Çağrı Çöltekin
Tübingen-CL at SemEval-2024 Task 1:Ensemble Learning for Semantic Relatedness Estimation
Oct 14, 2024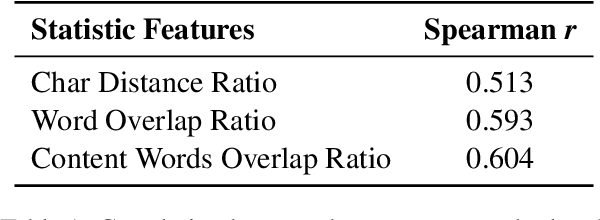
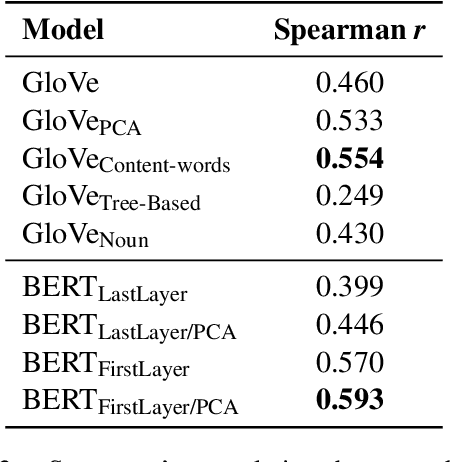
Abstract:The paper introduces our system for SemEval-2024 Task 1, which aims to predict the relatedness of sentence pairs. Operating under the hypothesis that semantic relatedness is a broader concept that extends beyond mere similarity of sentences, our approach seeks to identify useful features for relatedness estimation. We employ an ensemble approach integrating various systems, including statistical textual features and outputs of deep learning models to predict relatedness scores. The findings suggest that semantic relatedness can be inferred from various sources and ensemble models outperform many individual systems in estimating semantic relatedness.
* 5 pages
Multilingual Power and Ideology Identification in the Parliament: a Reference Dataset and Simple Baselines
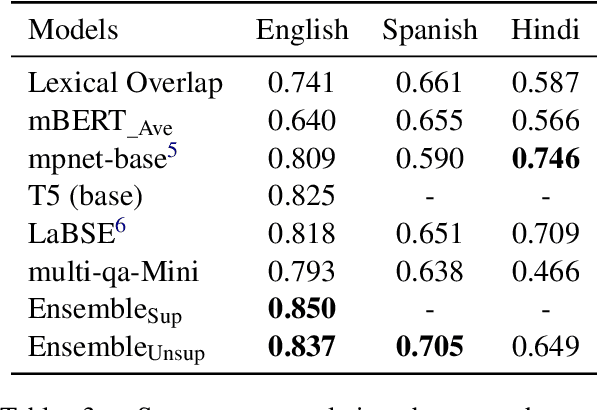
May 12, 2024Abstract:We introduce a dataset on political orientation and power position identification. The dataset is derived from ParlaMint, a set of comparable corpora of transcribed parliamentary speeches from 29 national and regional parliaments. We introduce the dataset, provide the reasoning behind some of the choices during its creation, present statistics on the dataset, and, using a simple classifier, some baseline results on predicting political orientation on the left-to-right axis, and on power position identification, i.e., distinguishing between the speeches delivered by governing coalition party members from those of opposition party members.
Findings of the VarDial Evaluation Campaign 2023
May 31, 2023Abstract:This report presents the results of the shared tasks organized as part of the VarDial Evaluation Campaign 2023. The campaign is part of the tenth workshop on Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects (VarDial), co-located with EACL 2023. Three separate shared tasks were included this year: Slot and intent detection for low-resource language varieties (SID4LR), Discriminating Between Similar Languages -- True Labels (DSL-TL), and Discriminating Between Similar Languages -- Speech (DSL-S). All three tasks were organized for the first time this year.
What do complexity measures measure? Correlating and validating corpus-based measures of morphological complexity
Apr 11, 2022



Abstract:We present an analysis of eight measures used for quantifying morphological complexity of natural languages. The measures we study are corpus-based measures of morphological complexity with varying requirements for corpus annotation. We present similarities and differences between these measures visually and through correlation analyses, as well as their relation to the relevant typological variables. Our analysis focuses on whether these `measures' are measures of the same underlying variable, or whether they measure more than one dimension of morphological complexity. The principal component analysis indicates that the first principal component explains 92.62 % of the variation in eight measures, indicating a strong linear dependence between the complexity measures studied.
Resources for Turkish Natural Language Processing: A critical survey
Apr 11, 2022



Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive survey of corpora and lexical resources available for Turkish. We review a broad range of resources, focusing on the ones that are publicly available. In addition to providing information about the available linguistic resources, we present a set of recommendations, and identify gaps in the data available for conducting research and building applications in Turkish Linguistics and Natural Language Processing.
SemEval-2020 Task 12: Multilingual Offensive Language Identification in Social Media (OffensEval 2020)
Jun 12, 2020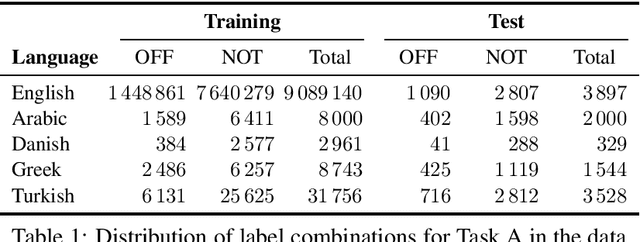
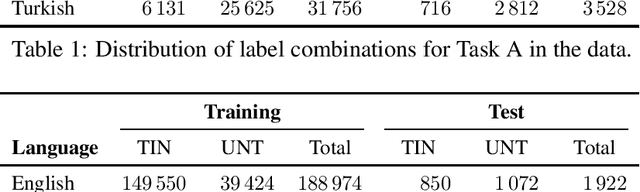
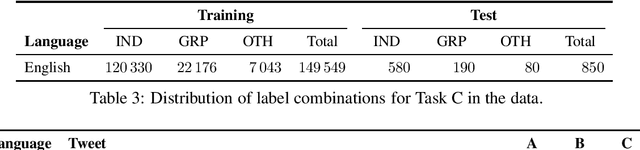

Abstract:We present the results and main findings of SemEval-2020 Task 12 on Multilingual Offensive Language Identification in Social Media (OffensEval 2020). The task involves three subtasks corresponding to the hierarchical taxonomy of the OLID schema (Zampieri et al., 2019a) from OffensEval 2019. The task featured five languages: English, Arabic, Danish, Greek, and Turkish for Subtask A. In addition, English also featured Subtasks B and C. OffensEval 2020 was one of the most popular tasks at SemEval-2020 attracting a large number of participants across all subtasks and also across all languages. A total of 528 teams signed up to participate in the task, 145 teams submitted systems during the evaluation period, and 70 submitted system description papers.
Tübingen-Oslo system: Linear regression works the best at Predicting Current and Future Psychological Health from Childhood Essays in the CLPsych 2018 Shared Task
Sep 13, 2018

Abstract:This paper describes our efforts in predicting current and future psychological health from childhood essays within the scope of the CLPsych-2018 Shared Task. We experimented with a number of different models, including recurrent and convolutional networks, Poisson regression, support vector regression, and L1 and L2 regularized linear regression. We obtained the best results on the training/development data with L2 regularized linear regression (ridge regression) which also got the best scores on main metrics in the official testing for task A (predicting psychological health from essays written at the age of 11 years) and task B (predicting later psychological health from essays written at the age of 11).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge