Yuling Sun
LLaVA-RadZ: Can Multimodal Large Language Models Effectively Tackle Zero-shot Radiology Recognition?
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Recently, multimodal large models (MLLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in visual understanding and reasoning across various vision-language tasks. However, MLLMs usually perform poorly in zero-shot medical disease recognition, as they do not fully exploit the captured features and available medical knowledge. To address this challenge, we propose LLaVA-RadZ, a simple yet effective framework for zero-shot medical disease recognition. Specifically, we design an end-to-end training strategy, termed Decoding-Side Feature Alignment Training (DFAT) to take advantage of the characteristics of the MLLM decoder architecture and incorporate modality-specific tokens tailored for different modalities, which effectively utilizes image and text representations and facilitates robust cross-modal alignment. Additionally, we introduce a Domain Knowledge Anchoring Module (DKAM) to exploit the intrinsic medical knowledge of large models, which mitigates the category semantic gap in image-text alignment. DKAM improves category-level alignment, allowing for accurate disease recognition. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our LLaVA-RadZ significantly outperforms traditional MLLMs in zero-shot disease recognition and exhibits the state-of-the-art performance compared to the well-established and highly-optimized CLIP-based approaches.
"It Felt Like I Was Left in the Dark": Exploring Information Needs and Design Opportunities for Family Caregivers of Older Adult Patients in Critical Care Settings
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Older adult patients constitute a rapidly growing subgroup of Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients. In these situations, their family caregivers are expected to represent the unconscious patients to access and interpret patients' medical information. However, caregivers currently have to rely on overloaded clinicians for information updates and typically lack the health literacy to understand complex medical information. Our project aims to explore the information needs of caregivers of ICU older adult patients, from which we can propose design opportunities to guide future AI systems. The project begins with formative interviews with 11 caregivers to identify their challenges in accessing and interpreting medical information; From these findings, we then synthesize design requirements and propose an AI system prototype to cope with caregivers' challenges. The system prototype has two key features: a timeline visualization to show the AI extracted and summarized older adult patients' key medical events; and an LLM-based chatbot to provide context-aware informational support. We conclude our paper by reporting on the follow-up user evaluation of the system and discussing future AI-based systems for ICU caregivers of older adults.
FairytaleCQA: Integrating a Commonsense Knowledge Graph into Children's Storybook Narratives
Nov 16, 2023
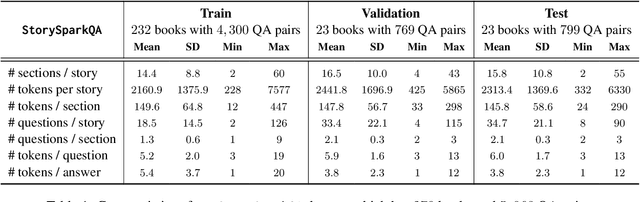
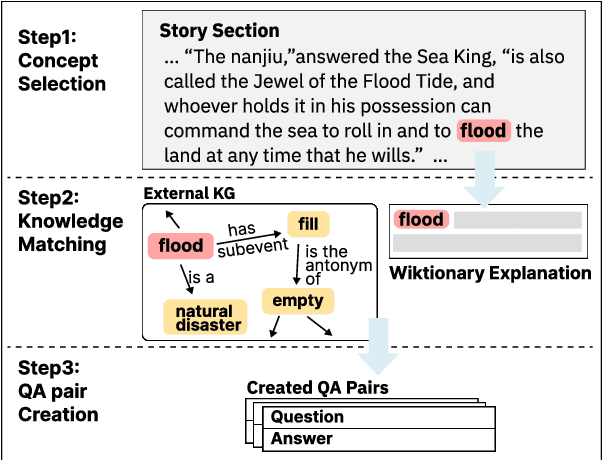
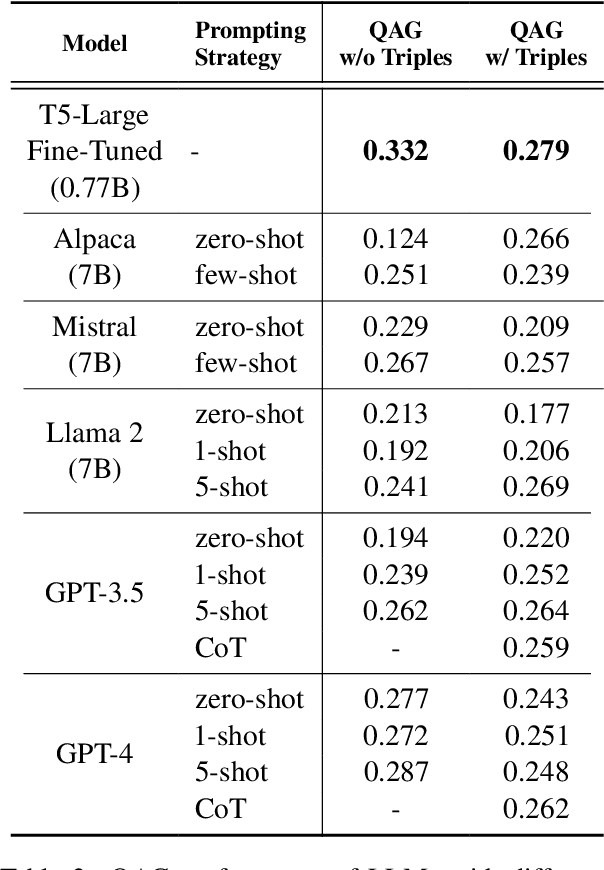
Abstract:AI models (including LLM) often rely on narrative question-answering (QA) datasets to provide customized QA functionalities to support downstream children education applications; however, existing datasets only include QA pairs that are grounded within the given storybook content, but children can learn more when teachers refer the storybook content to real-world knowledge (e.g., commonsense knowledge). We introduce the FairytaleCQA dataset, which is annotated by children education experts, to supplement 278 storybook narratives with educationally appropriate commonsense knowledge. The dataset has 5,868 QA pairs that not only originate from the storybook narrative but also contain the commonsense knowledge grounded by an external knowledge graph (i.e., ConceptNet). A follow-up experiment shows that a smaller model (T5-large) fine-tuned with FairytaleCQA reliably outperforms much larger prompt-engineered LLM (e.g., GPT-4) in this new QA-pair generation task (QAG). This result suggests that: 1) our dataset brings novel challenges to existing LLMs, and 2) human experts' data annotation are still critical as they have much nuanced knowledge that LLMs do not know in the children educational domain.
An Information Minimization Based Contrastive Learning Model for Unsupervised Sentence Embeddings Learning
Sep 22, 2022



Abstract:Unsupervised sentence embeddings learning has been recently dominated by contrastive learning methods (e.g., SimCSE), which keep positive pairs similar and push negative pairs apart. The contrast operation aims to keep as much information as possible by maximizing the mutual information between positive instances, which leads to redundant information in sentence embedding. To address this problem, we present an information minimization based contrastive learning (InforMin-CL) model to retain the useful information and discard the redundant information by maximizing the mutual information and minimizing the information entropy between positive instances meanwhile for unsupervised sentence representation learning. Specifically, we find that information minimization can be achieved by simple contrast and reconstruction objectives. The reconstruction operation reconstitutes the positive instance via the other positive instance to minimize the information entropy between positive instances. We evaluate our model on fourteen downstream tasks, including both supervised and unsupervised (semantic textual similarity) tasks. Extensive experimental results show that our InforMin-CL obtains a state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge