Zhengyang Yu
AutoRefiner: Improving Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models via Reflective Refinement Over the Stochastic Sampling Path
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive video diffusion models (AR-VDMs) show strong promise as scalable alternatives to bidirectional VDMs, enabling real-time and interactive applications. Yet there remains room for improvement in their sample fidelity. A promising solution is inference-time alignment, which optimizes the noise space to improve sample fidelity without updating model parameters. Yet, optimization- or search-based methods are computationally impractical for AR-VDMs. Recent text-to-image (T2I) works address this via feedforward noise refiners that modulate sampled noises in a single forward pass. Can such noise refiners be extended to AR-VDMs? We identify the failure of naively extending T2I noise refiners to AR-VDMs and propose AutoRefiner-a noise refiner tailored for AR-VDMs, with two key designs: pathwise noise refinement and a reflective KV-cache. Experiments demonstrate that AutoRefiner serves as an efficient plug-in for AR-VDMs, effectively enhancing sample fidelity by refining noise along stochastic denoising paths.
Simulated Cortical Magnification Supports Self-Supervised Object Learning
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Recent self-supervised learning models simulate the development of semantic object representations by training on visual experience similar to that of toddlers. However, these models ignore the foveated nature of human vision with high/low resolution in the center/periphery of the visual field. Here, we investigate the role of this varying resolution in the development of object representations. We leverage two datasets of egocentric videos that capture the visual experience of humans during interactions with objects. We apply models of human foveation and cortical magnification to modify these inputs, such that the visual content becomes less distinct towards the periphery. The resulting sequences are used to train two bio-inspired self-supervised learning models that implement a time-based learning objective. Our results show that modeling aspects of foveated vision improves the quality of the learned object representations in this setting. Our analysis suggests that this improvement comes from making objects appear bigger and inducing a better trade-off between central and peripheral visual information. Overall, this work takes a step towards making models of humans' learning of visual representations more realistic and performant.
Active Gaze Behavior Boosts Self-Supervised Object Learning
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Due to significant variations in the projection of the same object from different viewpoints, machine learning algorithms struggle to recognize the same object across various perspectives. In contrast, toddlers quickly learn to recognize objects from different viewpoints with almost no supervision. Recent works argue that toddlers develop this ability by mapping close-in-time visual inputs to similar representations while interacting with objects. High acuity vision is only available in the central visual field, which may explain why toddlers (much like adults) constantly move their gaze around during such interactions. It is unclear whether/how much toddlers curate their visual experience through these eye movements to support learning object representations. In this work, we explore whether a bio inspired visual learning model can harness toddlers' gaze behavior during a play session to develop view-invariant object recognition. Exploiting head-mounted eye tracking during dyadic play, we simulate toddlers' central visual field experience by cropping image regions centered on the gaze location. This visual stream feeds a time-based self-supervised learning algorithm. Our experiments demonstrate that toddlers' gaze strategy supports the learning of invariant object representations. Our analysis also reveals that the limited size of the central visual field where acuity is high is crucial for this. We further find that toddlers' visual experience elicits more robust representations compared to adults' mostly because toddlers look at objects they hold themselves for longer bouts. Overall, our work reveals how toddlers' gaze behavior supports self-supervised learning of view-invariant object recognition.
DreamSteerer: Enhancing Source Image Conditioned Editability using Personalized Diffusion Models
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Recent text-to-image personalization methods have shown great promise in teaching a diffusion model user-specified concepts given a few images for reusing the acquired concepts in a novel context. With massive efforts being dedicated to personalized generation, a promising extension is personalized editing, namely to edit an image using personalized concepts, which can provide a more precise guidance signal than traditional textual guidance. To address this, a straightforward solution is to incorporate a personalized diffusion model with a text-driven editing framework. However, such a solution often shows unsatisfactory editability on the source image. To address this, we propose DreamSteerer, a plug-in method for augmenting existing T2I personalization methods. Specifically, we enhance the source image conditioned editability of a personalized diffusion model via a novel Editability Driven Score Distillation (EDSD) objective. Moreover, we identify a mode trapping issue with EDSD, and propose a mode shifting regularization with spatial feature guided sampling to avoid such an issue. We further employ two key modifications to the Delta Denoising Score framework that enable high-fidelity local editing with personalized concepts. Extensive experiments validate that DreamSteerer can significantly improve the editability of several T2I personalization baselines while being computationally efficient.
Are Large Language Models Possible to Conduct Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:In contemporary society, the issue of psychological health has become increasingly prominent, characterized by the diversification, complexity, and universality of mental disorders. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), currently the most influential and clinically effective psychological treatment method with no side effects, has limited coverage and poor quality in most countries. In recent years, researches on the recognition and intervention of emotional disorders using large language models (LLMs) have been validated, providing new possibilities for psychological assistance therapy. However, are LLMs truly possible to conduct cognitive behavioral therapy? Many concerns have been raised by mental health experts regarding the use of LLMs for therapy. Seeking to answer this question, we collected real CBT corpus from online video websites, designed and conducted a targeted automatic evaluation framework involving the evaluation of emotion tendency of generated text, structured dialogue pattern and proactive inquiry ability. For emotion tendency, we calculate the emotion tendency score of the CBT dialogue text generated by each model. For structured dialogue pattern, we use a diverse range of automatic evaluation metrics to compare speaking style, the ability to maintain consistency of topic and the use of technology in CBT between different models . As for inquiring to guide the patient, we utilize PQA (Proactive Questioning Ability) metric. We also evaluated the CBT ability of the LLM after integrating a CBT knowledge base to explore the help of introducing additional knowledge to enhance the model's CBT counseling ability. Four LLM variants with excellent performance on natural language processing are evaluated, and the experimental result shows the great potential of LLMs in psychological counseling realm, especially after combining with other technological means.
IMPUS: Image Morphing with Perceptually-Uniform Sampling Using Diffusion Models
Nov 12, 2023
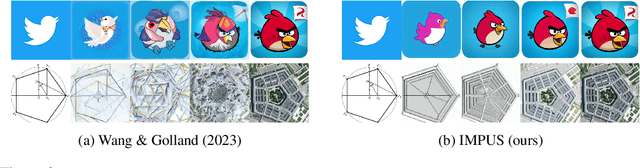
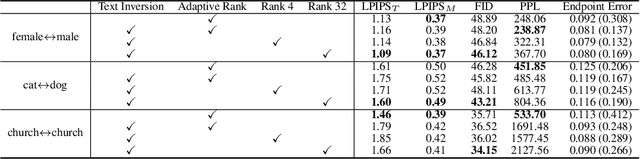
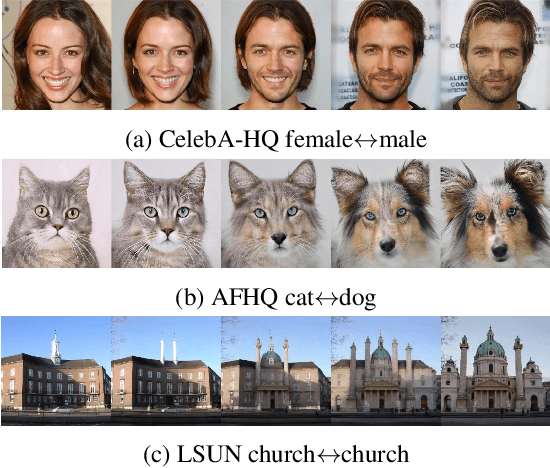
Abstract:We present a diffusion-based image morphing approach with perceptually-uniform sampling (IMPUS) that produces smooth, direct, and realistic interpolations given an image pair. A latent diffusion model has distinct conditional distributions and data embeddings for each of the two images, especially when they are from different classes. To bridge this gap, we interpolate in the locally linear and continuous text embedding space and Gaussian latent space. We first optimize the endpoint text embeddings and then map the images to the latent space using a probability flow ODE. Unlike existing work that takes an indirect morphing path, we show that the model adaptation yields a direct path and suppresses ghosting artifacts in the interpolated images. To achieve this, we propose an adaptive bottleneck constraint based on a novel relative perceptual path diversity score that automatically controls the bottleneck size and balances the diversity along the path with its directness. We also propose a perceptually-uniform sampling technique that enables visually smooth changes between the interpolated images. Extensive experiments validate that our IMPUS can achieve smooth, direct, and realistic image morphing and be applied to other image generation tasks.
Sequence and Circle: Exploring the Relationship Between Patches
Oct 19, 2022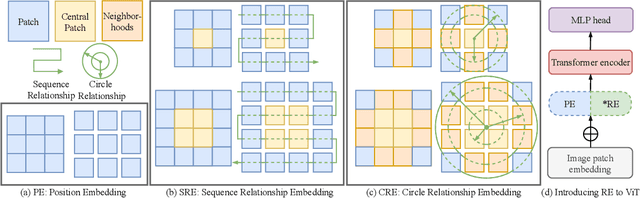
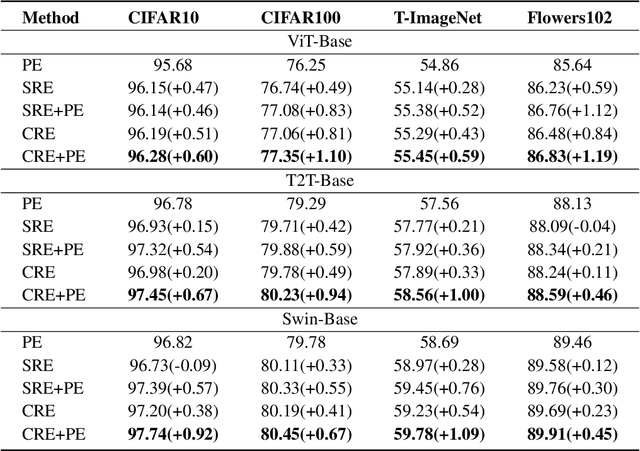
Abstract:The vision transformer (ViT) has achieved state-of-the-art results in various vision tasks. It utilizes a learnable position embedding (PE) mechanism to encode the location of each image patch. However, it is presently unclear if this learnable PE is really necessary and what its benefits are. This paper explores two alternative ways of encoding the location of individual patches that exploit prior knowledge about their spatial arrangement. One is called the sequence relationship embedding (SRE), and the other is called the circle relationship embedding (CRE). Among them, the SRE considers all patches to be in order, and adjacent patches have the same interval distance. The CRE considers the central patch as the center of the circle and measures the distance of the remaining patches from the center based on the four neighborhoods principle. Multiple concentric circles with different radii combine different patches. Finally, we implemented these two relations on three classic ViTs and tested them on four popular datasets. Experiments show that SRE and CRE can replace PE to reduce the random learnable parameters while achieving the same performance. Combining SRE or CRE with PE gets better performance than only using PE.
Self-supervised asymmetric deep hashing with margin-scalable constraint for image retrieval
Dec 07, 2020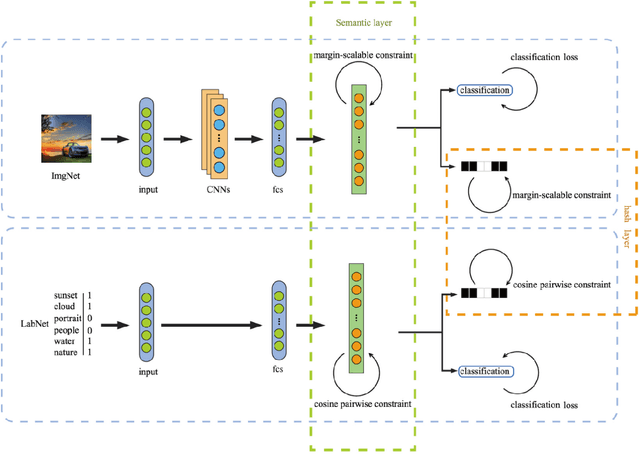
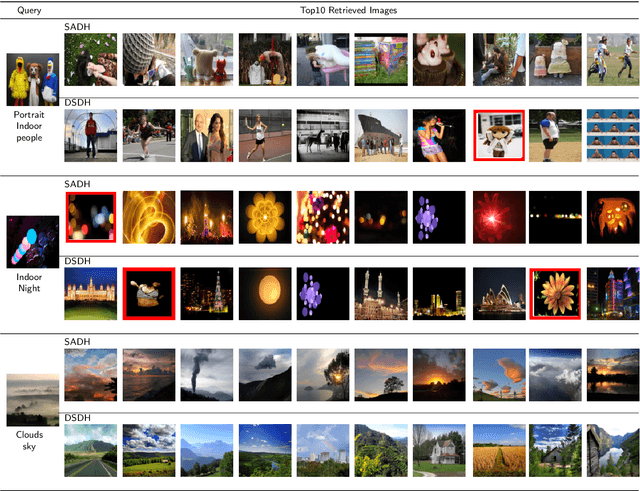
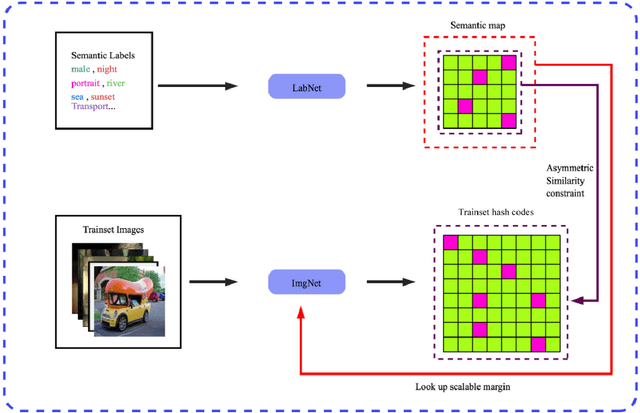
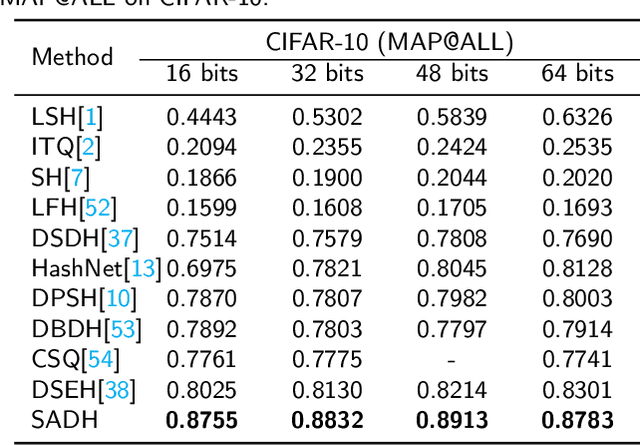
Abstract:Due to its validity and rapidity, image retrieval based on deep hashing approaches is widely concerned especially in large-scale visual search. However, many existing deep hashing methods inadequately utilize label information as guidance of feature learning network without more advanced exploration in semantic space, besides the similarity correlations in hamming space are not fully discovered and embedded into hash codes, by which the retrieval quality is diminished with inefficient preservation of pairwise correlations and multi-label semantics. To cope with these problems, we propose a novel self-supervised asymmetric deep hashing with margin-scalable constraint(SADH) approach for image retrieval. SADH implements a self-supervised network to preserve supreme semantic information in a semantic feature map and a semantic code map for each semantics of the given dataset, which efficiently-and-precisely guides a feature learning network to preserve multi-label semantic information with asymmetric learning strategy. Moreover, for the feature learning part, by further exploiting semantic maps, a new margin-scalable constraint is employed for both highly-accurate construction of pairwise correlation in the hamming space and more discriminative hash code representation. Extensive empirical research on three benchmark datasets validate that the proposed method outperforms several state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge