Abigail Morrison
SymSeqBench: a unified framework for the generation and analysis of rule-based symbolic sequences and datasets
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Sequential structure is a key feature of multiple domains of natural cognition and behavior, such as language, movement and decision-making. Likewise, it is also a central property of tasks to which we would like to apply artificial intelligence. It is therefore of great importance to develop frameworks that allow us to evaluate sequence learning and processing in a domain agnostic fashion, whilst simultaneously providing a link to formal theories of computation and computability. To address this need, we introduce two complementary software tools: SymSeq, designed to rigorously generate and analyze structured symbolic sequences, and SeqBench, a comprehensive benchmark suite of rule-based sequence processing tasks to evaluate the performance of artificial learning systems in cognitively relevant domains. In combination, SymSeqBench offers versatility in investigating sequential structure across diverse knowledge domains, including experimental psycholinguistics, cognitive psychology, behavioral analysis, neuromorphic computing and artificial intelligence. Due to its basis in Formal Language Theory (FLT), SymSeqBench provides researchers in multiple domains with a convenient and practical way to apply the concepts of FLT to conceptualize and standardize their experiments, thus advancing our understanding of cognition and behavior through shared computational frameworks and formalisms. The tool is modular, openly available and accessible to the research community.
Scalable Construction of Spiking Neural Networks using up to thousands of GPUs
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:Diverse scientific and engineering research areas deal with discrete, time-stamped changes in large systems of interacting delay differential equations. Simulating such complex systems at scale on high-performance computing clusters demands efficient management of communication and memory. Inspired by the human cerebral cortex -- a sparsely connected network of $\mathcal{O}(10^{10})$ neurons, each forming $\mathcal{O}(10^{3})$--$\mathcal{O}(10^{4})$ synapses and communicating via short electrical pulses called spikes -- we study the simulation of large-scale spiking neural networks for computational neuroscience research. This work presents a novel network construction method for multi-GPU clusters and upcoming exascale supercomputers using the Message Passing Interface (MPI), where each process builds its local connectivity and prepares the data structures for efficient spike exchange across the cluster during state propagation. We demonstrate scaling performance of two cortical models using point-to-point and collective communication, respectively.
Efficient Epistemic Uncertainty Estimation in Cerebrovascular Segmentation
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Brain vessel segmentation of MR scans is a critical step in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases. Due to the fine vessel structure, manual vessel segmentation is time consuming. Therefore, automatic deep learning (DL) based segmentation techniques are intensively investigated. As conventional DL models yield a high complexity and lack an indication of decision reliability, they are often considered as not trustworthy. This work aims to increase trust in DL based models by incorporating epistemic uncertainty quantification into cerebrovascular segmentation models for the first time. By implementing an efficient ensemble model combining the advantages of Bayesian Approximation and Deep Ensembles, we aim to overcome the high computational costs of conventional probabilistic networks. Areas of high model uncertainty and erroneous predictions are aligned which demonstrates the effectiveness and reliability of the approach. We perform extensive experiments applying the ensemble model on out-of-distribution (OOD) data. We demonstrate that for OOD-images, the estimated uncertainty increases. Additionally, omitting highly uncertain areas improves the segmentation quality, both for in- and out-of-distribution data. The ensemble model explains its limitations in a reliable manner and can maintain trustworthiness also for OOD data and could be considered in clinical applications
1LoRA: Summation Compression for Very Low-Rank Adaptation
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods have transformed the approach to fine-tuning large models for downstream tasks by enabling the adjustment of significantly fewer parameters than those in the original model matrices. In this work, we study the "very low rank regime", where we fine-tune the lowest amount of parameters per linear layer for each considered PEFT method. We propose 1LoRA (Summation Low-Rank Adaptation), a compute, parameter and memory efficient fine-tuning method which uses the feature sum as fixed compression and a single trainable vector as decompression. Differently from state-of-the-art PEFT methods like LoRA, VeRA, and the recent MoRA, 1LoRA uses fewer parameters per layer, reducing the memory footprint and the computational cost. We extensively evaluate our method against state-of-the-art PEFT methods on multiple fine-tuning tasks, and show that our method not only outperforms them, but is also more parameter, memory and computationally efficient. Moreover, thanks to its memory efficiency, 1LoRA allows to fine-tune more evenly across layers, instead of focusing on specific ones (e.g. attention layers), improving performance further.
Empirical Comparison between Cross-Validation and Mutation-Validation in Model Selection
Nov 23, 2023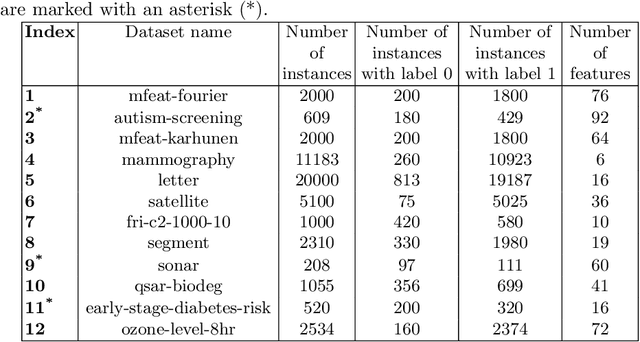
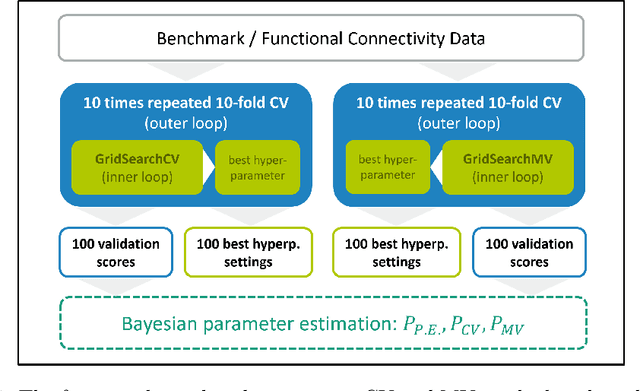
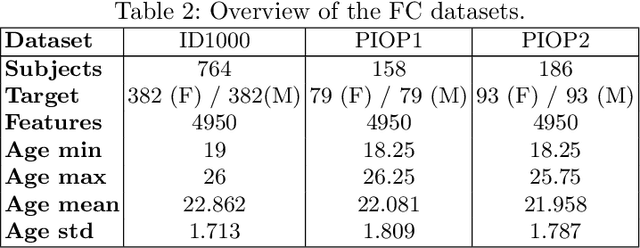
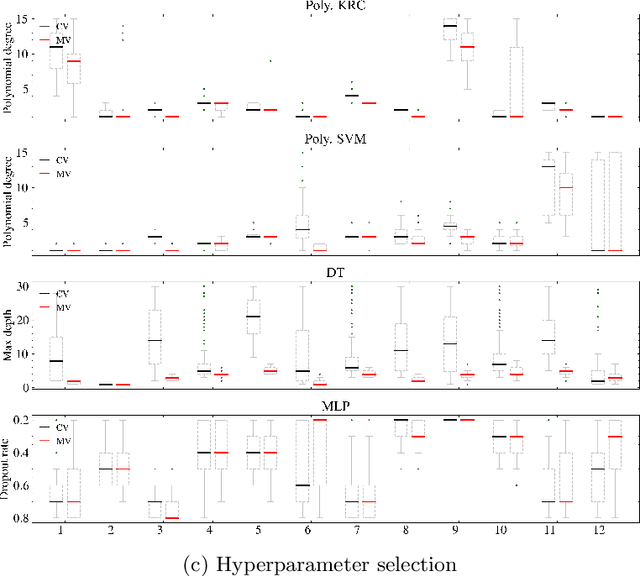
Abstract:Mutation validation (MV) is a recently proposed approach for model selection, garnering significant interest due to its unique characteristics and potential benefits compared to the widely used cross-validation (CV) method. In this study, we empirically compared MV and $k$-fold CV using benchmark and real-world datasets. By employing Bayesian tests, we compared generalization estimates yielding three posterior probabilities: practical equivalence, CV superiority, and MV superiority. We also evaluated the differences in the capacity of the selected models and computational efficiency. We found that both MV and CV select models with practically equivalent generalization performance across various machine learning algorithms and the majority of benchmark datasets. MV exhibited advantages in terms of selecting simpler models and lower computational costs. However, in some cases MV selected overly simplistic models leading to underfitting and showed instability in hyperparameter selection. These limitations of MV became more evident in the evaluation of a real-world neuroscientific task of predicting sex at birth using brain functional connectivity.
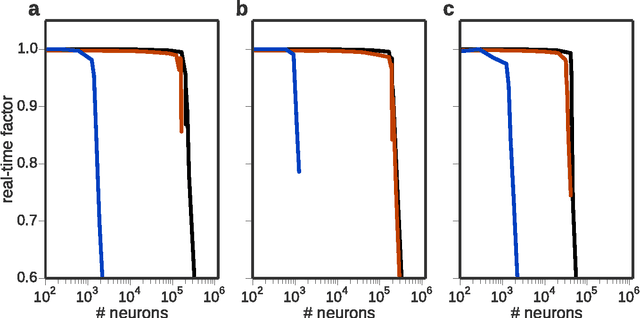
Runtime Construction of Large-Scale Spiking Neuronal Network Models on GPU Devices
Jun 16, 2023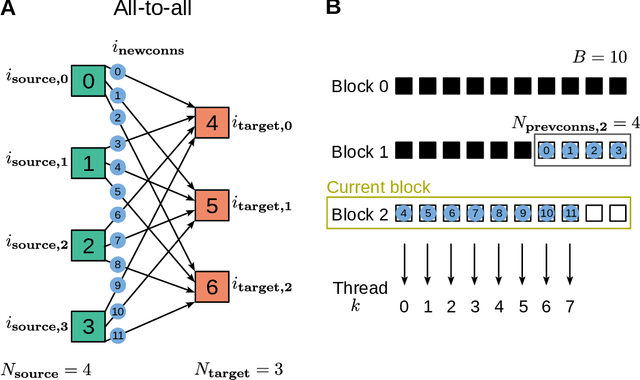
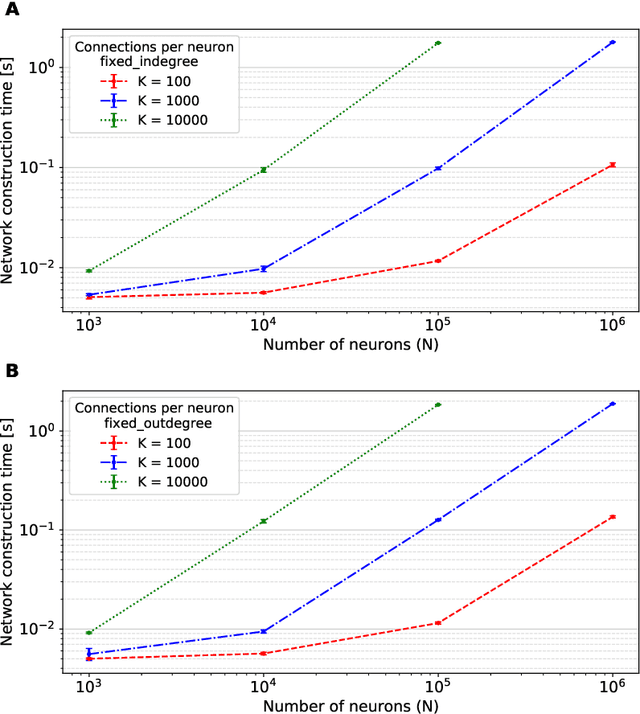


Abstract:Simulation speed matters for neuroscientific research: this includes not only how quickly the simulated model time of a large-scale spiking neuronal network progresses, but also how long it takes to instantiate the network model in computer memory. On the hardware side, acceleration via highly parallel GPUs is being increasingly utilized. On the software side, code generation approaches ensure highly optimized code, at the expense of repeated code regeneration and recompilation after modifications to the network model. Aiming for a greater flexibility with respect to iterative model changes, here we propose a new method for creating network connections interactively, dynamically, and directly in GPU memory through a set of commonly used high-level connection rules. We validate the simulation performance with both consumer and data center GPUs on two neuroscientifically relevant models: a cortical microcircuit of about 77,000 leaky-integrate-and-fire neuron models and 300 million static synapses, and a two-population network recurrently connected using a variety of connection rules. With our proposed ad hoc network instantiation, both network construction and simulation times are comparable or shorter than those obtained with other state-of-the-art simulation technologies, while still meeting the flexibility demands of explorative network modeling.
Emergent communication enhances foraging behaviour in evolved swarms controlled by Spiking Neural Networks
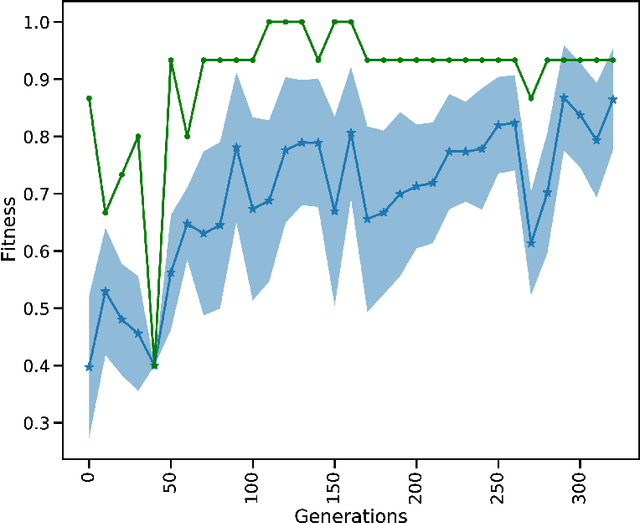
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:Social insects such as ants communicate via pheromones which allows them to coordinate their activity and solve complex tasks as a swarm, e.g. foraging for food. This behaviour was shaped through evolutionary processes. In computational models, self-coordination in swarms has been implemented using probabilistic or action rules to shape the decision of each agent and the collective behaviour. However, manual tuned decision rules may limit the behaviour of the swarm. In this work we investigate the emergence of self-coordination and communication in evolved swarms without defining any rule. We evolve a swarm of agents representing an ant colony. We use a genetic algorithm to optimize a spiking neural network (SNN) which serves as an artificial brain to control the behaviour of each agent. The goal of the colony is to find optimal ways to forage for food in the shortest amount of time. In the evolutionary phase, the ants are able to learn to collaborate by depositing pheromone near food piles and near the nest to guide its cohorts. The pheromone usage is not encoded into the network; instead, this behaviour is established through the optimization procedure. We observe that pheromone-based communication enables the ants to perform better in comparison to colonies where communication did not emerge. We assess the foraging performance by comparing the SNN based model to a rule based system. Our results show that the SNN based model can complete the foraging task more efficiently in a shorter time. Our approach illustrates that even in the absence of pre-defined rules, self coordination via pheromone emerges as a result of the network optimization. This work serves as a proof of concept for the possibility of creating complex applications utilizing SNNs as underlying architectures for multi-agent interactions where communication and self-coordination is desired.
Phenomenological modeling of diverse and heterogeneous synaptic dynamics at natural density
Dec 10, 2022Abstract:This chapter sheds light on the synaptic organization of the brain from the perspective of computational neuroscience. It provides an introductory overview on how to account for empirical data in mathematical models, implement them in software, and perform simulations reflecting experiments. This path is demonstrated with respect to four key aspects of synaptic signaling: the connectivity of brain networks, synaptic transmission, synaptic plasticity, and the heterogeneity across synapses. Each step and aspect of the modeling and simulation workflow comes with its own challenges and pitfalls, which are highlighted and addressed in detail.
Exploring hyper-parameter spaces of neuroscience models on high performance computers with Learning to Learn
Feb 28, 2022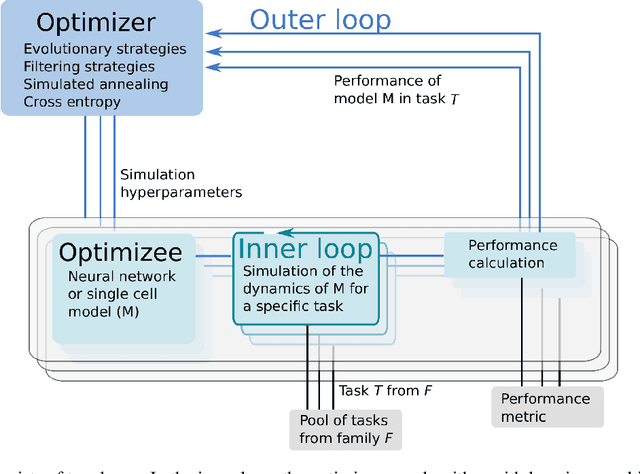
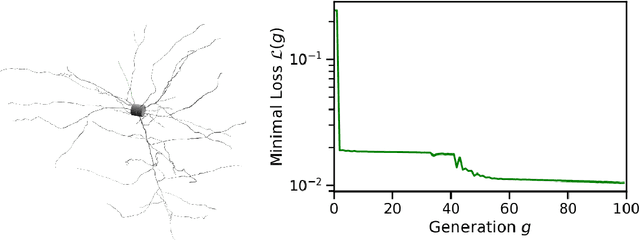
Abstract:Neuroscience models commonly have a high number of degrees of freedom and only specific regions within the parameter space are able to produce dynamics of interest. This makes the development of tools and strategies to efficiently find these regions of high importance to advance brain research. Exploring the high dimensional parameter space using numerical simulations has been a frequently used technique in the last years in many areas of computational neuroscience. High performance computing (HPC) can provide today a powerful infrastructure to speed up explorations and increase our general understanding of the model's behavior in reasonable times.
Closed loop interactions between spiking neural network and robotic simulators based on MUSIC and ROS
Apr 16, 2016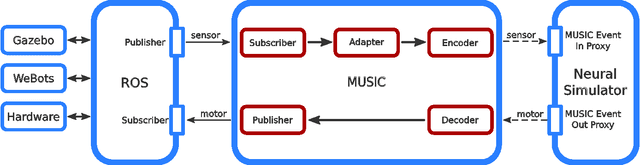
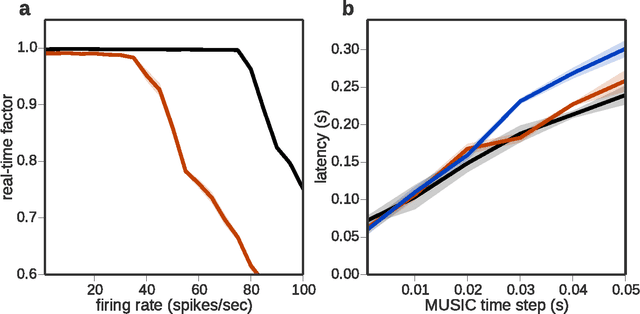
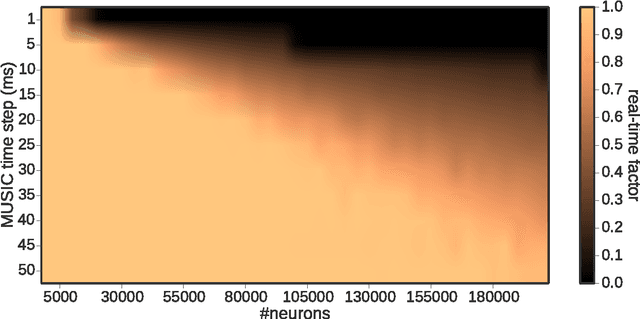
Abstract:In order to properly assess the function and computational properties of simulated neural systems, it is necessary to account for the nature of the stimuli that drive the system. However, providing stimuli that are rich and yet both reproducible and amenable to experimental manipulations is technically challenging, and even more so if a closed-loop scenario is required. In this work, we present a novel approach to solve this problem, connecting robotics and neural network simulators. We implement a middleware solution that bridges the Robotic Operating System (ROS) to the Multi-Simulator Coordinator (MUSIC). This enables any robotic and neural simulators that implement the corresponding interfaces to be efficiently coupled, allowing real-time performance for a wide range of configurations. This work extends the toolset available for researchers in both neurorobotics and computational neuroscience, and creates the opportunity to perform closed-loop experiments of arbitrary complexity to address questions in multiple areas, including embodiment, agency, and reinforcement learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge