Andrew Nam
Causal Head Gating: A Framework for Interpreting Roles of Attention Heads in Transformers
May 19, 2025Abstract:We present causal head gating (CHG), a scalable method for interpreting the functional roles of attention heads in transformer models. CHG learns soft gates over heads and assigns them a causal taxonomy - facilitating, interfering, or irrelevant - based on their impact on task performance. Unlike prior approaches in mechanistic interpretability, which are hypothesis-driven and require prompt templates or target labels, CHG applies directly to any dataset using standard next-token prediction. We evaluate CHG across multiple large language models (LLMs) in the Llama 3 model family and diverse tasks, including syntax, commonsense, and mathematical reasoning, and show that CHG scores yield causal - not merely correlational - insight, validated via ablation and causal mediation analyses. We also introduce contrastive CHG, a variant that isolates sub-circuits for specific task components. Our findings reveal that LLMs contain multiple sparse, sufficient sub-circuits, that individual head roles depend on interactions with others (low modularity), and that instruction following and in-context learning rely on separable mechanisms.
Understanding Task Representations in Neural Networks via Bayesian Ablation
May 19, 2025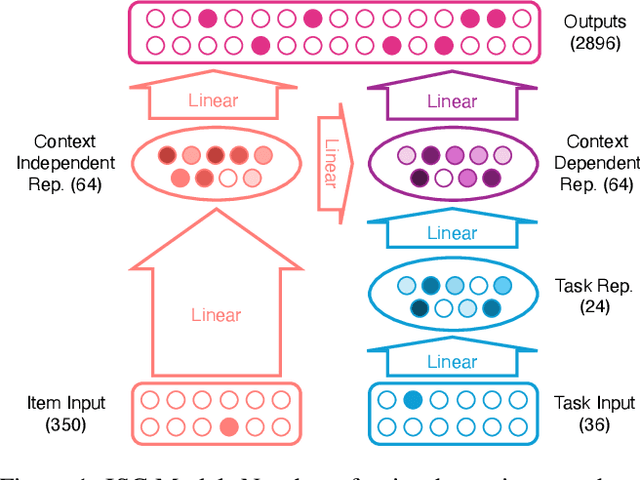
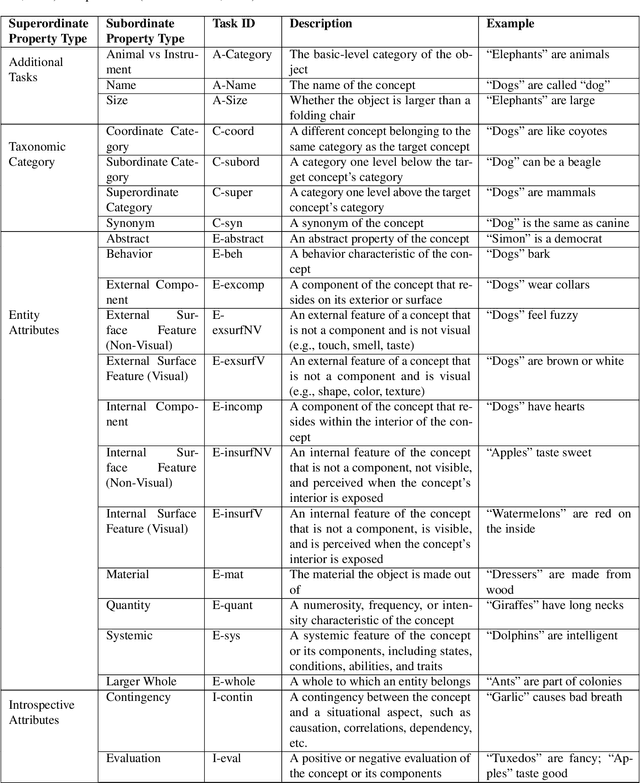
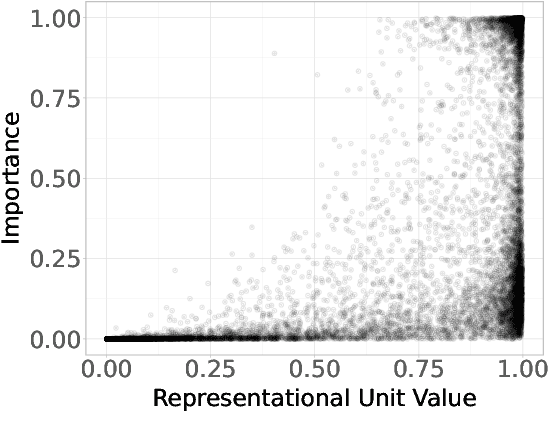
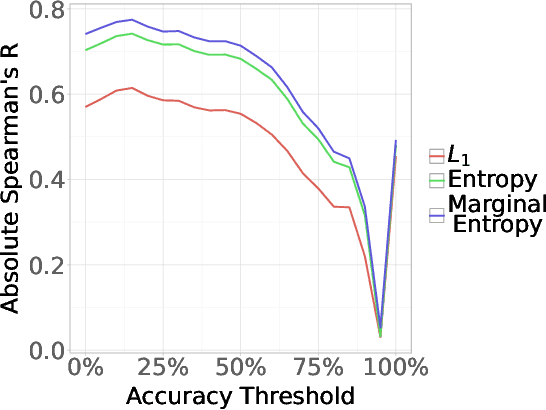
Abstract:Neural networks are powerful tools for cognitive modeling due to their flexibility and emergent properties. However, interpreting their learned representations remains challenging due to their sub-symbolic semantics. In this work, we introduce a novel probabilistic framework for interpreting latent task representations in neural networks. Inspired by Bayesian inference, our approach defines a distribution over representational units to infer their causal contributions to task performance. Using ideas from information theory, we propose a suite of tools and metrics to illuminate key model properties, including representational distributedness, manifold complexity, and polysemanticity.
Using the Tools of Cognitive Science to Understand Large Language Models at Different Levels of Analysis
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence systems, such as large language models, are increasingly powerful but also increasingly hard to understand. Recognizing this problem as analogous to the historical difficulties in understanding the human mind, we argue that methods developed in cognitive science can be useful for understanding large language models. We propose a framework for applying these methods based on Marr's three levels of analysis. By revisiting established cognitive science techniques relevant to each level and illustrating their potential to yield insights into the behavior and internal organization of large language models, we aim to provide a toolkit for making sense of these new kinds of minds.
Discrete, compositional, and symbolic representations through attractor dynamics
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:Compositionality is an important feature of discrete symbolic systems, such as language and programs, as it enables them to have infinite capacity despite a finite symbol set. It serves as a useful abstraction for reasoning in both cognitive science and in AI, yet the interface between continuous and symbolic processing is often imposed by fiat at the algorithmic level, such as by means of quantization or a softmax sampling step. In this work, we explore how discretization could be implemented in a more neurally plausible manner through the modeling of attractor dynamics that partition the continuous representation space into basins that correspond to sequences of symbols. Building on established work in attractor networks and introducing novel training methods, we show that imposing structure in the symbolic space can produce compositionality in the attractor-supported representation space of rich sensory inputs. Lastly, we argue that our model exhibits the process of an information bottleneck that is thought to play a role in conscious experience, decomposing the rich information of a sensory input into stable components encoding symbolic information.
Resource-Aware Pareto-Optimal Automated Machine Learning Platform
Oct 30, 2020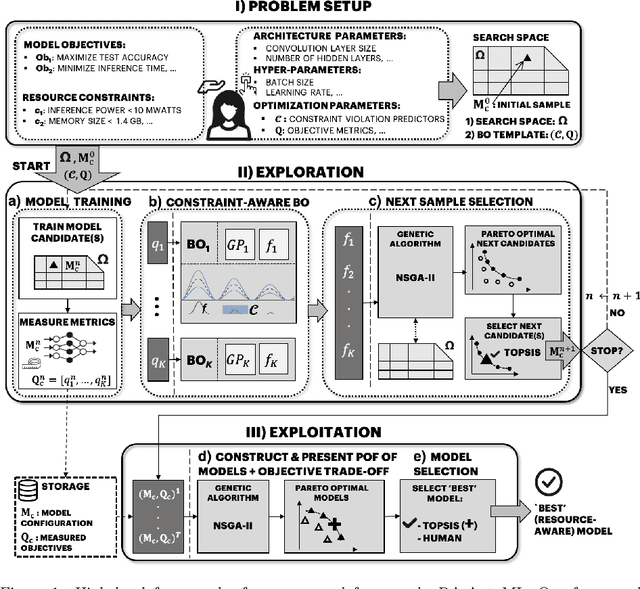
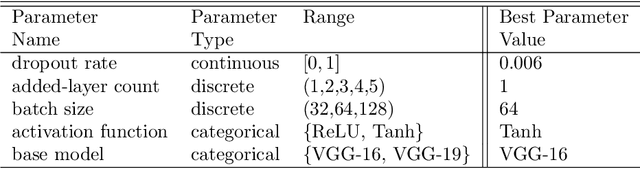
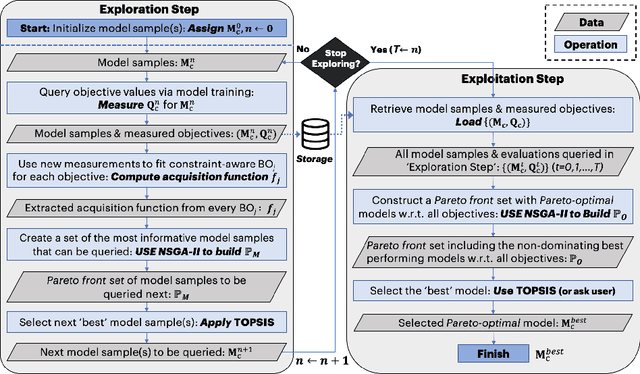
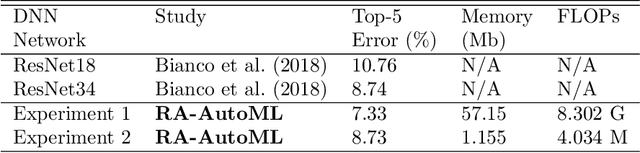
Abstract:In this study, we introduce a novel platform Resource-Aware AutoML (RA-AutoML) which enables flexible and generalized algorithms to build machine learning models subjected to multiple objectives, as well as resource and hard-ware constraints. RA-AutoML intelligently conducts Hyper-Parameter Search(HPS) as well as Neural Architecture Search (NAS) to build models optimizing predefined objectives. RA-AutoML is a versatile framework that allows user to prescribe many resource/hardware constraints along with objectives demanded by the problem at hand or business requirements. At its core, RA-AutoML relies on our in-house search-engine algorithm,MOBOGA, which combines a modified constraint-aware Bayesian Optimization and Genetic Algorithm to construct Pareto optimal candidates. Our experiments on CIFAR-10 dataset shows very good accuracy compared to results obtained by state-of-art neural network models, while subjected to resource constraints in the form of model size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge