Johanna Senk
Scalable Construction of Spiking Neural Networks using up to thousands of GPUs
Dec 10, 2025



Abstract:Diverse scientific and engineering research areas deal with discrete, time-stamped changes in large systems of interacting delay differential equations. Simulating such complex systems at scale on high-performance computing clusters demands efficient management of communication and memory. Inspired by the human cerebral cortex -- a sparsely connected network of $\mathcal{O}(10^{10})$ neurons, each forming $\mathcal{O}(10^{3})$--$\mathcal{O}(10^{4})$ synapses and communicating via short electrical pulses called spikes -- we study the simulation of large-scale spiking neural networks for computational neuroscience research. This work presents a novel network construction method for multi-GPU clusters and upcoming exascale supercomputers using the Message Passing Interface (MPI), where each process builds its local connectivity and prepares the data structures for efficient spike exchange across the cluster during state propagation. We demonstrate scaling performance of two cortical models using point-to-point and collective communication, respectively.
Metadata practices for simulation workflows
Aug 30, 2024Abstract:Computer simulations are an essential pillar of knowledge generation in science. Understanding, reproducing, and exploring the results of simulations relies on tracking and organizing metadata describing numerical experiments. However, the models used to understand real-world systems, and the computational machinery required to simulate them, are typically complex, and produce large amounts of heterogeneous metadata. Here, we present general practices for acquiring and handling metadata that are agnostic to software and hardware, and highly flexible for the user. These consist of two steps: 1) recording and storing raw metadata, and 2) selecting and structuring metadata. As a proof of concept, we develop the Archivist, a Python tool to help with the second step, and use it to apply our practices to distinct high-performance computing use cases from neuroscience and hydrology. Our practices and the Archivist can readily be applied to existing workflows without the need for substantial restructuring. They support sustainable numerical workflows, facilitating reproducibility and data reuse in generic simulation-based research.
Runtime Construction of Large-Scale Spiking Neuronal Network Models on GPU Devices
Jun 16, 2023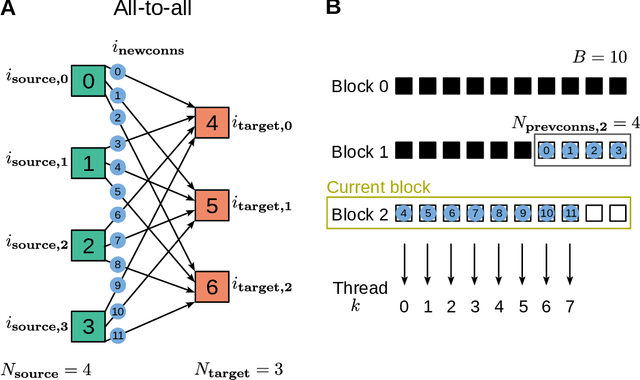
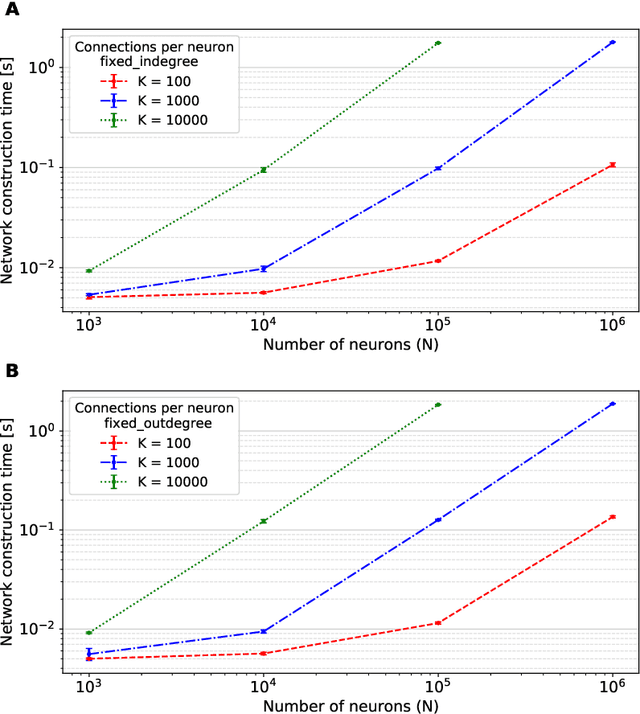


Abstract:Simulation speed matters for neuroscientific research: this includes not only how quickly the simulated model time of a large-scale spiking neuronal network progresses, but also how long it takes to instantiate the network model in computer memory. On the hardware side, acceleration via highly parallel GPUs is being increasingly utilized. On the software side, code generation approaches ensure highly optimized code, at the expense of repeated code regeneration and recompilation after modifications to the network model. Aiming for a greater flexibility with respect to iterative model changes, here we propose a new method for creating network connections interactively, dynamically, and directly in GPU memory through a set of commonly used high-level connection rules. We validate the simulation performance with both consumer and data center GPUs on two neuroscientifically relevant models: a cortical microcircuit of about 77,000 leaky-integrate-and-fire neuron models and 300 million static synapses, and a two-population network recurrently connected using a variety of connection rules. With our proposed ad hoc network instantiation, both network construction and simulation times are comparable or shorter than those obtained with other state-of-the-art simulation technologies, while still meeting the flexibility demands of explorative network modeling.
Phenomenological modeling of diverse and heterogeneous synaptic dynamics at natural density
Dec 10, 2022Abstract:This chapter sheds light on the synaptic organization of the brain from the perspective of computational neuroscience. It provides an introductory overview on how to account for empirical data in mathematical models, implement them in software, and perform simulations reflecting experiments. This path is demonstrated with respect to four key aspects of synaptic signaling: the connectivity of brain networks, synaptic transmission, synaptic plasticity, and the heterogeneity across synapses. Each step and aspect of the modeling and simulation workflow comes with its own challenges and pitfalls, which are highlighted and addressed in detail.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge