Yihua Du
A Mechanistic View on Video Generation as World Models: State and Dynamics
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Large-scale video generation models have demonstrated emergent physical coherence, positioning them as potential world models. However, a gap remains between contemporary "stateless" video architectures and classic state-centric world model theories. This work bridges this gap by proposing a novel taxonomy centered on two pillars: State Construction and Dynamics Modeling. We categorize state construction into implicit paradigms (context management) and explicit paradigms (latent compression), while dynamics modeling is analyzed through knowledge integration and architectural reformulation. Furthermore, we advocate for a transition in evaluation from visual fidelity to functional benchmarks, testing physical persistence and causal reasoning. We conclude by identifying two critical frontiers: enhancing persistence via data-driven memory and compressed fidelity, and advancing causality through latent factor decoupling and reasoning-prior integration. By addressing these challenges, the field can evolve from generating visually plausible videos to building robust, general-purpose world simulators.
VideoMemory: Toward Consistent Video Generation via Memory Integration
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Maintaining consistent characters, props, and environments across multiple shots is a central challenge in narrative video generation. Existing models can produce high-quality short clips but often fail to preserve entity identity and appearance when scenes change or when entities reappear after long temporal gaps. We present VideoMemory, an entity-centric framework that integrates narrative planning with visual generation through a Dynamic Memory Bank. Given a structured script, a multi-agent system decomposes the narrative into shots, retrieves entity representations from memory, and synthesizes keyframes and videos conditioned on these retrieved states. The Dynamic Memory Bank stores explicit visual and semantic descriptors for characters, props, and backgrounds, and is updated after each shot to reflect story-driven changes while preserving identity. This retrieval-update mechanism enables consistent portrayal of entities across distant shots and supports coherent long-form generation. To evaluate this setting, we construct a 54-case multi-shot consistency benchmark covering character-, prop-, and background-persistent scenarios. Extensive experiments show that VideoMemory achieves strong entity-level coherence and high perceptual quality across diverse narrative sequences.
StereoPilot: Learning Unified and Efficient Stereo Conversion via Generative Priors
Dec 18, 2025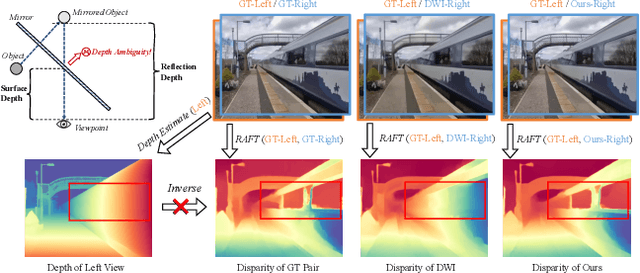
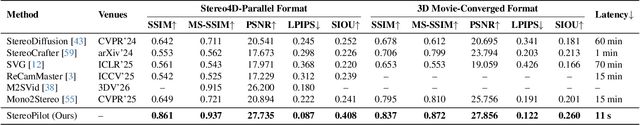
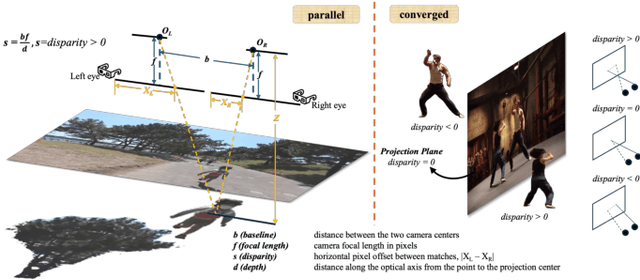

Abstract:The rapid growth of stereoscopic displays, including VR headsets and 3D cinemas, has led to increasing demand for high-quality stereo video content. However, producing 3D videos remains costly and complex, while automatic Monocular-to-Stereo conversion is hindered by the limitations of the multi-stage ``Depth-Warp-Inpaint'' (DWI) pipeline. This paradigm suffers from error propagation, depth ambiguity, and format inconsistency between parallel and converged stereo configurations. To address these challenges, we introduce UniStereo, the first large-scale unified dataset for stereo video conversion, covering both stereo formats to enable fair benchmarking and robust model training. Building upon this dataset, we propose StereoPilot, an efficient feed-forward model that directly synthesizes the target view without relying on explicit depth maps or iterative diffusion sampling. Equipped with a learnable domain switcher and a cycle consistency loss, StereoPilot adapts seamlessly to different stereo formats and achieves improved consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that StereoPilot significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both visual fidelity and computational efficiency. Project page: https://hit-perfect.github.io/StereoPilot/.
An Attention-Based Denoising Framework for Personality Detection in Social Media Texts
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:In social media networks, users produce a large amount of text content anytime, providing researchers with a valuable approach to digging for personality-related information. Personality detection based on user-generated texts is a universal method that can be used to build user portraits. The presence of noise in social media texts hinders personality detection. However, previous studies have not fully addressed this challenge. Inspired by the scanning reading technique, we propose an attention-based information extraction mechanism (AIEM) for long texts, which is applied to quickly locate valuable pieces of information, and focus more attention on the deep semantics of key pieces. Then, we provide a novel attention-based denoising framework (ADF) for personality detection tasks and achieve state-of-the-art performance on two commonly used datasets. Notably, we obtain an average accuracy improvement of 10.2% on the gold standard Twitter-Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (Twitter-MBTI) dataset. We made our code publicly available on GitHub. We shed light on how AIEM works to magnify personality-related signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge