Yuhui Yun
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
EICopilot: Search and Explore Enterprise Information over Large-scale Knowledge Graphs with LLM-driven Agents
Jan 23, 2025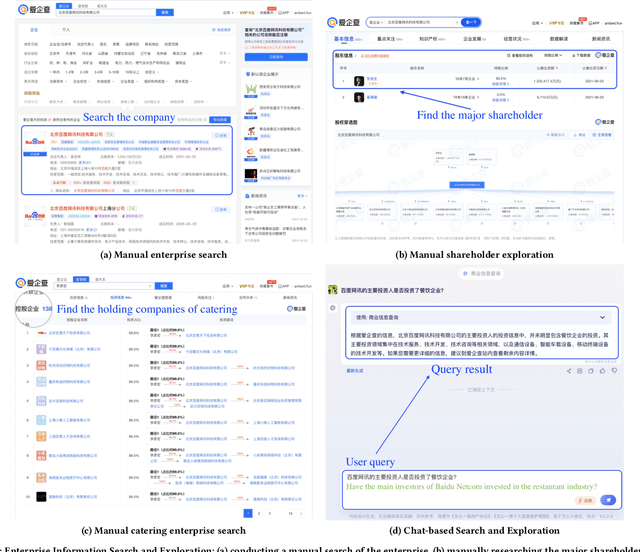
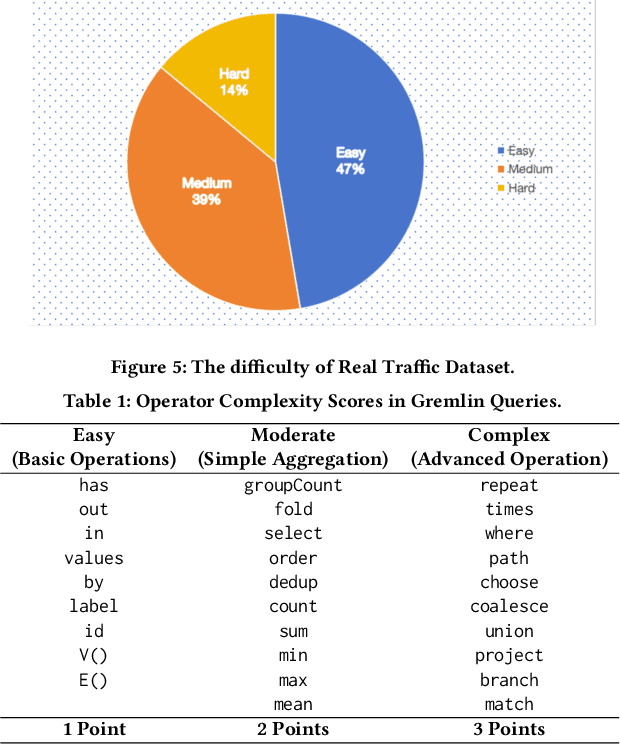
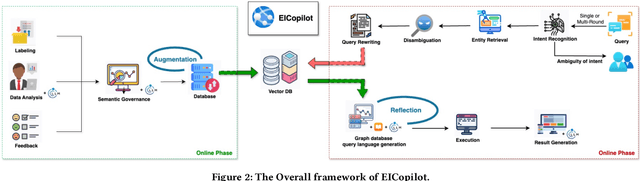
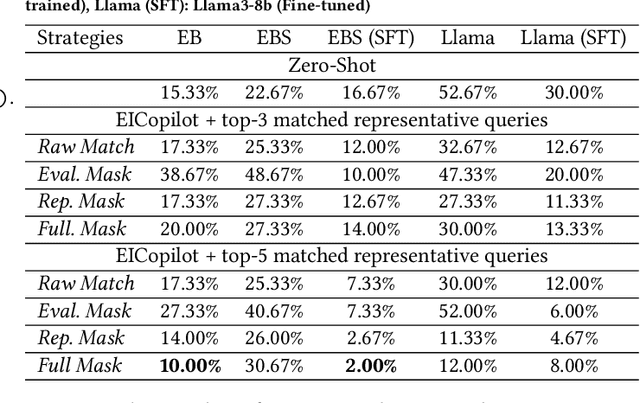
Abstract:The paper introduces EICopilot, an novel agent-based solution enhancing search and exploration of enterprise registration data within extensive online knowledge graphs like those detailing legal entities, registered capital, and major shareholders. Traditional methods necessitate text-based queries and manual subgraph explorations, often resulting in time-consuming processes. EICopilot, deployed as a chatbot via Baidu Enterprise Search, improves this landscape by utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) to interpret natural language queries. This solution automatically generates and executes Gremlin scripts, providing efficient summaries of complex enterprise relationships. Distinct feature a data pre-processing pipeline that compiles and annotates representative queries into a vector database of examples for In-context learning (ICL), a comprehensive reasoning pipeline combining Chain-of-Thought with ICL to enhance Gremlin script generation for knowledge graph search and exploration, and a novel query masking strategy that improves intent recognition for heightened script accuracy. Empirical evaluations demonstrate the superior performance of EICopilot, including speed and accuracy, over baseline methods, with the \emph{Full Mask} variant achieving a syntax error rate reduction to as low as 10.00% and an execution correctness of up to 82.14%. These components collectively contribute to superior querying capabilities and summarization of intricate datasets, positioning EICopilot as a groundbreaking tool in the exploration and exploitation of large-scale knowledge graphs for enterprise information search.
Efficient Federated Learning Using Dynamic Update and Adaptive Pruning with Momentum on Shared Server Data
Aug 11, 2024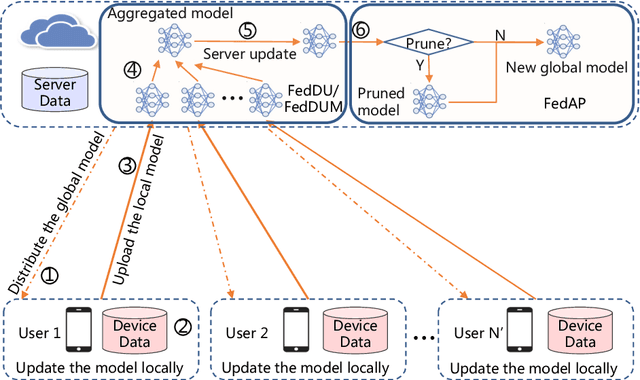

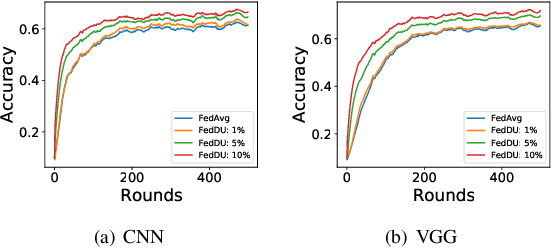
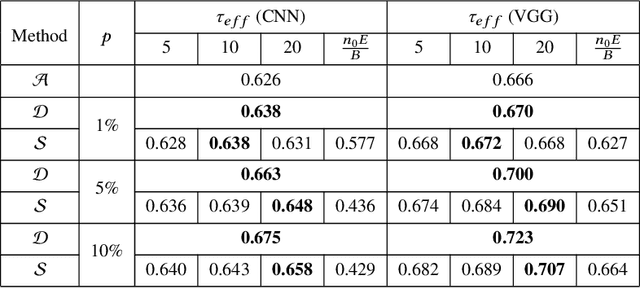
Abstract:Despite achieving remarkable performance, Federated Learning (FL) encounters two important problems, i.e., low training efficiency and limited computational resources. In this paper, we propose a new FL framework, i.e., FedDUMAP, with three original contributions, to leverage the shared insensitive data on the server in addition to the distributed data in edge devices so as to efficiently train a global model. First, we propose a simple dynamic server update algorithm, which takes advantage of the shared insensitive data on the server while dynamically adjusting the update steps on the server in order to speed up the convergence and improve the accuracy. Second, we propose an adaptive optimization method with the dynamic server update algorithm to exploit the global momentum on the server and each local device for superior accuracy. Third, we develop a layer-adaptive model pruning method to carry out specific pruning operations, which is adapted to the diverse features of each layer so as to attain an excellent trade-off between effectiveness and efficiency. Our proposed FL model, FedDUMAP, combines the three original techniques and has a significantly better performance compared with baseline approaches in terms of efficiency (up to 16.9 times faster), accuracy (up to 20.4% higher), and computational cost (up to 62.6% smaller).
Towards Automated Data Sciences with Natural Language and SageCopilot: Practices and Lessons Learned
Jul 21, 2024



Abstract:While the field of NL2SQL has made significant advancements in translating natural language instructions into executable SQL scripts for data querying and processing, achieving full automation within the broader data science pipeline - encompassing data querying, analysis, visualization, and reporting - remains a complex challenge. This study introduces SageCopilot, an advanced, industry-grade system system that automates the data science pipeline by integrating Large Language Models (LLMs), Autonomous Agents (AutoAgents), and Language User Interfaces (LUIs). Specifically, SageCopilot incorporates a two-phase design: an online component refining users' inputs into executable scripts through In-Context Learning (ICL) and running the scripts for results reporting & visualization, and an offline preparing demonstrations requested by ICL in the online phase. A list of trending strategies such as Chain-of-Thought and prompt-tuning have been used to augment SageCopilot for enhanced performance. Through rigorous testing and comparative analysis against prompt-based solutions, SageCopilot has been empirically validated to achieve superior end-to-end performance in generating or executing scripts and offering results with visualization, backed by real-world datasets. Our in-depth ablation studies highlight the individual contributions of various components and strategies used by SageCopilot to the end-to-end correctness for data sciences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge