Andrew Melbourne
Deep Learning-Based Fetal Lung Segmentation from Diffusion-weighted MRI Images and Lung Maturity Evaluation for Fetal Growth Restriction
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Fetal lung maturity is a critical indicator for predicting neonatal outcomes and the need for post-natal intervention, especially for pregnancies affected by fetal growth restriction. Intra-voxel incoherent motion analysis has shown promising results for non-invasive assessment of fetal lung development, but its reliance on manual segmentation is time-consuming, thus limiting its clinical applicability. In this work, we present an automated lung maturity evaluation pipeline for diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images that consists of a deep learning-based fetal lung segmentation model and a model-fitting lung maturity assessment. A 3D nnU-Net model was trained on manually segmented images selected from the baseline frames of 4D diffusion-weighted MRI scans. The segmentation model demonstrated robust performance, yielding a mean Dice coefficient of 82.14%. Next, voxel-wise model fitting was performed based on both the nnU-Net-predicted and manual lung segmentations to quantify IVIM parameters reflecting tissue microstructure and perfusion. The results suggested no differences between the two. Our work shows that a fully automated pipeline is possible for supporting fetal lung maturity assessment and clinical decision-making.
PIPPI2021: An Approach to Automated Diagnosis and Texture Analysis of the Fetal Liver & Placenta in Fetal Growth Restriction
Nov 01, 2022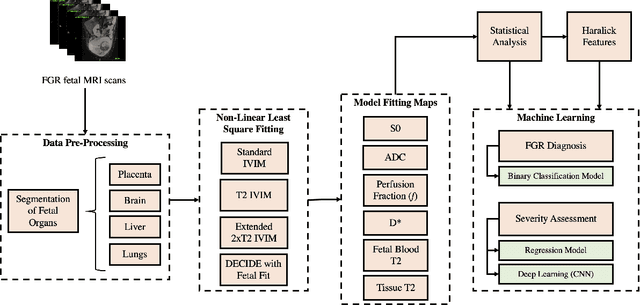
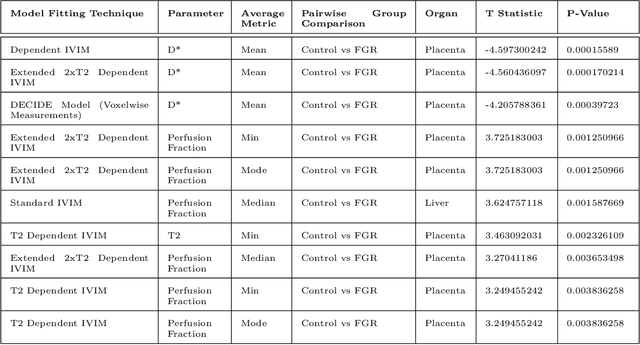
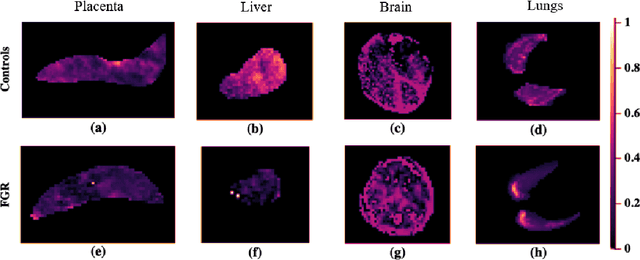
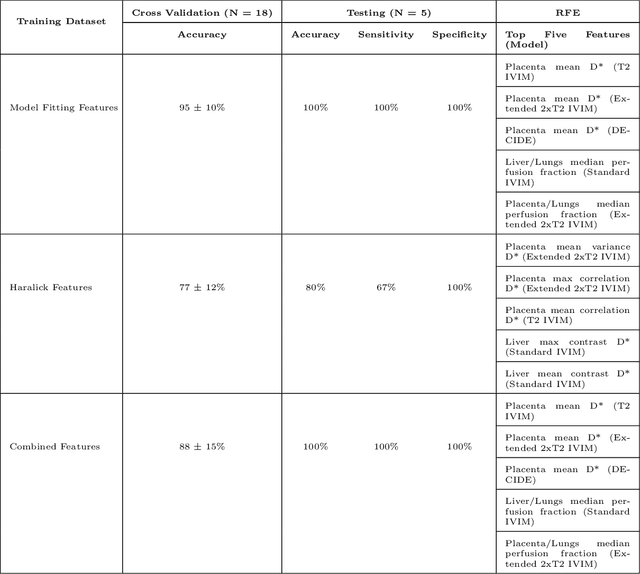
Abstract:Fetal growth restriction (FGR) is a prevalent pregnancy condition characterised by failure of the fetus to reach its genetically predetermined growth potential. We explore the application of model fitting techniques, linear regression machine learning models, deep learning regression, and Haralick textured features from multi-contrast MRI for multi-fetal organ analysis of FGR. We employed T2 relaxometry and diffusion-weighted MRI datasets (using a combined T2-diffusion scan) for 12 normally grown and 12 FGR gestational age (GA) matched pregnancies. We applied the Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Model and novel multi-compartment models for MRI fetal analysis, which exhibit potential to provide a multi-organ FGR assessment, overcoming the limitations of empirical indicators - such as abnormal artery Doppler findings - to evaluate placental dysfunction. The placenta and fetal liver presented key differentiators between FGR and normal controls (decreased perfusion, abnormal fetal blood motion and reduced fetal blood oxygenation. This may be associated with the preferential shunting of the fetal blood towards the fetal brain. These features were further explored to determine their role in assessing FGR severity, by employing simple machine learning models to predict FGR diagnosis (100\% accuracy in test data, n=5), GA at delivery, time from MRI scan to delivery, and baby weight. Moreover, we explored the use of deep learning to regress the latter three variables. Image texture analysis of the fetal organs demonstrated prominent textural variations in the placental perfusion fractions maps between the groups (p$<$0.0009), and spatial differences in the incoherent fetal capillary blood motion in the liver (p$<$0.009). This research serves as a proof-of-concept, investigating the effect of FGR on fetal organs.
A Dempster-Shafer approach to trustworthy AI with application to fetal brain MRI segmentation
Apr 05, 2022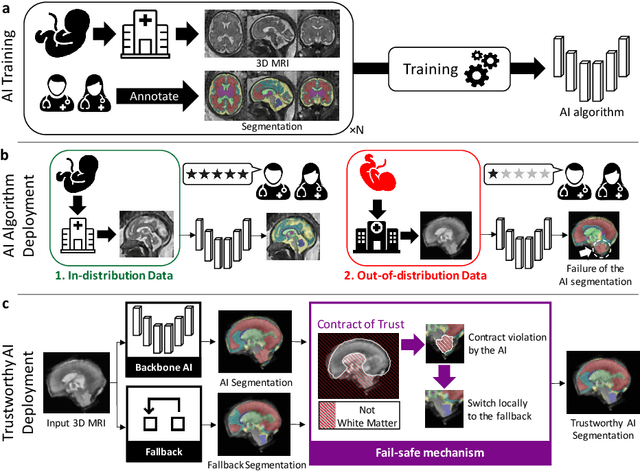
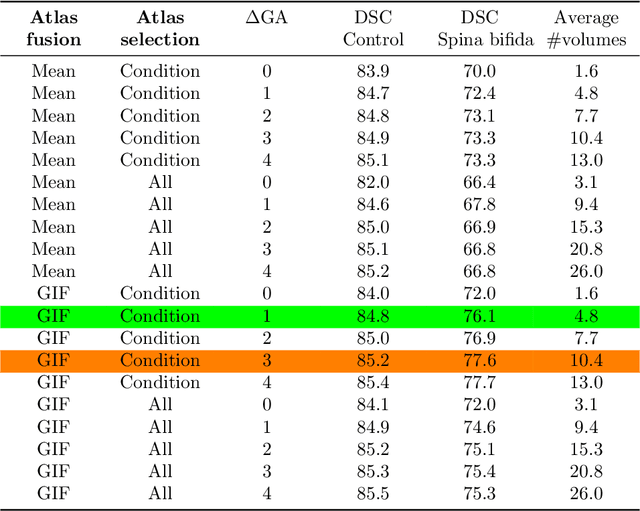
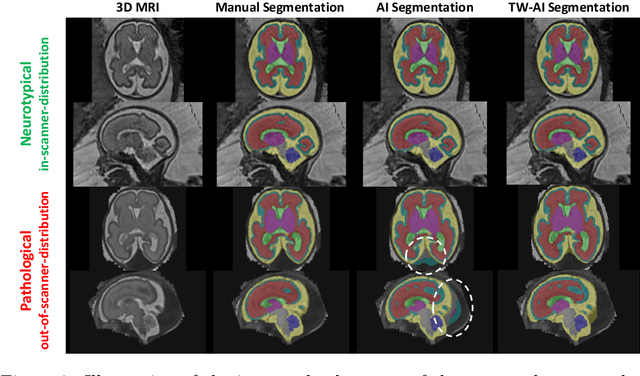
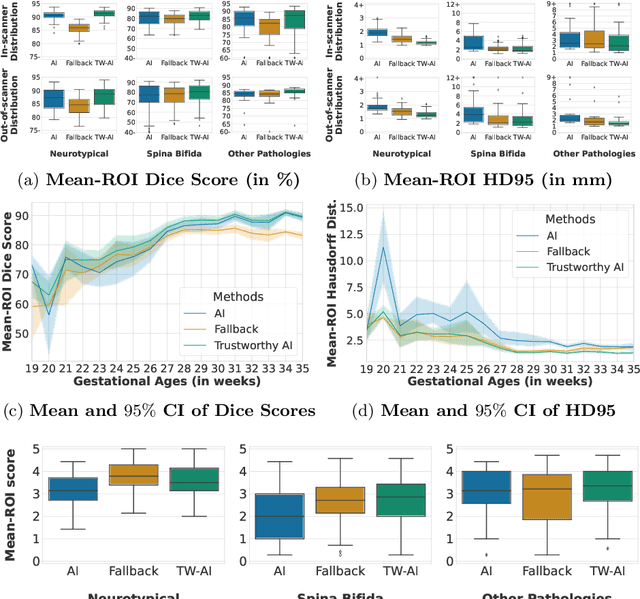
Abstract:Deep learning models for medical image segmentation can fail unexpectedly and spectacularly for pathological cases and for images acquired at different centers than those used for training, with labeling errors that violate expert knowledge about the anatomy and the intensity distribution of the regions to be segmented. Such errors undermine the trustworthiness of deep learning models developed for medical image segmentation. Mechanisms with a fallback method for detecting and correcting such failures are essential for safely translating this technology into clinics and are likely to be a requirement of future regulations on artificial intelligence (AI). Here, we propose a principled trustworthy AI theoretical framework and a practical system that can augment any backbone AI system using a fallback method and a fail-safe mechanism based on Dempster-Shafer theory. Our approach relies on an actionable definition of trustworthy AI. Our method automatically discards the voxel-level labeling predicted by the backbone AI that are likely to violate expert knowledge and relies on a fallback atlas-based segmentation method for those voxels. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed trustworthy AI approach on the largest reported annotated dataset of fetal T2w MRI consisting of 540 manually annotated fetal brain 3D MRIs with neurotypical or abnormal brain development and acquired from 13 sources of data across 6 countries. We show that our trustworthy AI method improves the robustness of a state-of-the-art backbone AI for fetal brain MRI segmentation on MRIs acquired across various centers and for fetuses with various brain abnormalities.
Distributionally Robust Segmentation of Abnormal Fetal Brain 3D MRI
Aug 09, 2021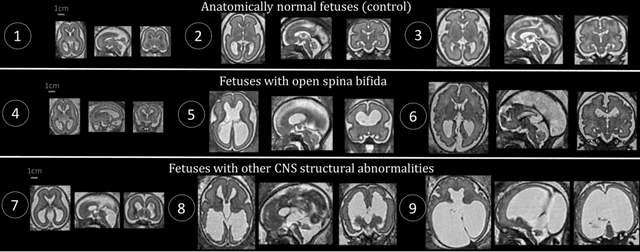
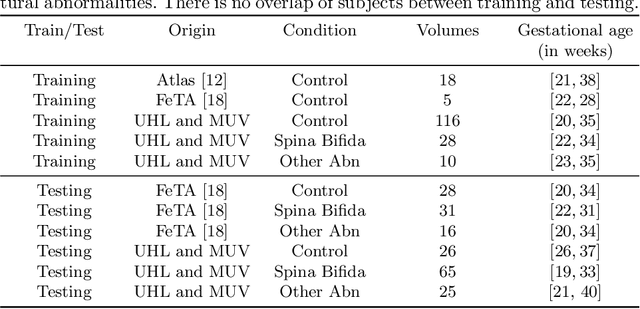
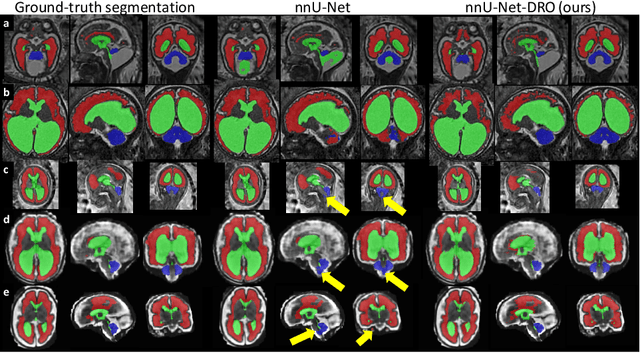
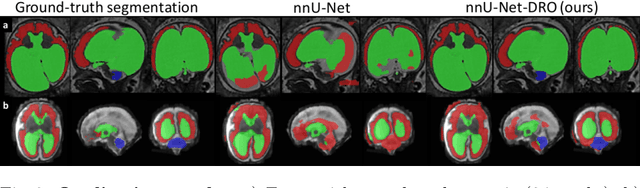
Abstract:The performance of deep neural networks typically increases with the number of training images. However, not all images have the same importance towards improved performance and robustness. In fetal brain MRI, abnormalities exacerbate the variability of the developing brain anatomy compared to non-pathological cases. A small number of abnormal cases, as is typically available in clinical datasets used for training, are unlikely to fairly represent the rich variability of abnormal developing brains. This leads machine learning systems trained by maximizing the average performance to be biased toward non-pathological cases. This problem was recently referred to as hidden stratification. To be suited for clinical use, automatic segmentation methods need to reliably achieve high-quality segmentation outcomes also for pathological cases. In this paper, we show that the state-of-the-art deep learning pipeline nnU-Net has difficulties to generalize to unseen abnormal cases. To mitigate this problem, we propose to train a deep neural network to minimize a percentile of the distribution of per-volume loss over the dataset. We show that this can be achieved by using Distributionally Robust Optimization (DRO). DRO automatically reweights the training samples with lower performance, encouraging nnU-Net to perform more consistently on all cases. We validated our approach using a dataset of 368 fetal brain T2w MRIs, including 124 MRIs of open spina bifida cases and 51 MRIs of cases with other severe abnormalities of brain development.
Label-set Loss Functions for Partial Supervision: Application to Fetal Brain 3D MRI Parcellation
Jul 09, 2021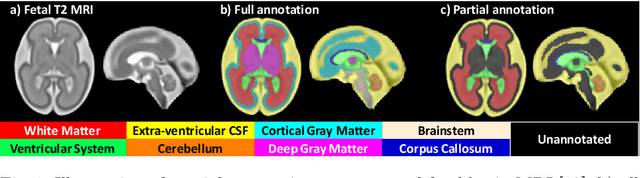
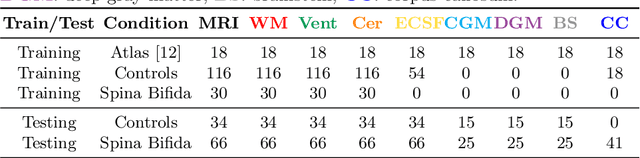
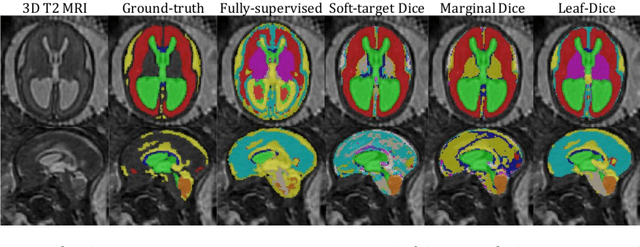
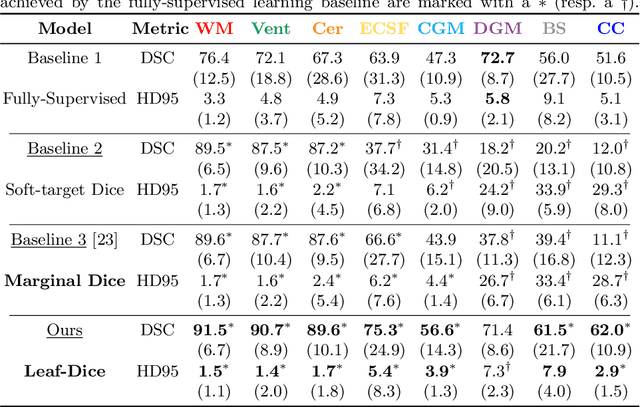
Abstract:Deep neural networks have increased the accuracy of automatic segmentation, however, their accuracy depends on the availability of a large number of fully segmented images. Methods to train deep neural networks using images for which some, but not all, regions of interest are segmented are necessary to make better use of partially annotated datasets. In this paper, we propose the first axiomatic definition of label-set loss functions that are the loss functions that can handle partially segmented images. We prove that there is one and only one method to convert a classical loss function for fully segmented images into a proper label-set loss function. Our theory also allows us to define the leaf-Dice loss, a label-set generalization of the Dice loss particularly suited for partial supervision with only missing labels. Using the leaf-Dice loss, we set a new state of the art in partially supervised learning for fetal brain 3D MRI segmentation. We achieve a deep neural network able to segment white matter, ventricles, cerebellum, extra-ventricular CSF, cortical gray matter, deep gray matter, brainstem, and corpus callosum based on fetal brain 3D MRI of anatomically normal fetuses or with open spina bifida. Our implementation of the proposed label-set loss functions is available at https://github.com/LucasFidon/label-set-loss-functions
Neuropsychiatric Disease Classification Using Functional Connectomics -- Results of the Connectomics in NeuroImaging Transfer Learning Challenge
Jun 05, 2020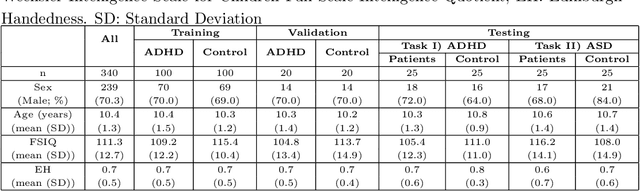
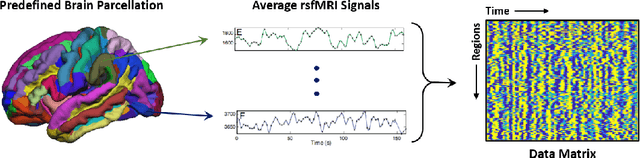
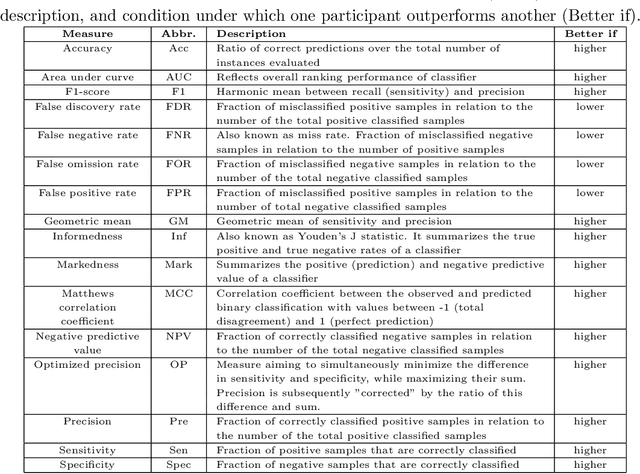
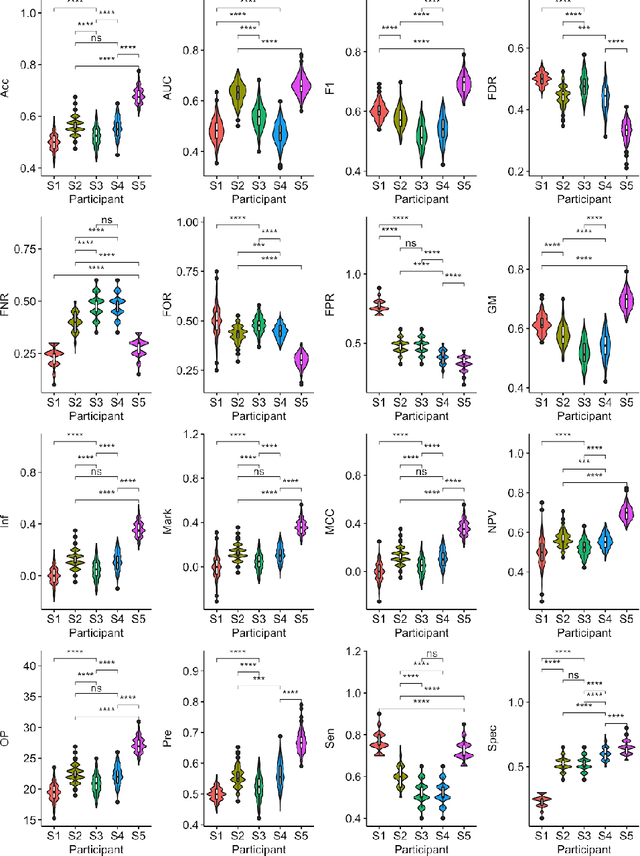
Abstract:Large, open-source consortium datasets have spurred the development of new and increasingly powerful machine learning approaches in brain connectomics. However, one key question remains: are we capturing biologically relevant and generalizable information about the brain, or are we simply overfitting to the data? To answer this, we organized a scientific challenge, the Connectomics in NeuroImaging Transfer Learning Challenge (CNI-TLC), held in conjunction with MICCAI 2019. CNI-TLC included two classification tasks: (1) diagnosis of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) within a pre-adolescent cohort; and (2) transference of the ADHD model to a related cohort of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) patients with an ADHD comorbidity. In total, 240 resting-state fMRI time series averaged according to three standard parcellation atlases, along with clinical diagnosis, were released for training and validation (120 neurotypical controls and 120 ADHD). We also provided demographic information of age, sex, IQ, and handedness. A second set of 100 subjects (50 neurotypical controls, 25 ADHD, and 25 ASD with ADHD comorbidity) was used for testing. Models were submitted in a standardized format as Docker images through ChRIS, an open-source image analysis platform. Utilizing an inclusive approach, we ranked the methods based on 16 different metrics. The final rank was calculated using the rank product for each participant across all measures. Furthermore, we assessed the calibration curves of each method. Five participants submitted their model for evaluation, with one outperforming all other methods in both ADHD and ASD classification. However, further improvements are needed to reach the clinical translation of functional connectomics. We are keeping the CNI-TLC open as a publicly available resource for developing and validating new classification methodologies in the field of connectomics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge