Yury Polyanskiy
Price of universality in vector quantization is at most 0.11 bit
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Fast computation of a matrix product $W^\top X$ is a workhorse of modern LLMs. To make their deployment more efficient, a popular approach is that of using a low-precision approximation $\widehat W$ in place of true $W$ ("weight-only quantization''). Information theory demonstrates that an optimal algorithm for reducing precision of $W$ depends on the (second order) statistics of $X$ and requires a careful alignment of vector quantization codebook with PCA directions of $X$ (a process known as "waterfilling allocation''). Dependence of the codebook on statistics of $X$, however, is highly impractical. This paper proves that there exist a universal codebook that is simultaneously near-optimal for all possible statistics of $X$, in the sense of being at least as good as an $X$-adapted waterfilling codebook with rate reduced by 0.11 bit per dimension. Such universal codebook would be an ideal candidate for the low-precision storage format, a topic of active modern research, but alas the existence proof is non-constructive. Equivalently, our result shows existence of a net in $\mathbb{R}^n$ that is a nearly-optimal covering of a sphere simultaneously with respect to all Hilbert norms.
YuriiFormer: A Suite of Nesterov-Accelerated Transformers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We propose a variational framework that interprets transformer layers as iterations of an optimization algorithm acting on token embeddings. In this view, self-attention implements a gradient step of an interaction energy, while MLP layers correspond to gradient updates of a potential energy. Standard GPT-style transformers emerge as vanilla gradient descent on the resulting composite objective, implemented via Lie--Trotter splitting between these two energy functionals. This perspective enables principled architectural design using classical optimization ideas. As a proof of concept, we introduce a Nesterov-style accelerated transformer that preserves the same attention and MLP oracles. The resulting architecture consistently outperforms a nanoGPT baseline on TinyStories and OpenWebText, demonstrating that optimization-theoretic insights can translate into practical gains.
High-Rate Quantized Matrix Multiplication: Theory and Practice
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:This work investigates the problem of quantized matrix multiplication (MatMul), which has become crucial for the efficient deployment of large language models (LLMs). We consider two settings: 1) Generic MatMul, where both matrices must be quantized (weight+activation quantization); and 2) weight-only quantization, where the second matrix is only known through covariance matrix $Σ_X$ of its columns. For each setting, we first review the fundamental information-theoretic tradeoff between quantization rate and distortion (high-rate theory), and then analyze the performance of several popular quantization schemes, comparing them to these fundamental limits. Specifically, we discuss rate loss (compared to information theoretic optima) of absmax INT and floating-point (FP) quantization, for which we also derive remarkably accurate heuristic approximations. Weight-only quantization is related to the problem of weighted mean squared error (WMSE) source coding, whose classical (reverse) waterfilling solution dictates how one should distribute rate between coordinates of the vector. We show how waterfilling can be used to improve practical LLM quantization algorithms (GPTQ), which at present allocate rate equally. This new scheme (termed ``WaterSIC'') only uses scalar INT quantizers, but its high-rate performance is basis free (it depends only on the determinant of $Σ_X$ and, thus, unlike existing schemes, is immune to applying random rotations) and is within a multiplicative factor of $\frac{2πe}{12}$ (or 0.25 bit/entry) of the information-theoretic distortion limit (!). GPTQ's performance is affected by the choice of basis, but for a random rotation and actual $Σ_X$ from Llama-3-8B we find GPTQ to be within 0.1 bit (depending on the layer type) of WaterSIC, suggesting that GPTQ with random rotation is also near optimal (for high-rate quantization).
Synchronization of mean-field models on the circle
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:This paper considers a mean-field model of $n$ interacting particles whose state space is the unit circle, a generalization of the classical Kuramoto model. Global synchronization is said to occur if after starting from almost any initial state, all particles coalesce to a common point on the circle. We propose a general synchronization criterion in terms of $L_1$-norm of the third derivative of the particle interaction function. As an application we resolve a conjecture for the so-called self-attention dynamics (stylized model of transformers), by showing synchronization for all $\beta \ge -0.16$, which significantly extends the previous bound of $0\le \beta \le 1$ from Criscitiello, Rebjock, McRae, and Boumal (2024). We also show that global synchronization does not occur when $\beta < -2/3$.
Quantitative Clustering in Mean-Field Transformer Models
Apr 20, 2025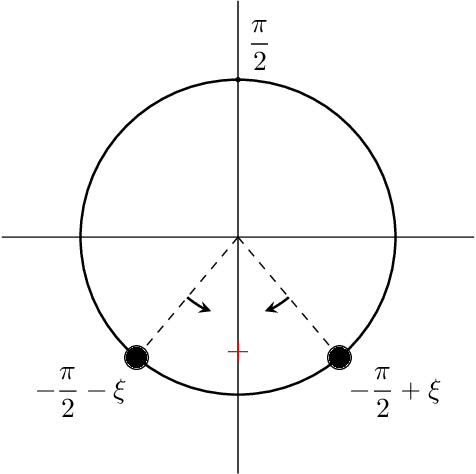
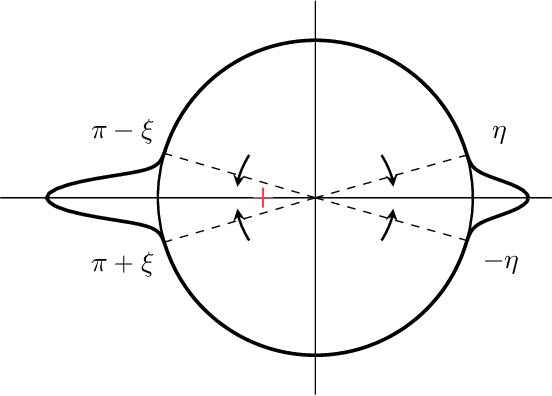
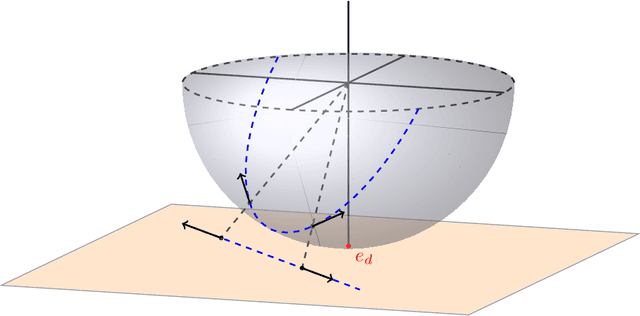
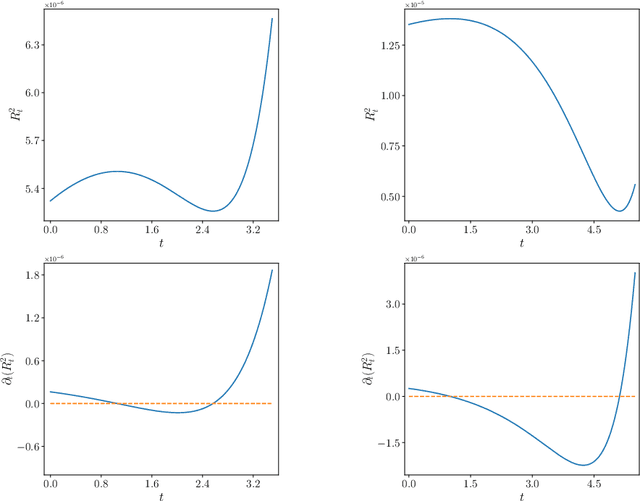
Abstract:The evolution of tokens through a deep transformer models can be modeled as an interacting particle system that has been shown to exhibit an asymptotic clustering behavior akin to the synchronization phenomenon in Kuramoto models. In this work, we investigate the long-time clustering of mean-field transformer models. More precisely, we establish exponential rates of contraction to a Dirac point mass for any suitably regular initialization under some assumptions on the parameters of transformer models, any suitably regular mean-field initialization synchronizes exponentially fast with some quantitative rates.
Nonparametric MLE for Gaussian Location Mixtures: Certified Computation and Generic Behavior
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:We study the nonparametric maximum likelihood estimator $\widehat{\pi}$ for Gaussian location mixtures in one dimension. It has been known since (Lindsay, 1983) that given an $n$-point dataset, this estimator always returns a mixture with at most $n$ components, and more recently (Wu-Polyanskiy, 2020) gave a sharp $O(\log n)$ bound for subgaussian data. In this work we study computational aspects of $\widehat{\pi}$. We provide an algorithm which for small enough $\varepsilon>0$ computes an $\varepsilon$-approximation of $\widehat\pi$ in Wasserstein distance in time $K+Cnk^2\log\log(1/\varepsilon)$. Here $K$ is data-dependent but independent of $\varepsilon$, while $C$ is an absolute constant and $k=|supp(\widehat{\pi})|\leq n$ is the number of atoms in $\widehat\pi$. We also certifiably compute the exact value of $|supp(\widehat\pi)|$ in finite time. These guarantees hold almost surely whenever the dataset $(x_1,\dots,x_n)\in [-cn^{1/4},cn^{1/4}]$ consists of independent points from a probability distribution with a density (relative to Lebesgue measure). We also show the distribution of $\widehat\pi$ conditioned to be $k$-atomic admits a density on the associated $2k-1$ dimensional parameter space for all $k\leq \sqrt{n}/3$, and almost sure locally linear convergence of the EM algorithm. One key tool is a classical Fourier analytic estimate for non-degenerate curves.
Residual connections provably mitigate oversmoothing in graph neural networks
Jan 04, 2025



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have achieved remarkable empirical success in processing and representing graph-structured data across various domains. However, a significant challenge known as "oversmoothing" persists, where vertex features become nearly indistinguishable in deep GNNs, severely restricting their expressive power and practical utility. In this work, we analyze the asymptotic oversmoothing rates of deep GNNs with and without residual connections by deriving explicit convergence rates for a normalized vertex similarity measure. Our analytical framework is grounded in the multiplicative ergodic theorem. Furthermore, we demonstrate that adding residual connections effectively mitigates or prevents oversmoothing across several broad families of parameter distributions. The theoretical findings are strongly supported by numerical experiments.
Clustering in Causal Attention Masking
Nov 07, 2024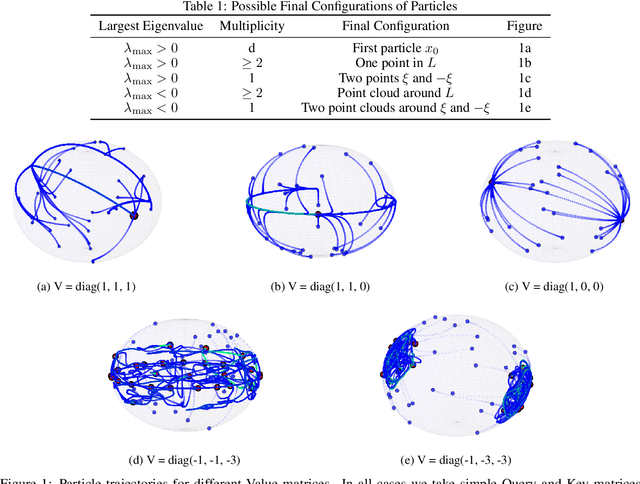
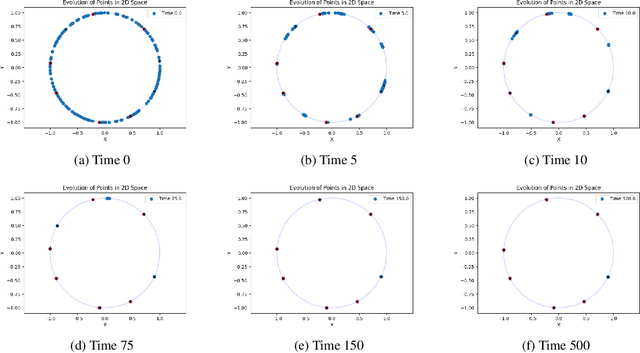
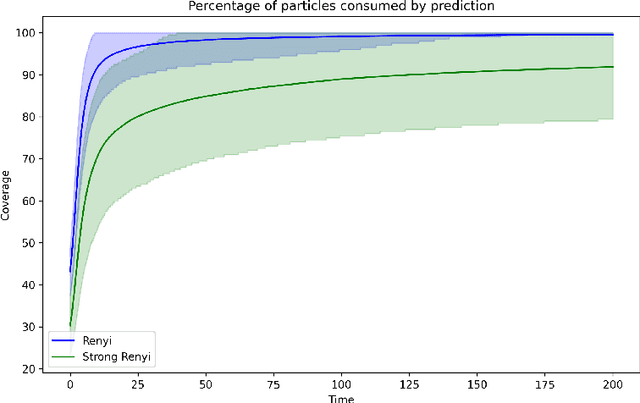
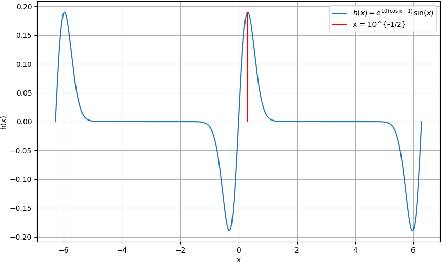
Abstract:This work presents a modification of the self-attention dynamics proposed by Geshkovski et al. (arXiv:2312.10794) to better reflect the practically relevant, causally masked attention used in transformer architectures for generative AI. This modification translates into an interacting particle system that cannot be interpreted as a mean-field gradient flow. Despite this loss of structure, we significantly strengthen the results of Geshkovski et al. (arXiv:2312.10794) in this context: While previous rigorous results focused on cases where all three matrices (Key, Query, and Value) were scaled identities, we prove asymptotic convergence to a single cluster for arbitrary key-query matrices and a value matrix equal to the identity. Additionally, we establish a connection to the classical R\'enyi parking problem from combinatorial geometry to make initial theoretical steps towards demonstrating the existence of meta-stable states.
Optimal Quantization for Matrix Multiplication
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:Recent work in machine learning community proposed multiple methods for performing lossy compression (quantization) of large matrices. This quantization is important for accelerating matrix multiplication (main component of large language models), which is often bottlenecked by the speed of loading these matrices from memory. Unlike classical vector quantization and rate-distortion theory, the goal of these new compression algorithms is to be able to approximate not the matrices themselves, but their matrix product. Specifically, given a pair of real matrices $A,B$ an encoder (compressor) is applied to each of them independently producing descriptions with $R$ bits per entry. These representations subsequently are used by the decoder to estimate matrix product $A^\top B$. In this work, we provide a non-asymptotic lower bound on the mean squared error of this approximation (as a function of rate $R$) for the case of matrices $A,B$ with iid Gaussian entries. Algorithmically, we construct a universal quantizer based on nested lattices with an explicit guarantee of approximation error for any (non-random) pair of matrices $A$, $B$ in terms of only Frobenius norms $\|A\|_F, \|B\|_F$ and $\|A^\top B\|_F$. For iid Gaussian matrices our quantizer achieves the lower bound and is, thus, asymptotically optimal. A practical low-complexity version of our quantizer achieves performance quite close to optimal. In information-theoretic terms we derive rate-distortion function for matrix multiplication of iid Gaussian matrices.
Dynamic metastability in the self-attention model
Oct 09, 2024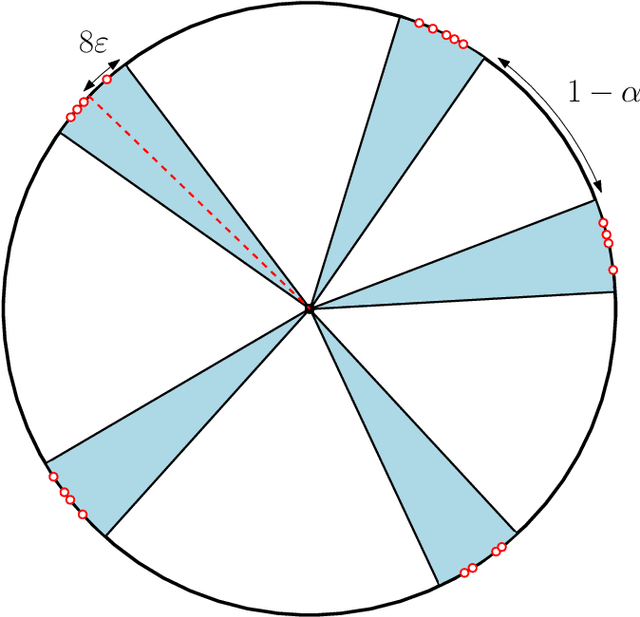

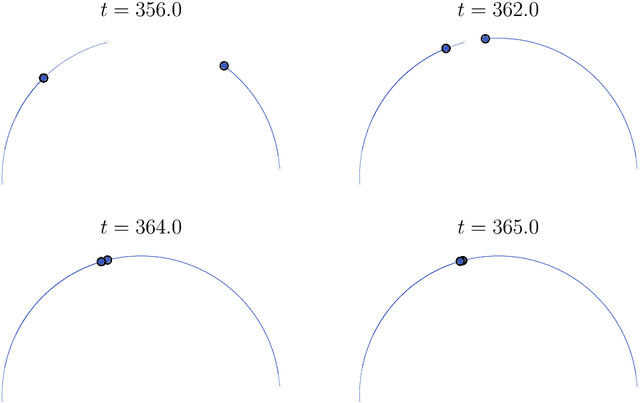

Abstract:We consider the self-attention model - an interacting particle system on the unit sphere, which serves as a toy model for Transformers, the deep neural network architecture behind the recent successes of large language models. We prove the appearance of dynamic metastability conjectured in [GLPR23] - although particles collapse to a single cluster in infinite time, they remain trapped near a configuration of several clusters for an exponentially long period of time. By leveraging a gradient flow interpretation of the system, we also connect our result to an overarching framework of slow motion of gradient flows proposed by Otto and Reznikoff [OR07] in the context of coarsening and the Allen-Cahn equation. We finally probe the dynamics beyond the exponentially long period of metastability, and illustrate that, under an appropriate time-rescaling, the energy reaches its global maximum in finite time and has a staircase profile, with trajectories manifesting saddle-to-saddle-like behavior, reminiscent of recent works in the analysis of training dynamics via gradient descent for two-layer neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge