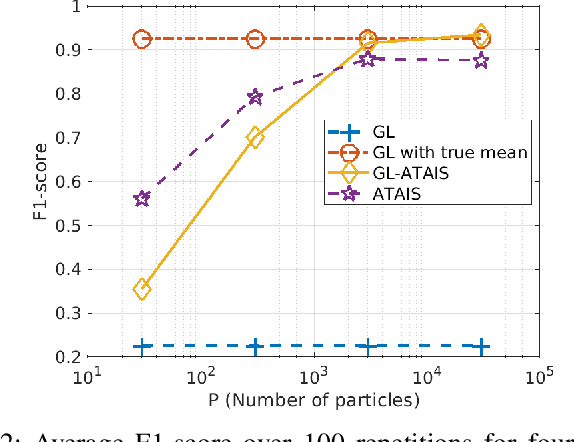
Abstract:This work addresses the problem of graph learning from data following a Gaussian Graphical Model (GGM) with a time-varying mean. Graphical Lasso (GL), the standard method for estimating sparse precision matrices, assumes that the observed data follows a zero-mean Gaussian distribution. However, this assumption is often violated in real-world scenarios where the mean evolves over time due to external influences, trends, or regime shifts. When the mean is not properly accounted for, applying GL directly can lead to estimating a biased precision matrix, hence hindering the graph learning task. To overcome this limitation, we propose Graphical Lasso with Adaptive Targeted Adaptive Importance Sampling (GL-ATAIS), an iterative method that jointly estimates the time-varying mean and the precision matrix. Our approach integrates Bayesian inference with frequentist estimation, leveraging importance sampling to obtain an estimate of the mean while using a regularized maximum likelihood estimator to infer the precision matrix. By iteratively refining both estimates, GL-ATAIS mitigates the bias introduced by time-varying means, leading to more accurate graph recovery. Our numerical evaluation demonstrates the impact of properly accounting for time-dependent means and highlights the advantages of GL-ATAIS over standard GL in recovering the true graph structure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge