Ansel Blume
PARTONOMY: Large Multimodal Models with Part-Level Visual Understanding
May 27, 2025Abstract:Real-world objects are composed of distinctive, object-specific parts. Identifying these parts is key to performing fine-grained, compositional reasoning-yet, large multimodal models (LMMs) struggle to perform this seemingly straightforward task. In this work, we introduce PARTONOMY, an LMM benchmark designed for pixel-level part grounding. We construct PARTONOMY from existing part datasets and our own rigorously annotated set of images, encompassing 862 part labels and 534 object labels for evaluation. Unlike existing datasets that simply ask models to identify generic parts, PARTONOMY uses specialized concepts (e.g., agricultural airplane), and challenges models to compare objects' parts, consider part-whole relationships, and justify textual predictions with visual segmentations. Our experiments demonstrate significant limitations in state-of-the-art LMMs (e.g., LISA-13B achieves only 5.9% gIoU), highlighting a critical gap in their part grounding abilities. We note that existing segmentation-enabled LMMs (segmenting LMMs) have two key architectural shortcomings: they use special [SEG] tokens not seen during pretraining which induce distribution shift, and they discard predicted segmentations instead of using past predictions to guide future ones. To address these deficiencies, we train several part-centric LMMs and propose PLUM, a novel segmenting LMM that uses span tagging instead of segmentation tokens and that conditions on prior predictions in a feedback loop. We find that pretrained PLUM outperforms existing segmenting LMMs on reasoning segmentation, VQA, and visual hallucination benchmarks. In addition, PLUM finetuned on our proposed Explanatory Part Segmentation task is competitive with segmenting LMMs trained on significantly more segmentation data. Our work opens up new avenues towards enabling fine-grained, grounded visual understanding in LMMs.
Synthia: Novel Concept Design with Affordance Composition
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) models enable rapid concept design, making them widely used in AI-driven design. While recent studies focus on generating semantic and stylistic variations of given design concepts, functional coherence--the integration of multiple affordances into a single coherent concept--remains largely overlooked. In this paper, we introduce SYNTHIA, a framework for generating novel, functionally coherent designs based on desired affordances. Our approach leverages a hierarchical concept ontology that decomposes concepts into parts and affordances, serving as a crucial building block for functionally coherent design. We also develop a curriculum learning scheme based on our ontology that contrastively fine-tunes T2I models to progressively learn affordance composition while maintaining visual novelty. To elaborate, we (i) gradually increase affordance distance, guiding models from basic concept-affordance association to complex affordance compositions that integrate parts of distinct affordances into a single, coherent form, and (ii) enforce visual novelty by employing contrastive objectives to push learned representations away from existing concepts. Experimental results show that SYNTHIA outperforms state-of-the-art T2I models, demonstrating absolute gains of 25.1% and 14.7% for novelty and functional coherence in human evaluation, respectively.
Search and Detect: Training-Free Long Tail Object Detection via Web-Image Retrieval
Sep 26, 2024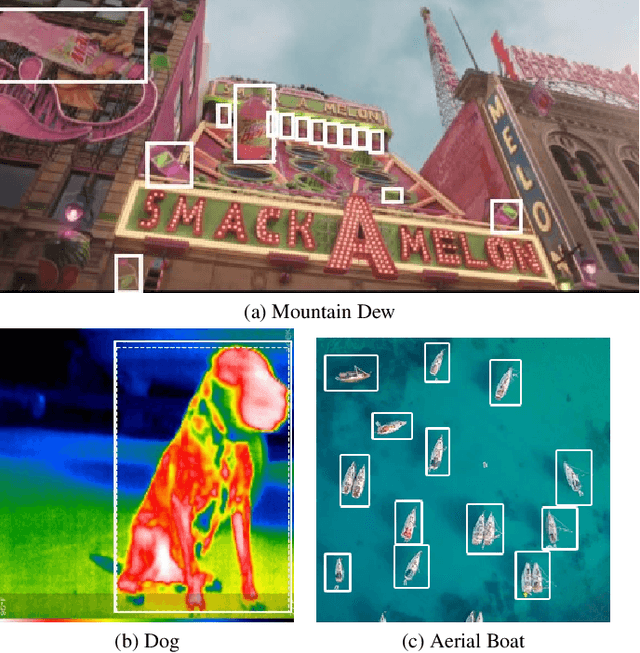
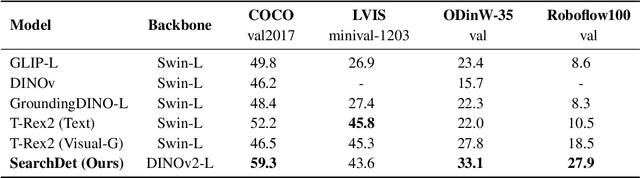
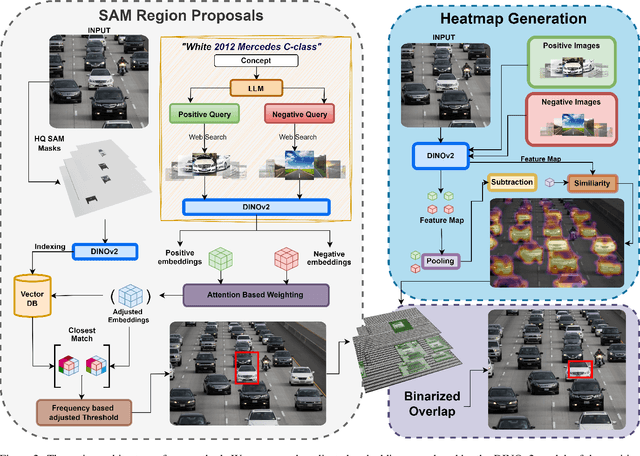
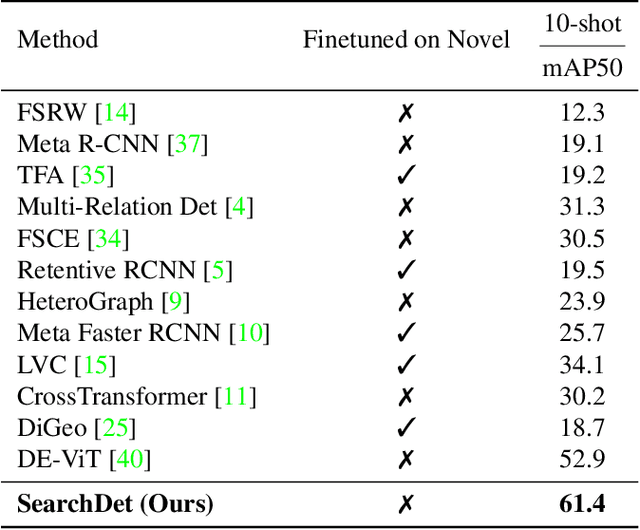
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce SearchDet, a training-free long-tail object detection framework that significantly enhances open-vocabulary object detection performance. SearchDet retrieves a set of positive and negative images of an object to ground, embeds these images, and computes an input image-weighted query which is used to detect the desired concept in the image. Our proposed method is simple and training-free, yet achieves over 48.7% mAP improvement on ODinW and 59.1% mAP improvement on LVIS compared to state-of-the-art models such as GroundingDINO. We further show that our approach of basing object detection on a set of Web-retrieved exemplars is stable with respect to variations in the exemplars, suggesting a path towards eliminating costly data annotation and training procedures.
Region-Based Representations Revisited
Feb 04, 2024Abstract:We investigate whether region-based representations are effective for recognition. Regions were once a mainstay in recognition approaches, but pixel and patch-based features are now used almost exclusively. We show that recent class-agnostic segmenters like SAM can be effectively combined with strong unsupervised representations like DINOv2 and used for a wide variety of tasks, including semantic segmentation, object-based image retrieval, and multi-image analysis. Once the masks and features are extracted, these representations, even with linear decoders, enable competitive performance, making them well suited to applications that require custom queries. The compactness of the representation also makes it well-suited to video analysis and other problems requiring inference across many images.
Paxion: Patching Action Knowledge in Video-Language Foundation Models
May 26, 2023



Abstract:Action knowledge involves the understanding of textual, visual, and temporal aspects of actions. We introduce the Action Dynamics Benchmark (ActionBench) containing two carefully designed probing tasks: Action Antonym and Video Reversal, which targets multimodal alignment capabilities and temporal understanding skills of the model, respectively. Despite recent video-language models' (VidLM) impressive performance on various benchmark tasks, our diagnostic tasks reveal their surprising deficiency (near-random performance) in action knowledge, suggesting that current models rely on object recognition abilities as a shortcut for action understanding. To remedy this, we propose a novel framework, Paxion, along with a new Discriminative Video Dynamics Modeling (DVDM) objective. The Paxion framework utilizes a Knowledge Patcher network to encode new action knowledge and a Knowledge Fuser component to integrate the Patcher into frozen VidLMs without compromising their existing capabilities. Due to limitations of the widely-used Video-Text Contrastive (VTC) loss for learning action knowledge, we introduce the DVDM objective to train the Knowledge Patcher. DVDM forces the model to encode the correlation between the action text and the correct ordering of video frames. Our extensive analyses show that Paxion and DVDM together effectively fill the gap in action knowledge understanding (~50% to 80%), while maintaining or improving performance on a wide spectrum of both object- and action-centric downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge