Network Intrusion Detection
Network intrusion detection is the process of identifying and preventing unauthorized access to computer networks.
Papers and Code
Gotham Dataset 2025: A Reproducible Large-Scale IoT Network Dataset for Intrusion Detection and Security Research
Feb 05, 2025In this paper, a dataset of IoT network traffic is presented. Our dataset was generated by utilising the Gotham testbed, an emulated large-scale Internet of Things (IoT) network designed to provide a realistic and heterogeneous environment for network security research. The testbed includes 78 emulated IoT devices operating on various protocols, including MQTT, CoAP, and RTSP. Network traffic was captured in Packet Capture (PCAP) format using tcpdump, and both benign and malicious traffic were recorded. Malicious traffic was generated through scripted attacks, covering a variety of attack types, such as Denial of Service (DoS), Telnet Brute Force, Network Scanning, CoAP Amplification, and various stages of Command and Control (C&C) communication. The data were subsequently processed in Python for feature extraction using the Tshark tool, and the resulting data was converted to Comma Separated Values (CSV) format and labelled. The data repository includes the raw network traffic in PCAP format and the processed labelled data in CSV format. Our dataset was collected in a distributed manner, where network traffic was captured separately for each IoT device at the interface between the IoT gateway and the device. Our dataset was collected in a distributed manner, where network traffic was separately captured for each IoT device at the interface between the IoT gateway and the device. With its diverse traffic patterns and attack scenarios, this dataset provides a valuable resource for developing Intrusion Detection Systems and security mechanisms tailored to complex, large-scale IoT environments. The dataset is publicly available at Zenodo.
Strengthening Anomaly Awareness
Apr 15, 2025We present a refined version of the Anomaly Awareness framework for enhancing unsupervised anomaly detection. Our approach introduces minimal supervision into Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) through a two-stage training strategy: the model is first trained in an unsupervised manner on background data, and then fine-tuned using a small sample of labeled anomalies to encourage larger reconstruction errors for anomalous samples. We validate the method across diverse domains, including the MNIST dataset with synthetic anomalies, network intrusion data from the CICIDS benchmark, collider physics data from the LHCO2020 dataset, and simulated events from the Standard Model Effective Field Theory (SMEFT). The latter provides a realistic example of subtle kinematic deviations in Higgs boson production. In all cases, the model demonstrates improved sensitivity to unseen anomalies, achieving better separation between normal and anomalous samples. These results indicate that even limited anomaly information, when incorporated through targeted fine-tuning, can substantially improve the generalization and performance of unsupervised models for anomaly detection.
Continual Learning with Strategic Selection and Forgetting for Network Intrusion Detection
Dec 20, 2024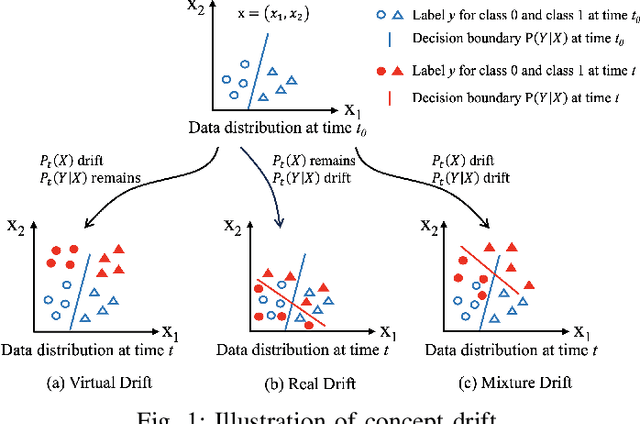
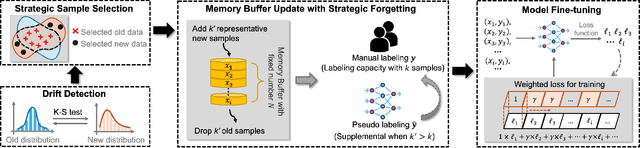
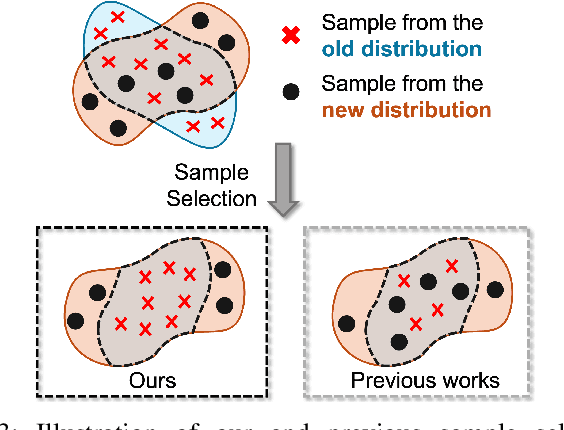
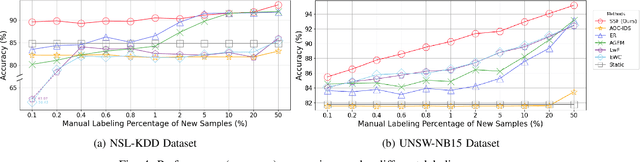
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are crucial for safeguarding digital infrastructure. In dynamic network environments, both threat landscapes and normal operational behaviors are constantly changing, resulting in concept drift. While continuous learning mitigates the adverse effects of concept drift, insufficient attention to drift patterns and excessive preservation of outdated knowledge can still hinder the IDS's adaptability. In this paper, we propose SSF (Strategic Selection and Forgetting), a novel continual learning method for IDS, providing continuous model updates with a constantly refreshed memory buffer. Our approach features a strategic sample selection algorithm to select representative new samples and a strategic forgetting mechanism to drop outdated samples. The proposed strategic sample selection algorithm prioritizes new samples that cause the `drifted' pattern, enabling the model to better understand the evolving landscape. Additionally, we introduce strategic forgetting upon detecting significant drift by discarding outdated samples to free up memory, allowing the incorporation of more recent data. SSF captures evolving patterns effectively and ensures the model is aligned with the change of data patterns, significantly enhancing the IDS's adaptability to concept drift. The state-of-the-art performance of SSF on NSL-KDD and UNSW-NB15 datasets demonstrates its superior adaptability to concept drift for network intrusion detection.
Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Intrusion Detection in IoT: Leveraging a Real-World IoT Dataset
Feb 17, 2025



The rapid growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized industries, enabling unprecedented connectivity and functionality. However, this expansion also increases vulnerabilities, exposing IoT networks to increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are crucial for mitigating these threats, and recent advancements in Machine Learning (ML) offer promising avenues for improvement. This research explores a hybrid approach, combining several standalone ML models such as Random Forest (RF), XGBoost, K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and AdaBoost, in a voting-based hybrid classifier for effective IoT intrusion detection. This ensemble method leverages the strengths of individual algorithms to enhance accuracy and address challenges related to data complexity and scalability. Using the widely-cited IoT-23 dataset, a prominent benchmark in IoT cybersecurity research, we evaluate our hybrid classifiers for both binary and multi-class intrusion detection problems, ensuring a fair comparison with existing literature. Results demonstrate that our proposed hybrid models, designed for robustness and scalability, outperform standalone approaches in IoT environments. This work contributes to the development of advanced, intelligent IDS frameworks capable of addressing evolving cyber threats.
Feature Selection for Network Intrusion Detection
Nov 18, 2024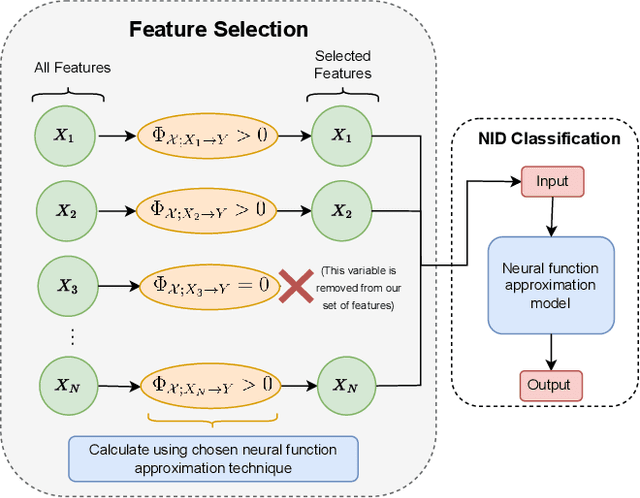
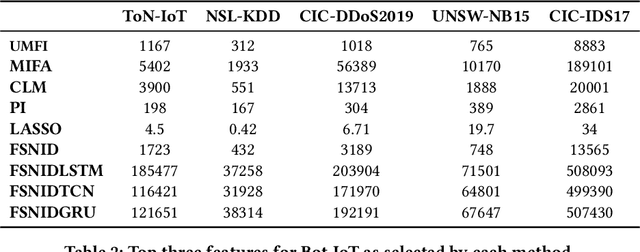
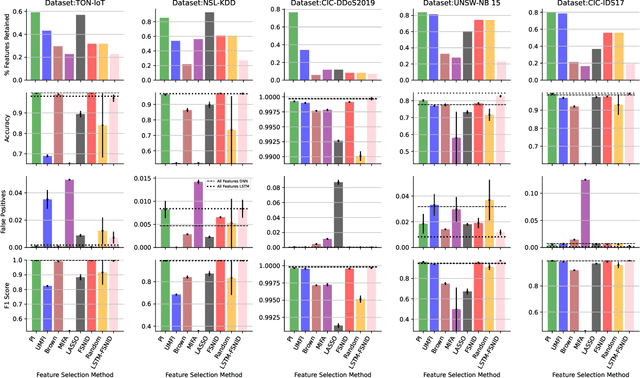
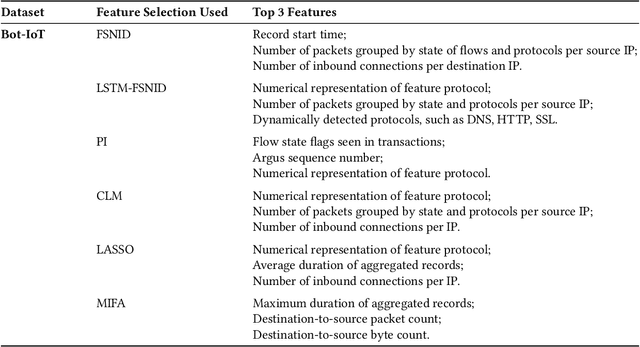
Network Intrusion Detection (NID) remains a key area of research within the information security community, while also being relevant to Machine Learning (ML) practitioners. The latter generally aim to detect attacks using network features, which have been extracted from raw network data typically using dimensionality reduction methods, such as principal component analysis (PCA). However, PCA is not able to assess the relevance of features for the task at hand. Consequently, the features available are of varying quality, with some being entirely non-informative. From this, two major drawbacks arise. Firstly, trained and deployed models have to process large amounts of unnecessary data, therefore draining potentially costly resources. Secondly, the noise caused by the presence of irrelevant features can, in some cases, impede a model's ability to detect an attack. In order to deal with these challenges, we present Feature Selection for Network Intrusion Detection (FSNID) a novel information-theoretic method that facilitates the exclusion of non-informative features when detecting network intrusions. The proposed method is based on function approximation using a neural network, which enables a version of our approach that incorporates a recurrent layer. Consequently, this version uniquely enables the integration of temporal dependencies. Through an extensive set of experiments, we demonstrate that the proposed method selects a significantly reduced feature set, while maintaining NID performance. Code will be made available upon publication.
A Comparative Analysis of DNN-based White-Box Explainable AI Methods in Network Security
Jan 14, 2025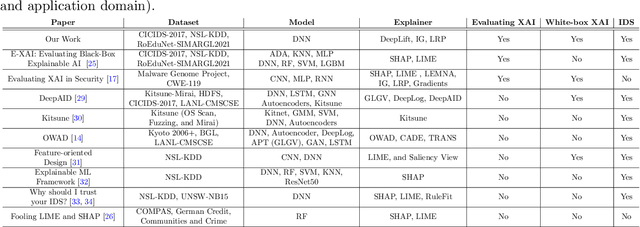
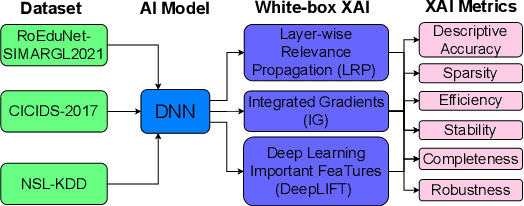
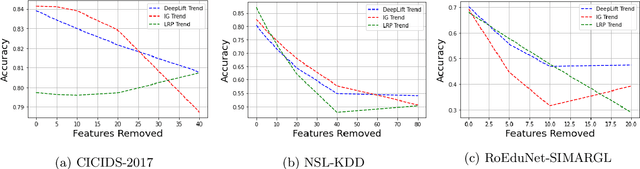
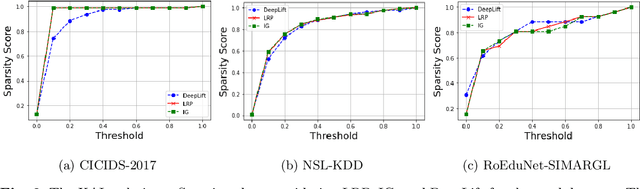
New research focuses on creating artificial intelligence (AI) solutions for network intrusion detection systems (NIDS), drawing its inspiration from the ever-growing number of intrusions on networked systems, increasing its complexity and intelligibility. Hence, the use of explainable AI (XAI) techniques in real-world intrusion detection systems comes from the requirement to comprehend and elucidate black-box AI models to security analysts. In an effort to meet such requirements, this paper focuses on applying and evaluating White-Box XAI techniques (particularly LRP, IG, and DeepLift) for NIDS via an end-to-end framework for neural network models, using three widely used network intrusion datasets (NSL-KDD, CICIDS-2017, and RoEduNet-SIMARGL2021), assessing its global and local scopes, and examining six distinct assessment measures (descriptive accuracy, sparsity, stability, robustness, efficiency, and completeness). We also compare the performance of white-box XAI methods with black-box XAI methods. The results show that using White-box XAI techniques scores high in robustness and completeness, which are crucial metrics for IDS. Moreover, the source codes for the programs developed for our XAI evaluation framework are available to be improved and used by the research community.
A Conditional Tabular GAN-Enhanced Intrusion Detection System for Rare Attacks in IoT Networks
Feb 09, 2025Internet of things (IoT) networks, boosted by 6G technology, are transforming various industries. However, their widespread adoption introduces significant security risks, particularly in detecting rare but potentially damaging cyber-attacks. This makes the development of robust IDS crucial for monitoring network traffic and ensuring their safety. Traditional IDS often struggle with detecting rare attacks due to severe class imbalances in IoT data. In this paper, we propose a novel two-stage system called conditional tabular generative synthetic minority data generation with deep neural network (CTGSM-DNN). In the first stage, a conditional tabular generative adversarial network (CTGAN) is employed to generate synthetic data for rare attack classes. In the second stage, the SMOTEENN method is applied to improve dataset quality. The full study was conducted using the CSE-CIC-IDS2018 dataset, and we assessed the performance of the proposed IDS using different evaluation metrics. The experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed multiclass classifier, achieving an overall accuracy of 99.90% and 80% accuracy in detecting rare attacks.
PolyLUT: Ultra-low Latency Polynomial Inference with Hardware-Aware Structured Pruning
Jan 14, 2025



Standard deep neural network inference involves the computation of interleaved linear maps and nonlinear activation functions. Prior work for ultra-low latency implementations has hardcoded these operations inside FPGA lookup tables (LUTs). However, FPGA LUTs can implement a much greater variety of functions. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to training DNNs for FPGA deployment using multivariate polynomials as the basic building block. Our method takes advantage of the flexibility offered by the soft logic, hiding the polynomial evaluation inside the LUTs with minimal overhead. By using polynomial building blocks, we achieve the same accuracy using considerably fewer layers of soft logic than by using linear functions, leading to significant latency and area improvements. LUT-based implementations also face a significant challenge: the LUT size grows exponentially with the number of inputs. Prior work relies on a priori fixed sparsity, with results heavily dependent on seed selection. To address this, we propose a structured pruning strategy using a bespoke hardware-aware group regularizer that encourages a particular sparsity pattern that leads to a small number of inputs per neuron. We demonstrate the effectiveness of PolyLUT on three tasks: network intrusion detection, jet identification at the CERN Large Hadron Collider, and MNIST.
CND-IDS: Continual Novelty Detection for Intrusion Detection Systems
Feb 19, 2025Intrusion detection systems (IDS) play a crucial role in IoT and network security by monitoring system data and alerting to suspicious activities. Machine learning (ML) has emerged as a promising solution for IDS, offering highly accurate intrusion detection. However, ML-IDS solutions often overlook two critical aspects needed to build reliable systems: continually changing data streams and a lack of attack labels. Streaming network traffic and associated cyber attacks are continually changing, which can degrade the performance of deployed ML models. Labeling attack data, such as zero-day attacks, in real-world intrusion scenarios may not be feasible, making the use of ML solutions that do not rely on attack labels necessary. To address both these challenges, we propose CND-IDS, a continual novelty detection IDS framework which consists of (i) a learning-based feature extractor that continuously updates new feature representations of the system data, and (ii) a novelty detector that identifies new cyber attacks by leveraging principal component analysis (PCA) reconstruction. Our results on realistic intrusion datasets show that CND-IDS achieves up to 6.1x F-score improvement, and up to 6.5x improved forward transfer over the SOTA unsupervised continual learning algorithm. Our code will be released upon acceptance.
An AutoML-based approach for Network Intrusion Detection
Nov 24, 2024
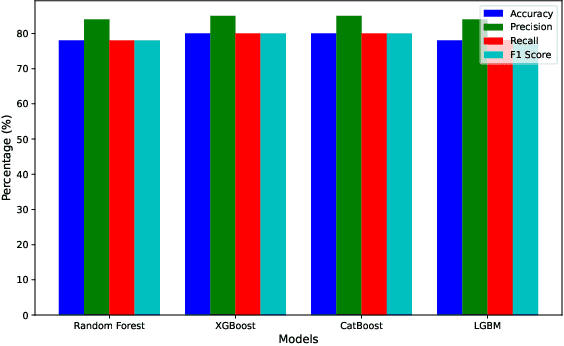
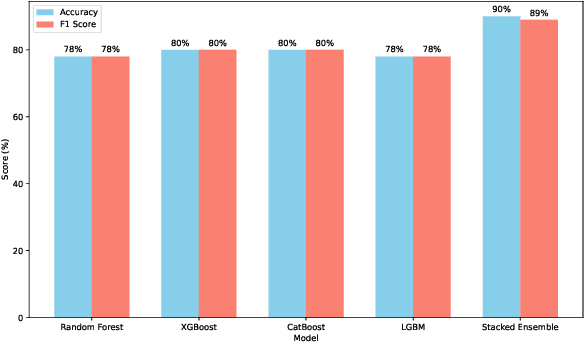

In this paper, we present an automated machine learning (AutoML) approach for network intrusion detection, leveraging a stacked ensemble model developed using the MLJAR AutoML framework. Our methodology combines multiple machine learning algorithms, including LightGBM, CatBoost, and XGBoost, to enhance detection accuracy and robustness. By automating model selection, feature engineering, and hyperparameter tuning, our approach reduces the manual overhead typically associated with traditional machine learning methods. Extensive experimentation on the NSL-KDD dataset demonstrates that the stacked ensemble model outperforms individual models, achieving high accuracy and minimizing false positives. Our findings underscore the benefits of using AutoML for network intrusion detection, as the AutoML-driven stacked ensemble achieved the highest performance with 90\% accuracy and an 89\% F1 score, outperforming individual models like Random Forest (78\% accuracy, 78\% F1 score), XGBoost and CatBoost (both 80\% accuracy, 80\% F1 score), and LightGBM (78\% accuracy, 78\% F1 score), providing a more adaptable and efficient solution for network security applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge