Cristina Soguero-Ruiz
Early Detection of Multidrug Resistance Using Multivariate Time Series Analysis and Interpretable Patient-Similarity Representations
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Background and Objectives: Multidrug Resistance (MDR) is a critical global health issue, causing increased hospital stays, healthcare costs, and mortality. This study proposes an interpretable Machine Learning (ML) framework for MDR prediction, aiming for both accurate inference and enhanced explainability. Methods: Patients are modeled as Multivariate Time Series (MTS), capturing clinical progression and patient-to-patient interactions. Similarity among patients is quantified using MTS-based methods: descriptive statistics, Dynamic Time Warping, and Time Cluster Kernel. These similarity measures serve as inputs for MDR classification via Logistic Regression, Random Forest, and Support Vector Machines, with dimensionality reduction and kernel transformations improving model performance. For explainability, patient similarity networks are constructed from these metrics. Spectral clustering and t-SNE are applied to identify MDR-related subgroups and visualize high-risk clusters, enabling insight into clinically relevant patterns. Results: The framework was validated on ICU Electronic Health Records from the University Hospital of Fuenlabrada, achieving an AUC of 81%. It outperforms baseline ML and deep learning models by leveraging graph-based patient similarity. The approach identifies key risk factors -- prolonged antibiotic use, invasive procedures, co-infections, and extended ICU stays -- and reveals clinically meaningful clusters. Code and results are available at \https://github.com/oscarescuderoarnanz/DM4MTS. Conclusions: Patient similarity representations combined with graph-based analysis provide accurate MDR prediction and interpretable insights. This method supports early detection, risk factor identification, and patient stratification, highlighting the potential of explainable ML in critical care.
Explainable Spatio-Temporal GCNNs for Irregular Multivariate Time Series: Architecture and Application to ICU Patient Data
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we present XST-GCNN (eXplainable Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Network), a novel architecture for processing heterogeneous and irregular Multivariate Time Series (MTS) data. Our approach captures temporal and feature dependencies within a unified spatio-temporal pipeline by leveraging a GCNN that uses a spatio-temporal graph aimed at optimizing predictive accuracy and interoperability. For graph estimation, we introduce techniques, including one based on the (heterogeneous) Gower distance. Once estimated, we propose two methods for graph construction: one based on the Cartesian product, treating temporal instants homogeneously, and another spatio-temporal approach with distinct graphs per time step. We also propose two GCNN architectures: a standard GCNN with a normalized adjacency matrix and a higher-order polynomial GCNN. In addition to accuracy, we emphasize explainability by designing an inherently interpretable model and performing a thorough interpretability analysis, identifying key feature-time combinations that drive predictions. We evaluate XST-GCNN using real-world Electronic Health Record data from University Hospital of Fuenlabrada to predict Multidrug Resistance (MDR) in ICU patients, a critical healthcare challenge linked to high mortality and complex treatments. Our architecture outperforms traditional models, achieving a mean ROC-AUC score of 81.03 +- 2.43. Furthermore, the interpretability analysis provides actionable insights into clinical factors driving MDR predictions, enhancing model transparency. This work sets a benchmark for tackling complex inference tasks with heterogeneous MTS, offering a versatile, interpretable solution for real-world applications.
On the Use of Time Series Kernel and Dimensionality Reduction to Identify the Acquisition of Antimicrobial Multidrug Resistance in the Intensive Care Unit
Jul 07, 2021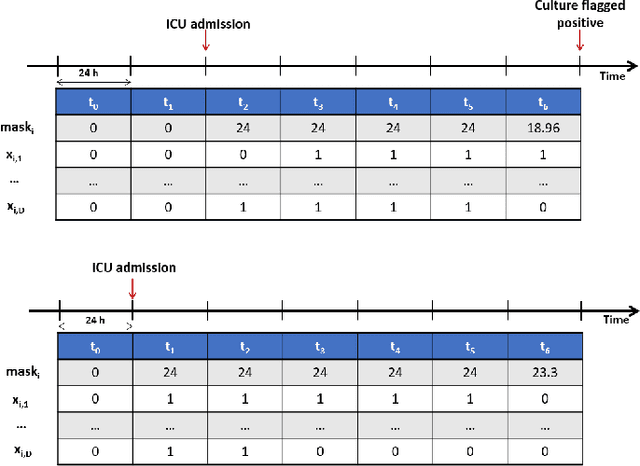
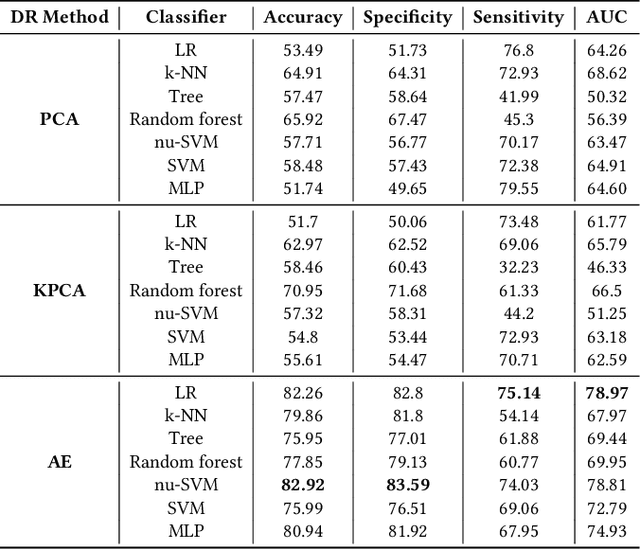
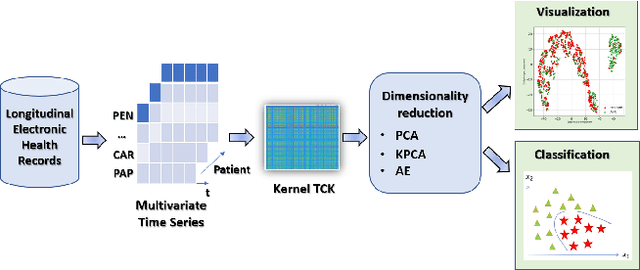
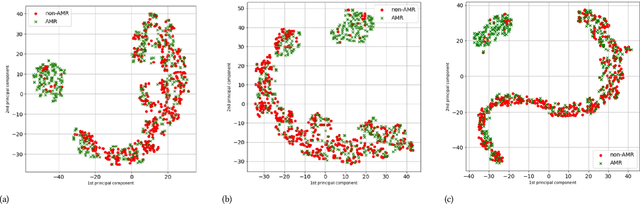
Abstract:The acquisition of Antimicrobial Multidrug Resistance (AMR) in patients admitted to the Intensive Care Units (ICU) is a major global concern. This study analyses data in the form of multivariate time series (MTS) from 3476 patients recorded at the ICU of University Hospital of Fuenlabrada (Madrid) from 2004 to 2020. 18\% of the patients acquired AMR during their stay in the ICU. The goal of this paper is an early prediction of the development of AMR. Towards that end, we leverage the time-series cluster kernel (TCK) to learn similarities between MTS. To evaluate the effectiveness of TCK as a kernel, we applied several dimensionality reduction techniques for visualization and classification tasks. The experimental results show that TCK allows identifying a group of patients that acquire the AMR during the first 48 hours of their ICU stay, and it also provides good classification capabilities.
A Kernel to Exploit Informative Missingness in Multivariate Time Series from EHRs
Feb 27, 2020
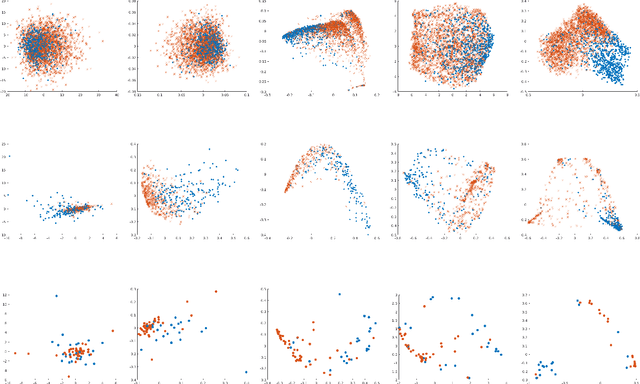
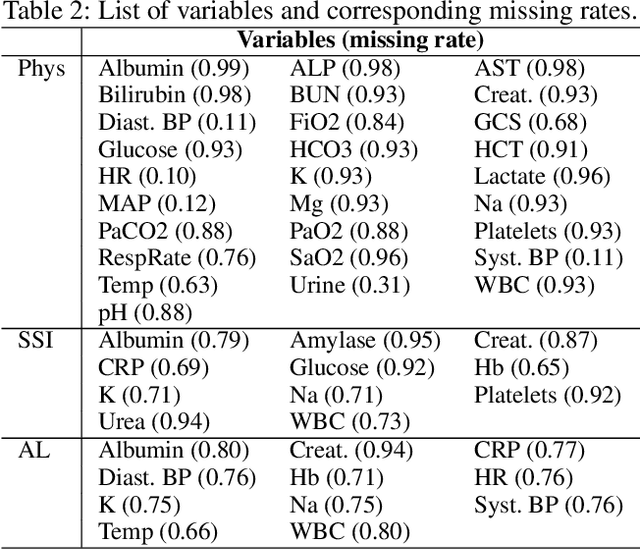
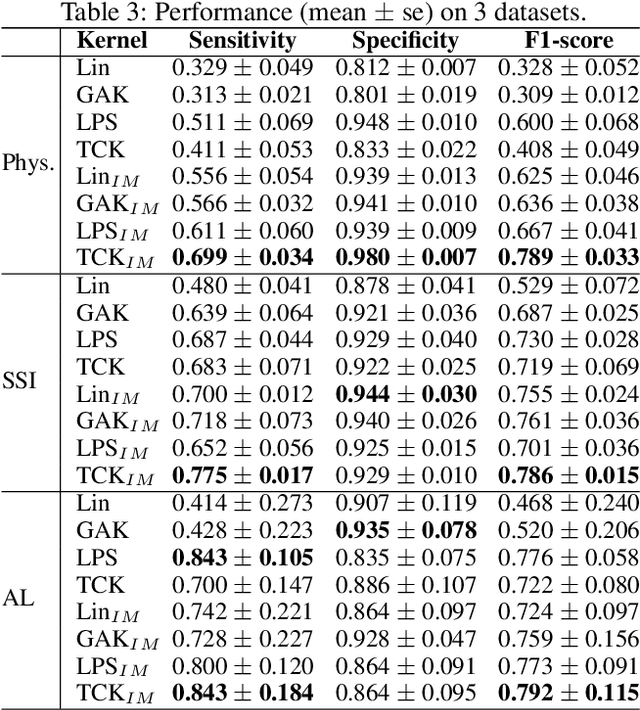
Abstract:A large fraction of the electronic health records (EHRs) consists of clinical measurements collected over time, such as lab tests and vital signs, which provide important information about a patient's health status. These sequences of clinical measurements are naturally represented as time series, characterized by multiple variables and large amounts of missing data, which complicate the analysis. In this work, we propose a novel kernel which is capable of exploiting both the information from the observed values as well the information hidden in the missing patterns in multivariate time series (MTS) originating e.g. from EHRs. The kernel, called TCK$_{IM}$, is designed using an ensemble learning strategy in which the base models are novel mixed mode Bayesian mixture models which can effectively exploit informative missingness without having to resort to imputation methods. Moreover, the ensemble approach ensures robustness to hyperparameters and therefore TCK$_{IM}$ is particularly well suited if there is a lack of labels - a known challenge in medical applications. Experiments on three real-world clinical datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed kernel.
Time series cluster kernels to exploit informative missingness and incomplete label information
Jul 10, 2019
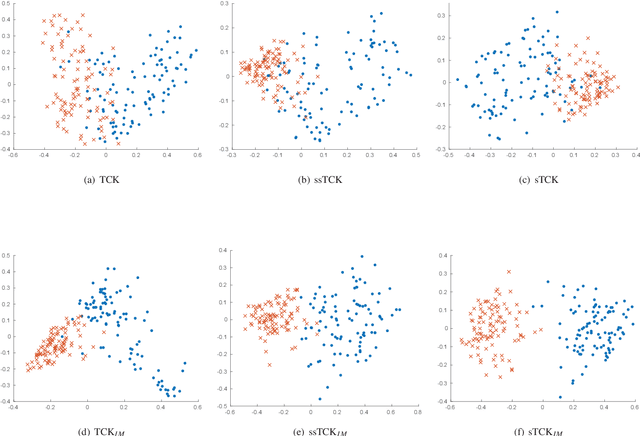
Abstract:The time series cluster kernel (TCK) provides a powerful tool for analysing multivariate time series subject to missing data. TCK is designed using an ensemble learning approach in which Bayesian mixture models form the base models. Because of the Bayesian approach, TCK can naturally deal with missing values without resorting to imputation and the ensemble strategy ensures robustness to hyperparameters, making it particularly well suited for unsupervised learning. However, TCK assumes missing at random and that the underlying missingness mechanism is ignorable, i.e. uninformative, an assumption that does not hold in many real-world applications, such as e.g. medicine. To overcome this limitation, we present a kernel capable of exploiting the potentially rich information in the missing values and patterns, as well as the information from the observed data. In our approach, we create a representation of the missing pattern, which is incorporated into mixed mode mixture models in such a way that the information provided by the missing patterns is effectively exploited. Moreover, we also propose a semi-supervised kernel, capable of taking advantage of incomplete label information to learn more accurate similarities. Experiments on benchmark data, as well as a real-world case study of patients described by longitudinal electronic health record data who potentially suffer from hospital-acquired infections, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods.
Noisy multi-label semi-supervised dimensionality reduction
Feb 20, 2019



Abstract:Noisy labeled data represent a rich source of information that often are easily accessible and cheap to obtain, but label noise might also have many negative consequences if not accounted for. How to fully utilize noisy labels has been studied extensively within the framework of standard supervised machine learning over a period of several decades. However, very little research has been conducted on solving the challenge posed by noisy labels in non-standard settings. This includes situations where only a fraction of the samples are labeled (semi-supervised) and each high-dimensional sample is associated with multiple labels. In this work, we present a novel semi-supervised and multi-label dimensionality reduction method that effectively utilizes information from both noisy multi-labels and unlabeled data. With the proposed Noisy multi-label semi-supervised dimensionality reduction (NMLSDR) method, the noisy multi-labels are denoised and unlabeled data are labeled simultaneously via a specially designed label propagation algorithm. NMLSDR then learns a projection matrix for reducing the dimensionality by maximizing the dependence between the enlarged and denoised multi-label space and the features in the projected space. Extensive experiments on synthetic data, benchmark datasets, as well as a real-world case study, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and show that it outperforms state-of-the-art multi-label feature extraction algorithms.
* 38 pages
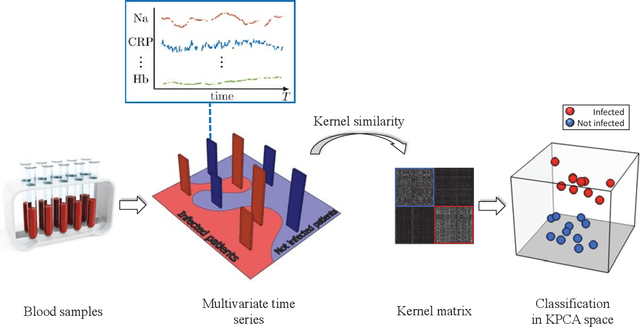
An Unsupervised Multivariate Time Series Kernel Approach for Identifying Patients with Surgical Site Infection from Blood Samples
Mar 21, 2018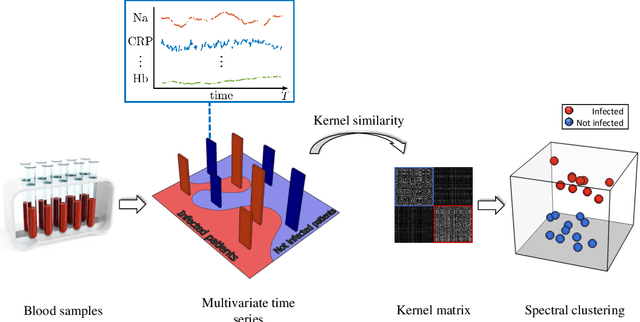
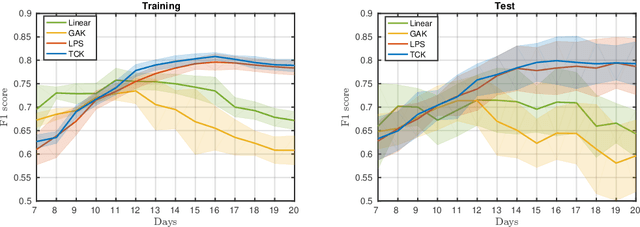
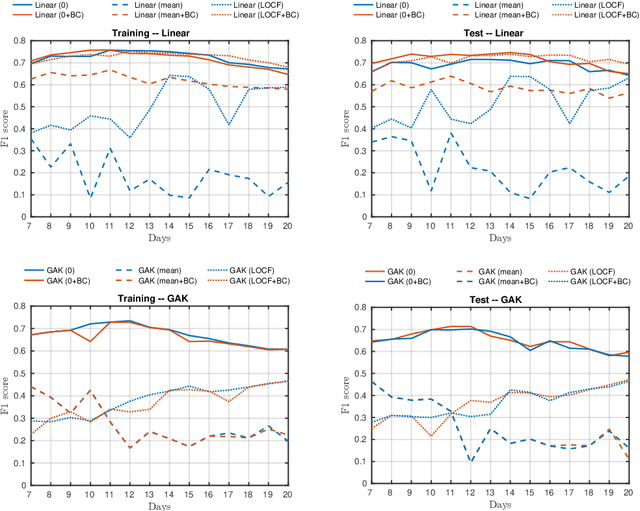
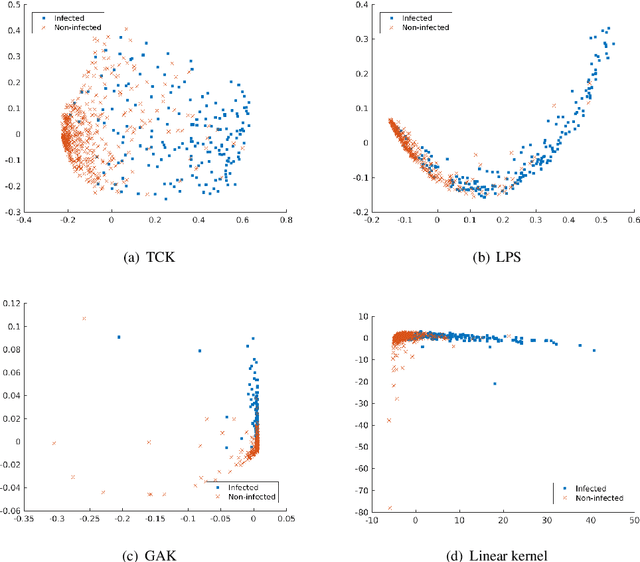
Abstract:A large fraction of the electronic health records consists of clinical measurements collected over time, such as blood tests, which provide important information about the health status of a patient. These sequences of clinical measurements are naturally represented as time series, characterized by multiple variables and the presence of missing data, which complicate analysis. In this work, we propose a surgical site infection detection framework for patients undergoing colorectal cancer surgery that is completely unsupervised, hence alleviating the problem of getting access to labelled training data. The framework is based on powerful kernels for multivariate time series that account for missing data when computing similarities. Our approach show superior performance compared to baselines that have to resort to imputation techniques and performs comparable to a supervised classification baseline.
Classification of postoperative surgical site infections from blood measurements with missing data using recurrent neural networks
Nov 17, 2017



Abstract:Clinical measurements that can be represented as time series constitute an important fraction of the electronic health records and are often both uncertain and incomplete. Recurrent neural networks are a special class of neural networks that are particularly suitable to process time series data but, in their original formulation, cannot explicitly deal with missing data. In this paper, we explore imputation strategies for handling missing values in classifiers based on recurrent neural network (RNN) and apply a recently proposed recurrent architecture, the Gated Recurrent Unit with Decay, specifically designed to handle missing data. We focus on the problem of detecting surgical site infection in patients by analyzing time series of their blood sample measurements and we compare the results obtained with different RNN-based classifiers.
Time Series Cluster Kernel for Learning Similarities between Multivariate Time Series with Missing Data
Jun 29, 2017



Abstract:Similarity-based approaches represent a promising direction for time series analysis. However, many such methods rely on parameter tuning, and some have shortcomings if the time series are multivariate (MTS), due to dependencies between attributes, or the time series contain missing data. In this paper, we address these challenges within the powerful context of kernel methods by proposing the robust \emph{time series cluster kernel} (TCK). The approach taken leverages the missing data handling properties of Gaussian mixture models (GMM) augmented with informative prior distributions. An ensemble learning approach is exploited to ensure robustness to parameters by combining the clustering results of many GMM to form the final kernel. We evaluate the TCK on synthetic and real data and compare to other state-of-the-art techniques. The experimental results demonstrate that the TCK is robust to parameter choices, provides competitive results for MTS without missing data and outstanding results for missing data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge