Gianmarco Tiddia
Scalable Construction of Spiking Neural Networks using up to thousands of GPUs
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:Diverse scientific and engineering research areas deal with discrete, time-stamped changes in large systems of interacting delay differential equations. Simulating such complex systems at scale on high-performance computing clusters demands efficient management of communication and memory. Inspired by the human cerebral cortex -- a sparsely connected network of $\mathcal{O}(10^{10})$ neurons, each forming $\mathcal{O}(10^{3})$--$\mathcal{O}(10^{4})$ synapses and communicating via short electrical pulses called spikes -- we study the simulation of large-scale spiking neural networks for computational neuroscience research. This work presents a novel network construction method for multi-GPU clusters and upcoming exascale supercomputers using the Message Passing Interface (MPI), where each process builds its local connectivity and prepares the data structures for efficient spike exchange across the cluster during state propagation. We demonstrate scaling performance of two cortical models using point-to-point and collective communication, respectively.
Runtime Construction of Large-Scale Spiking Neuronal Network Models on GPU Devices
Jun 16, 2023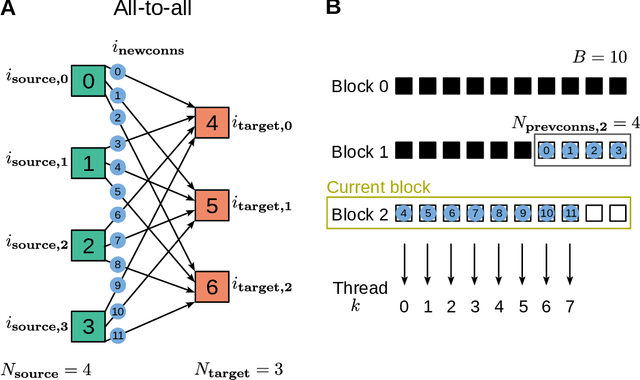


Abstract:Simulation speed matters for neuroscientific research: this includes not only how quickly the simulated model time of a large-scale spiking neuronal network progresses, but also how long it takes to instantiate the network model in computer memory. On the hardware side, acceleration via highly parallel GPUs is being increasingly utilized. On the software side, code generation approaches ensure highly optimized code, at the expense of repeated code regeneration and recompilation after modifications to the network model. Aiming for a greater flexibility with respect to iterative model changes, here we propose a new method for creating network connections interactively, dynamically, and directly in GPU memory through a set of commonly used high-level connection rules. We validate the simulation performance with both consumer and data center GPUs on two neuroscientifically relevant models: a cortical microcircuit of about 77,000 leaky-integrate-and-fire neuron models and 300 million static synapses, and a two-population network recurrently connected using a variety of connection rules. With our proposed ad hoc network instantiation, both network construction and simulation times are comparable or shorter than those obtained with other state-of-the-art simulation technologies, while still meeting the flexibility demands of explorative network modeling.
A new GPU library for fast simulation of large-scale networks of spiking neurons
Jul 29, 2020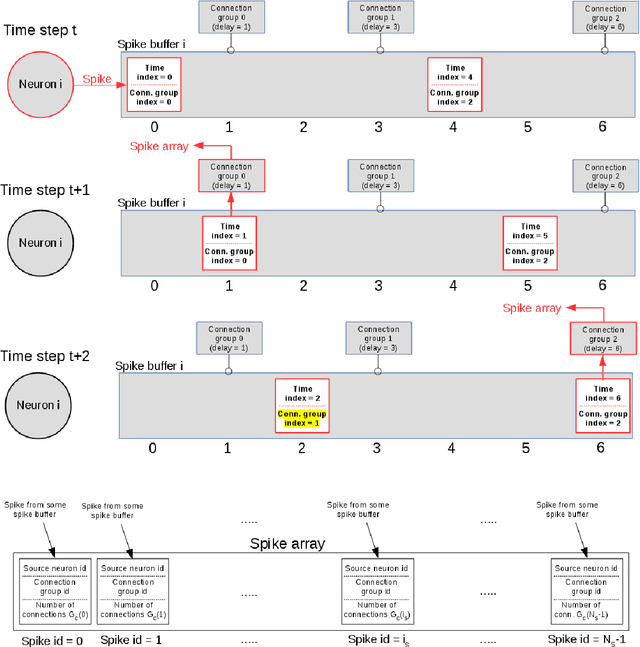
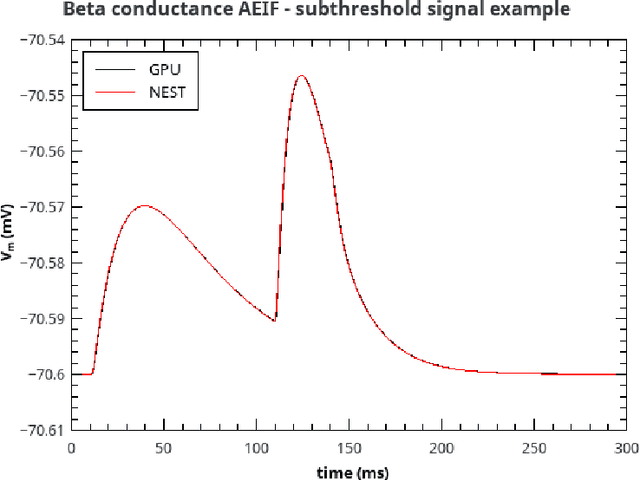
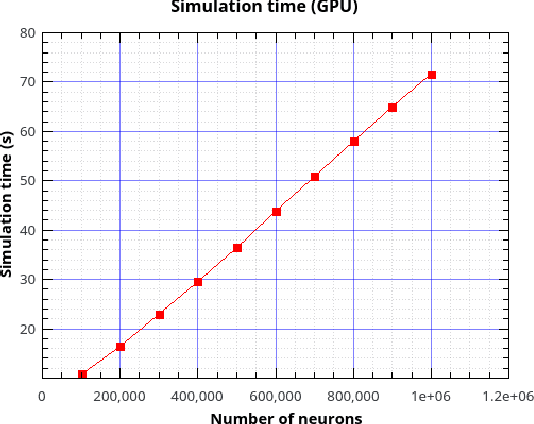

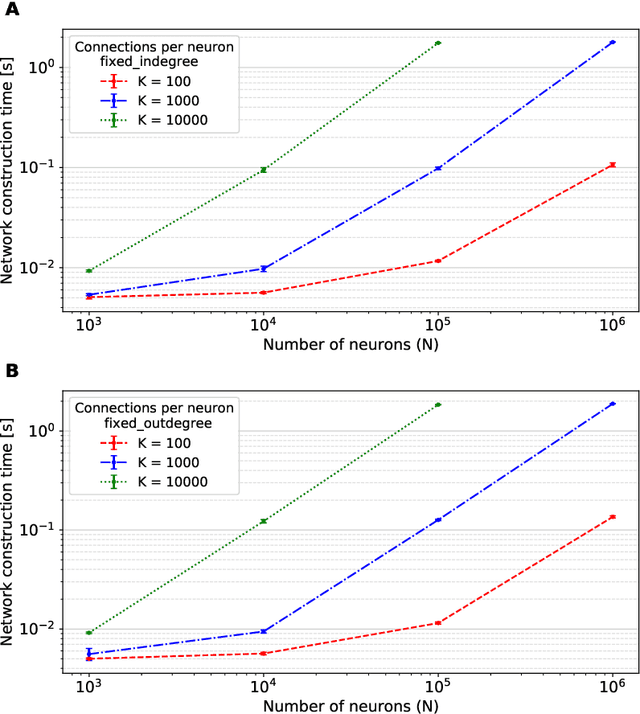
Abstract:Over the past decade there has been a growing interest in the development of parallel hardware systems for simulating large-scale networks of spiking neurons. Compared to other highly-parallel systems, GPU-accelerated solutions have the advantage of a relatively low cost and a great versatility, thanks also to the possibility of using the CUDA-C/C++ programming languages. NeuronGPU is a GPU library for large-scale simulations of spiking neural network models, written in the C++ and CUDA-C++ programming languages, based on a novel spike-delivery algorithm. This library includes simple LIF (leaky-integrate-and-fire) neuron models as well as several multisynapse AdEx (adaptive-exponential-integrate-and-fire) neuron models with current or conductance based synapses, user definable models and different devices. The numerical solution of the differential equations of the dynamics of the AdEx models is performed through a parallel implementation, written in CUDA-C++, of the fifth-order Runge-Kutta method with adaptive step-size control. In this work we evaluate the performance of this library on the simulation of a well-known cortical microcircuit model, based on LIF neurons and current-based synapses, and on a balanced networks of excitatory and inhibitory neurons, using AdEx neurons and conductance-based synapses. On these models, we will show that the proposed library achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of simulation time per second of biological activity. In particular, using a single NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPU board, the full-scale cortical-microcircuit model, which includes about 77,000 neurons and $3 \cdot 10^8$ connections, can be simulated at a speed very close to real time, while the simulation time of a balanced network of 1,000,000 AdEx neurons with 1,000 connections per neuron was about 70 s per second of biological activity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge