Yuliang Wu
Event-Based Eye Tracking. 2025 Event-based Vision Workshop
Apr 25, 2025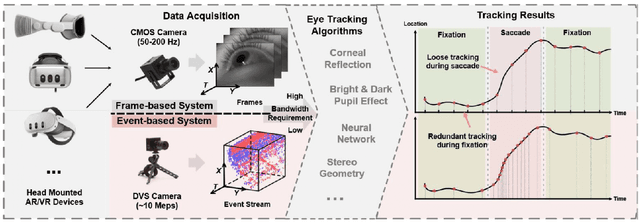
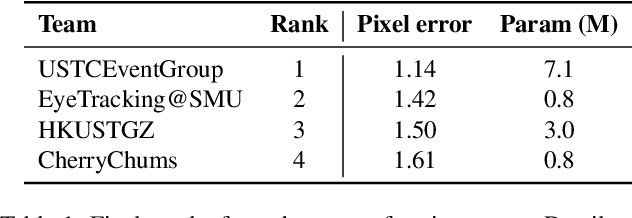
Abstract:This survey serves as a review for the 2025 Event-Based Eye Tracking Challenge organized as part of the 2025 CVPR event-based vision workshop. This challenge focuses on the task of predicting the pupil center by processing event camera recorded eye movement. We review and summarize the innovative methods from teams rank the top in the challenge to advance future event-based eye tracking research. In each method, accuracy, model size, and number of operations are reported. In this survey, we also discuss event-based eye tracking from the perspective of hardware design.
MambaPupil: Bidirectional Selective Recurrent model for Event-based Eye tracking
Apr 18, 2024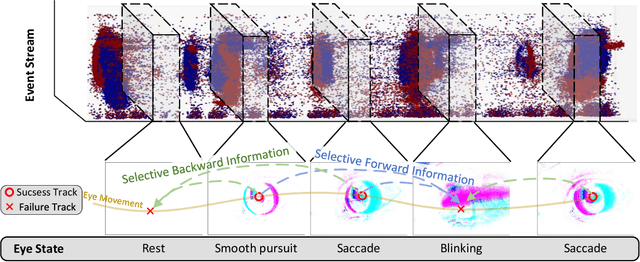
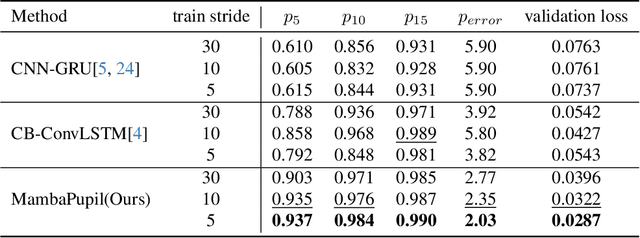
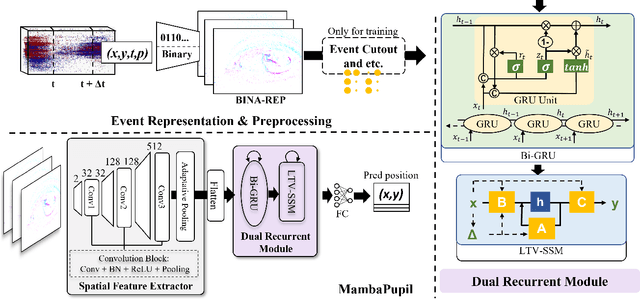

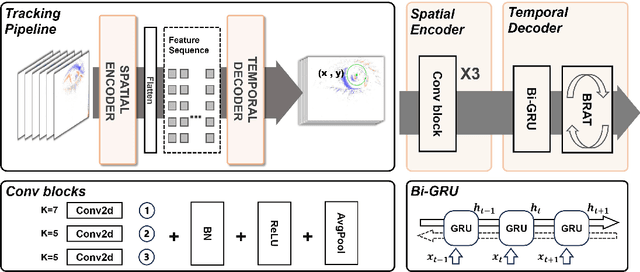
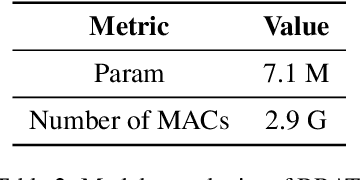
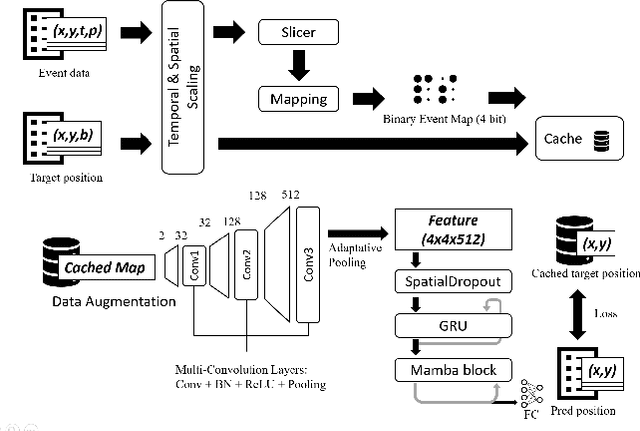
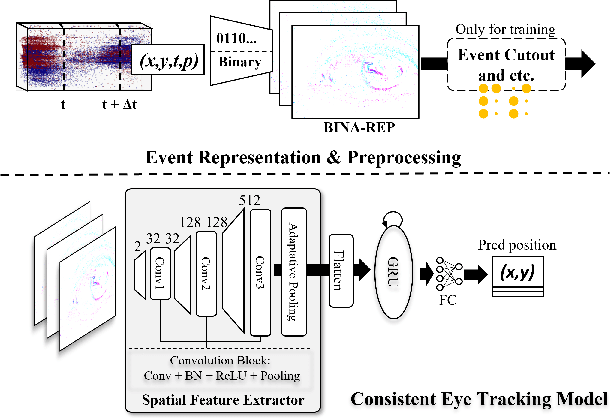
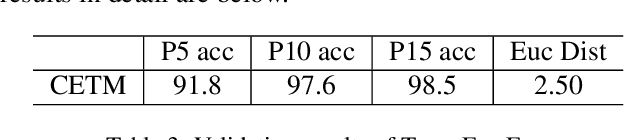
Abstract:Event-based eye tracking has shown great promise with the high temporal resolution and low redundancy provided by the event camera. However, the diversity and abruptness of eye movement patterns, including blinking, fixating, saccades, and smooth pursuit, pose significant challenges for eye localization. To achieve a stable event-based eye-tracking system, this paper proposes a bidirectional long-term sequence modeling and time-varying state selection mechanism to fully utilize contextual temporal information in response to the variability of eye movements. Specifically, the MambaPupil network is proposed, which consists of the multi-layer convolutional encoder to extract features from the event representations, a bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), and a Linear Time-Varying State Space Module (LTV-SSM), to selectively capture contextual correlation from the forward and backward temporal relationship. Furthermore, the Bina-rep is utilized as a compact event representation, and the tailor-made data augmentation, called as Event-Cutout, is proposed to enhance the model's robustness by applying spatial random masking to the event image. The evaluation on the ThreeET-plus benchmark shows the superior performance of the MambaPupil, which secured the 1st place in CVPR'2024 AIS Event-based Eye Tracking challenge.
Event-Based Eye Tracking. AIS 2024 Challenge Survey
Apr 17, 2024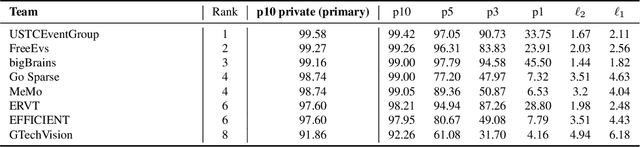
Abstract:This survey reviews the AIS 2024 Event-Based Eye Tracking (EET) Challenge. The task of the challenge focuses on processing eye movement recorded with event cameras and predicting the pupil center of the eye. The challenge emphasizes efficient eye tracking with event cameras to achieve good task accuracy and efficiency trade-off. During the challenge period, 38 participants registered for the Kaggle competition, and 8 teams submitted a challenge factsheet. The novel and diverse methods from the submitted factsheets are reviewed and analyzed in this survey to advance future event-based eye tracking research.
Event-based Asynchronous HDR Imaging by Temporal Incident Light Modulation
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:Dynamic Range (DR) is a pivotal characteristic of imaging systems. Current frame-based cameras struggle to achieve high dynamic range imaging due to the conflict between globally uniform exposure and spatially variant scene illumination. In this paper, we propose AsynHDR, a Pixel-Asynchronous HDR imaging system, based on key insights into the challenges in HDR imaging and the unique event-generating mechanism of Dynamic Vision Sensors (DVS). Our proposed AsynHDR system integrates the DVS with a set of LCD panels. The LCD panels modulate the irradiance incident upon the DVS by altering their transparency, thereby triggering the pixel-independent event streams. The HDR image is subsequently decoded from the event streams through our temporal-weighted algorithm. Experiments under standard test platform and several challenging scenes have verified the feasibility of the system in HDR imaging task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge