Yusheng Dai
Omni2Sound: Towards Unified Video-Text-to-Audio Generation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Training a unified model integrating video-to-audio (V2A), text-to-audio (T2A), and joint video-text-to-audio (VT2A) generation offers significant application flexibility, yet faces two unexplored foundational challenges: (1) the scarcity of high-quality audio captions with tight A-V-T alignment, leading to severe semantic conflict between multimodal conditions, and (2) cross-task and intra-task competition, manifesting as an adverse V2A-T2A performance trade-off and modality bias in the VT2A task. First, to address data scarcity, we introduce SoundAtlas, a large-scale dataset (470k pairs) that significantly outperforms existing benchmarks and even human experts in quality. Powered by a novel agentic pipeline, it integrates Vision-to-Language Compression to mitigate visual bias of MLLMs, a Junior-Senior Agent Handoff for a 5 times cost reduction, and rigorous Post-hoc Filtering to ensure fidelity. Consequently, SoundAtlas delivers semantically rich and temporally detailed captions with tight V-A-T alignment. Second, we propose Omni2Sound, a unified VT2A diffusion model supporting flexible input modalities. To resolve the inherent cross-task and intra-task competition, we design a three-stage multi-task progressive training schedule that converts cross-task competition into joint optimization and mitigates modality bias in the VT2A task, maintaining both audio-visual alignment and off-screen audio generation faithfulness. Finally, we construct VGGSound-Omni, a comprehensive benchmark for unified evaluation, including challenging off-screen tracks. With a standard DiT backbone, Omni2Sound achieves unified SOTA performance across all three tasks within a single model, demonstrating strong generalization across benchmarks with heterogeneous input conditions. The project page is at https://swapforward.github.io/Omni2Sound.
Latent Swap Joint Diffusion for Long-Form Audio Generation
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Previous work on long-form audio generation using global-view diffusion or iterative generation demands significant training or inference costs. While recent advancements in multi-view joint diffusion for panoramic generation provide an efficient option, they struggle with spectrum generation with severe overlap distortions and high cross-view consistency costs. We initially explore this phenomenon through the connectivity inheritance of latent maps and uncover that averaging operations excessively smooth the high-frequency components of the latent map. To address these issues, we propose Swap Forward (SaFa), a frame-level latent swap framework that synchronizes multiple diffusions to produce a globally coherent long audio with more spectrum details in a forward-only manner. At its core, the bidirectional Self-Loop Latent Swap is applied between adjacent views, leveraging stepwise diffusion trajectory to adaptively enhance high-frequency components without disrupting low-frequency components. Furthermore, to ensure cross-view consistency, the unidirectional Reference-Guided Latent Swap is applied between the reference and the non-overlap regions of each subview during the early stages, providing centralized trajectory guidance. Quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that SaFa significantly outperforms existing joint diffusion methods and even training-based long audio generation models. Moreover, we find that it also adapts well to panoramic generation, achieving comparable state-of-the-art performance with greater efficiency and model generalizability. Project page is available at https://swapforward.github.io/.
A Study of Dropout-Induced Modality Bias on Robustness to Missing Video Frames for Audio-Visual Speech Recognition
Mar 07, 2024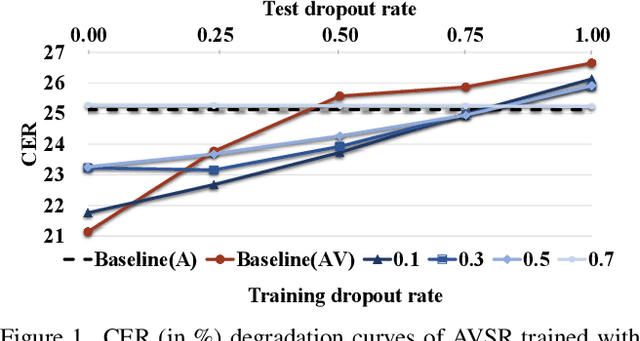
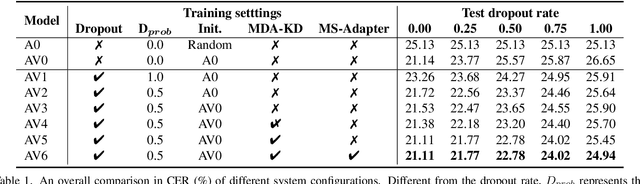
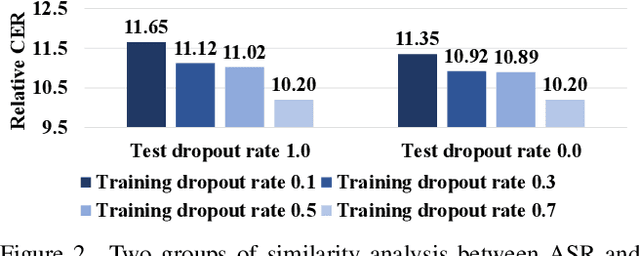
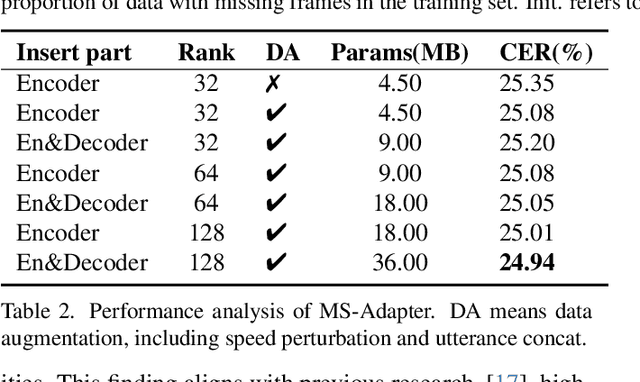
Abstract:Advanced Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) systems have been observed to be sensitive to missing video frames, performing even worse than single-modality models. While applying the dropout technique to the video modality enhances robustness to missing frames, it simultaneously results in a performance loss when dealing with complete data input. In this paper, we investigate this contrasting phenomenon from the perspective of modality bias and reveal that an excessive modality bias on the audio caused by dropout is the underlying reason. Moreover, we present the Modality Bias Hypothesis (MBH) to systematically describe the relationship between modality bias and robustness against missing modality in multimodal systems. Building on these findings, we propose a novel Multimodal Distribution Approximation with Knowledge Distillation (MDA-KD) framework to reduce over-reliance on the audio modality and to maintain performance and robustness simultaneously. Finally, to address an entirely missing modality, we adopt adapters to dynamically switch decision strategies. The effectiveness of our proposed approach is evaluated and validated through a series of comprehensive experiments using the MISP2021 and MISP2022 datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/dalision/ModalBiasAVSR
The Multimodal Information Based Speech Processing (MISP) 2023 Challenge: Audio-Visual Target Speaker Extraction
Sep 15, 2023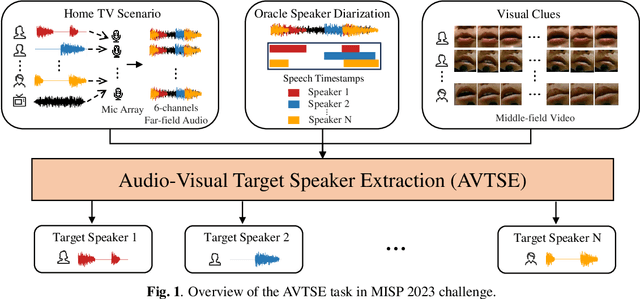
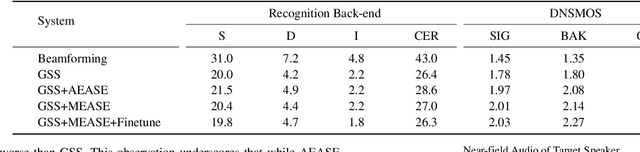
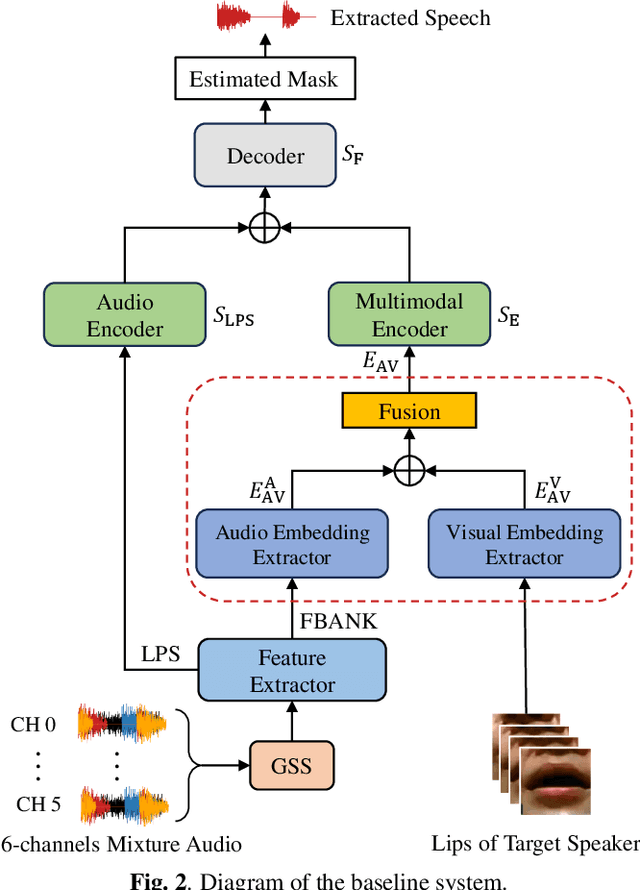

Abstract:Previous Multimodal Information based Speech Processing (MISP) challenges mainly focused on audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR) with commendable success. However, the most advanced back-end recognition systems often hit performance limits due to the complex acoustic environments. This has prompted a shift in focus towards the Audio-Visual Target Speaker Extraction (AVTSE) task for the MISP 2023 challenge in ICASSP 2024 Signal Processing Grand Challenges. Unlike existing audio-visual speech enhance-ment challenges primarily focused on simulation data, the MISP 2023 challenge uniquely explores how front-end speech processing, combined with visual clues, impacts back-end tasks in real-world scenarios. This pioneering effort aims to set the first benchmark for the AVTSE task, offering fresh insights into enhancing the ac-curacy of back-end speech recognition systems through AVTSE in challenging and real acoustic environments. This paper delivers a thorough overview of the task setting, dataset, and baseline system of the MISP 2023 challenge. It also includes an in-depth analysis of the challenges participants may encounter. The experimental results highlight the demanding nature of this task, and we look forward to the innovative solutions participants will bring forward.
Improving Audio-Visual Speech Recognition by Lip-Subword Correlation Based Visual Pre-training and Cross-Modal Fusion Encoder
Aug 14, 2023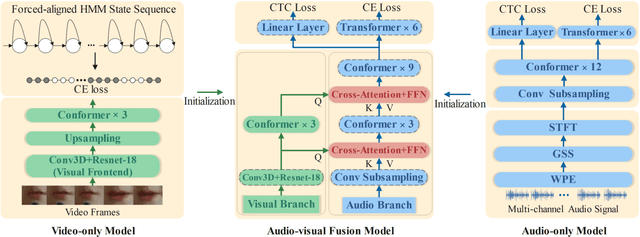
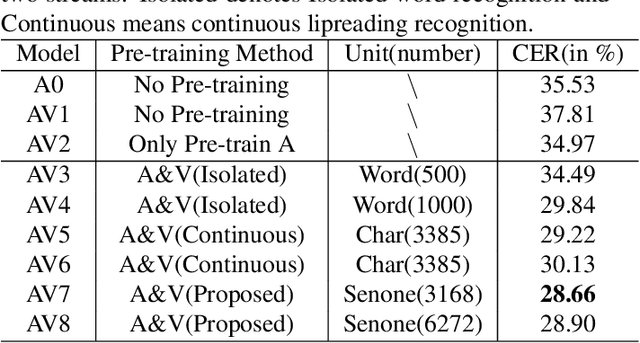
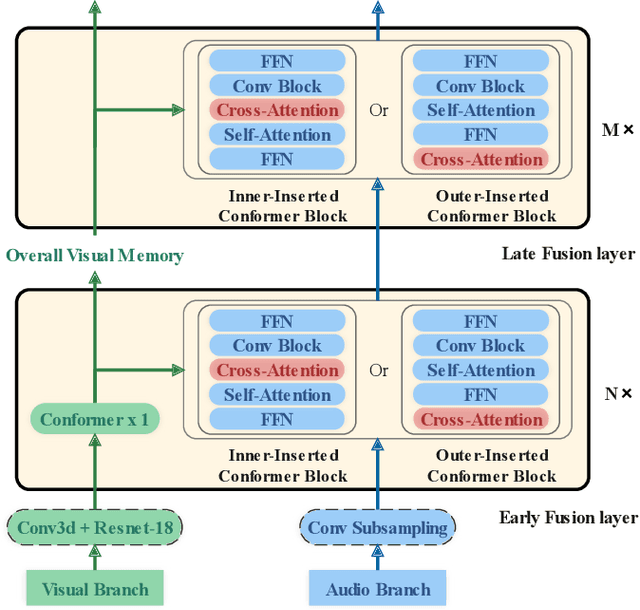
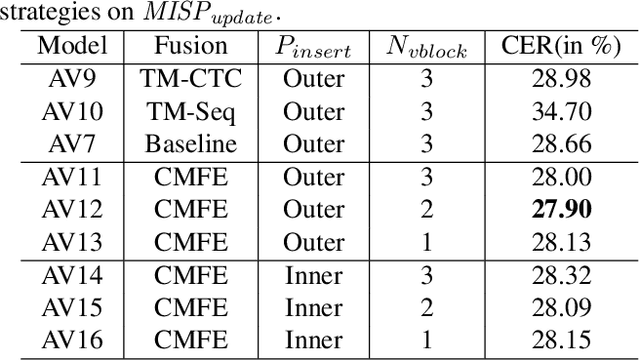
Abstract:In recent research, slight performance improvement is observed from automatic speech recognition systems to audio-visual speech recognition systems in the end-to-end framework with low-quality videos. Unmatching convergence rates and specialized input representations between audio and visual modalities are considered to cause the problem. In this paper, we propose two novel techniques to improve audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR) under a pre-training and fine-tuning training framework. First, we explore the correlation between lip shapes and syllable-level subword units in Mandarin to establish good frame-level syllable boundaries from lip shapes. This enables accurate alignment of video and audio streams during visual model pre-training and cross-modal fusion. Next, we propose an audio-guided cross-modal fusion encoder (CMFE) neural network to utilize main training parameters for multiple cross-modal attention layers to make full use of modality complementarity. Experiments on the MISP2021-AVSR data set show the effectiveness of the two proposed techniques. Together, using only a relatively small amount of training data, the final system achieves better performances than state-of-the-art systems with more complex front-ends and back-ends.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge