Zeliang Ma
The RoboDrive Challenge: Drive Anytime Anywhere in Any Condition
May 14, 2024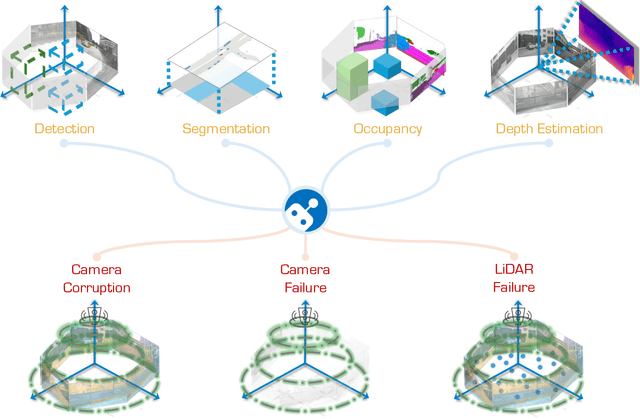


Abstract:In the realm of autonomous driving, robust perception under out-of-distribution conditions is paramount for the safe deployment of vehicles. Challenges such as adverse weather, sensor malfunctions, and environmental unpredictability can severely impact the performance of autonomous systems. The 2024 RoboDrive Challenge was crafted to propel the development of driving perception technologies that can withstand and adapt to these real-world variabilities. Focusing on four pivotal tasks -- BEV detection, map segmentation, semantic occupancy prediction, and multi-view depth estimation -- the competition laid down a gauntlet to innovate and enhance system resilience against typical and atypical disturbances. This year's challenge consisted of five distinct tracks and attracted 140 registered teams from 93 institutes across 11 countries, resulting in nearly one thousand submissions evaluated through our servers. The competition culminated in 15 top-performing solutions, which introduced a range of innovative approaches including advanced data augmentation, multi-sensor fusion, self-supervised learning for error correction, and new algorithmic strategies to enhance sensor robustness. These contributions significantly advanced the state of the art, particularly in handling sensor inconsistencies and environmental variability. Participants, through collaborative efforts, pushed the boundaries of current technologies, showcasing their potential in real-world scenarios. Extensive evaluations and analyses provided insights into the effectiveness of these solutions, highlighting key trends and successful strategies for improving the resilience of driving perception systems. This challenge has set a new benchmark in the field, providing a rich repository of techniques expected to guide future research in this field.
MLS-Track: Multilevel Semantic Interaction in RMOT
Apr 18, 2024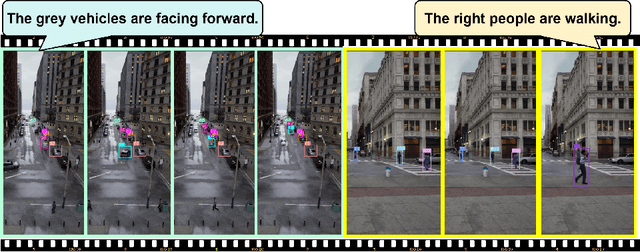
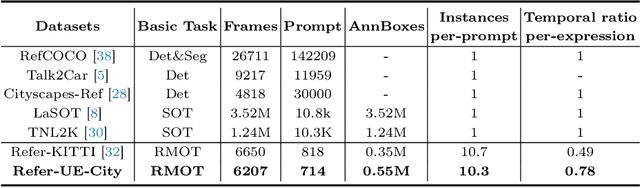
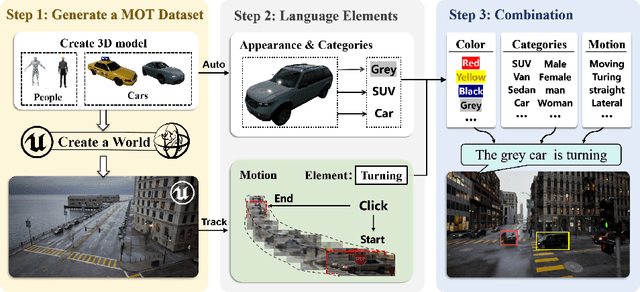
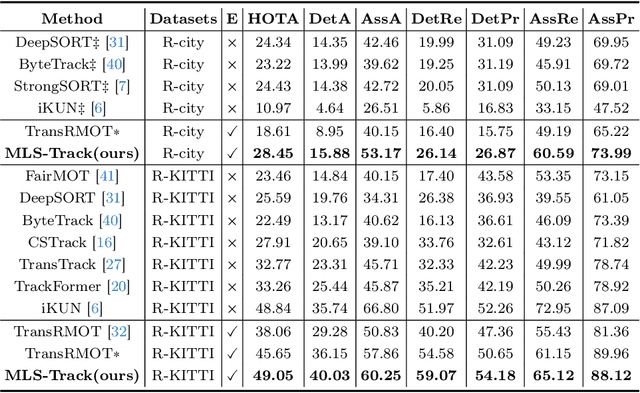
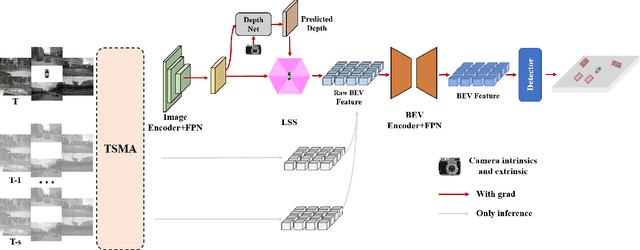
Abstract:The new trend in multi-object tracking task is to track objects of interest using natural language. However, the scarcity of paired prompt-instance data hinders its progress. To address this challenge, we propose a high-quality yet low-cost data generation method base on Unreal Engine 5 and construct a brand-new benchmark dataset, named Refer-UE-City, which primarily includes scenes from intersection surveillance videos, detailing the appearance and actions of people and vehicles. Specifically, it provides 14 videos with a total of 714 expressions, and is comparable in scale to the Refer-KITTI dataset. Additionally, we propose a multi-level semantic-guided multi-object framework called MLS-Track, where the interaction between the model and text is enhanced layer by layer through the introduction of Semantic Guidance Module (SGM) and Semantic Correlation Branch (SCB). Extensive experiments on Refer-UE-City and Refer-KITTI datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework and it achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code and datatsets will be available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge