Yanmin Zhu
Universal Spectral Transfer with Physical Prior-Informed Deep Generative Learning
Jul 22, 2024Abstract:Spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique for characterizing matter across physical and biological realms1-5. However, its fundamental principle necessitates specialized instrumentation per physical phenomena probed, limiting broad adoption and use in all relevant research. In this study, we introduce SpectroGen, a novel physical prior-informed deep generative model for generating relevant spectral signatures across modalities using experimentally collected spectral input only from a single modality. We achieve this by reimagining the representation of spectral data as mathematical constructs of distributions instead of their traditional physical and molecular state representations. The results from 319 standard mineral samples tested demonstrate generating with 99% correlation and 0.01 root mean square error with superior resolution than experimentally acquired ground truth spectra. We showed transferring capability across Raman, Infrared, and X-ray Diffraction modalities with Gaussian, Lorentzian, and Voigt distribution priors respectively6-10. This approach however is globally generalizable for any spectral input that can be represented by a distribution prior, making it universally applicable. We believe our work revolutionizes the application sphere of spectroscopy, which has traditionally been limited by access to the required sophisticated and often expensive equipment towards accelerating material, pharmaceutical, and biological discoveries.
Modeling Multi-aspect Preferences and Intents for Multi-behavioral Sequential Recommendation
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:Multi-behavioral sequential recommendation has recently attracted increasing attention. However, existing methods suffer from two major limitations. Firstly, user preferences and intents can be described in fine-grained detail from multiple perspectives; yet, these methods fail to capture their multi-aspect nature. Secondly, user behaviors may contain noises, and most existing methods could not effectively deal with noises. In this paper, we present an attentive recurrent model with multiple projections to capture Multi-Aspect preferences and INTents (MAINT in short). To extract multi-aspect preferences from target behaviors, we propose a multi-aspect projection mechanism for generating multiple preference representations from multiple aspects. To extract multi-aspect intents from multi-typed behaviors, we propose a behavior-enhanced LSTM and a multi-aspect refinement attention mechanism. The attention mechanism can filter out noises and generate multiple intent representations from different aspects. To adaptively fuse user preferences and intents, we propose a multi-aspect gated fusion mechanism. Extensive experiments conducted on real-world datasets have demonstrated the effectiveness of our model.
Contrastive Self-supervised Learning in Recommender Systems: A Survey
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning-based recommender systems have achieved remarkable success in recent years. However, these methods usually heavily rely on labeled data (i.e., user-item interactions), suffering from problems such as data sparsity and cold-start. Self-supervised learning, an emerging paradigm that extracts information from unlabeled data, provides insights into addressing these problems. Specifically, contrastive self-supervised learning, due to its flexibility and promising performance, has attracted considerable interest and recently become a dominant branch in self-supervised learning-based recommendation methods. In this survey, we provide an up-to-date and comprehensive review of current contrastive self-supervised learning-based recommendation methods. Firstly, we propose a unified framework for these methods. We then introduce a taxonomy based on the key components of the framework, including view generation strategy, contrastive task, and contrastive objective. For each component, we provide detailed descriptions and discussions to guide the choice of the appropriate method. Finally, we outline open issues and promising directions for future research.
Incorporating Heterogeneous User Behaviors and Social Influences for Predictive Analysis
Jul 24, 2022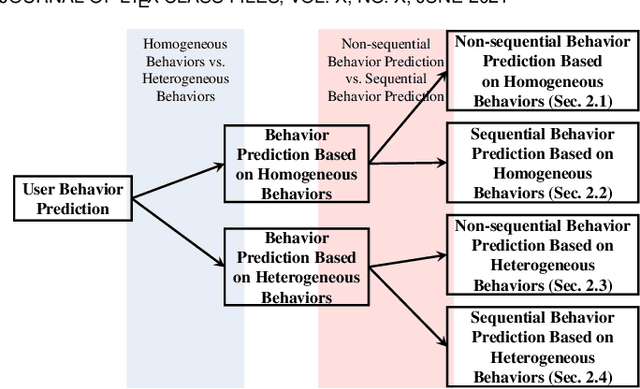
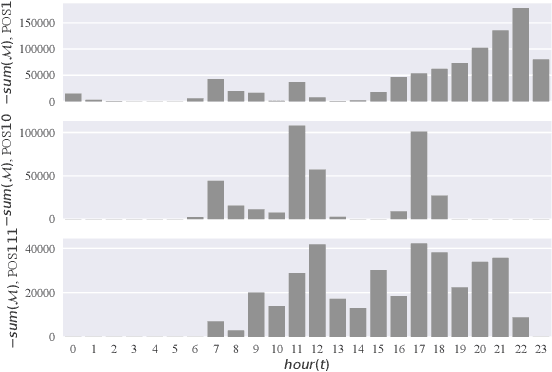
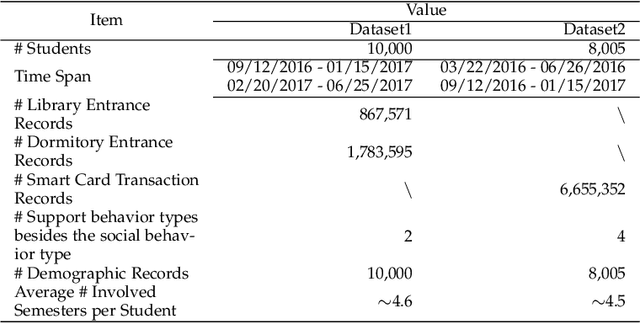
Abstract:Behavior prediction based on historical behavioral data have practical real-world significance. It has been applied in recommendation, predicting academic performance, etc. With the refinement of user data description, the development of new functions, and the fusion of multiple data sources, heterogeneous behavioral data which contain multiple types of behaviors become more and more common. In this paper, we aim to incorporate heterogeneous user behaviors and social influences for behavior predictions. To this end, this paper proposes a variant of Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) which can consider context information while modeling a behavior sequence, a projection mechanism which can model multi-faceted relationships among different types of behaviors, and a multi-faceted attention mechanism which can dynamically find out informative periods from different facets. Many kinds of behavioral data belong to spatio-temporal data. An unsupervised way to construct a social behavior graph based on spatio-temporal data and to model social influences is proposed. Moreover, a residual learning-based decoder is designed to automatically construct multiple high-order cross features based on social behavior representation and other types of behavior representations. Qualitative and quantitative experiments on real-world datasets have demonstrated the effectiveness of this model.
Deep Meta-learning in Recommendation Systems: A Survey
Jun 09, 2022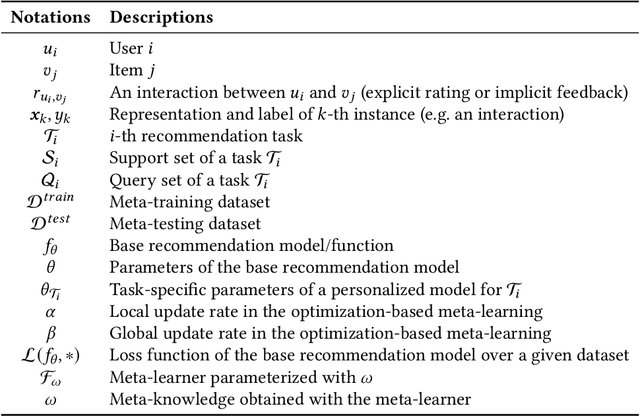
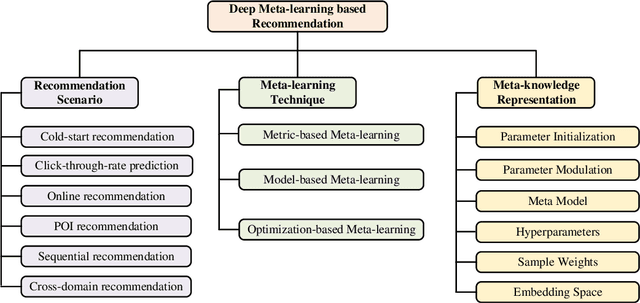
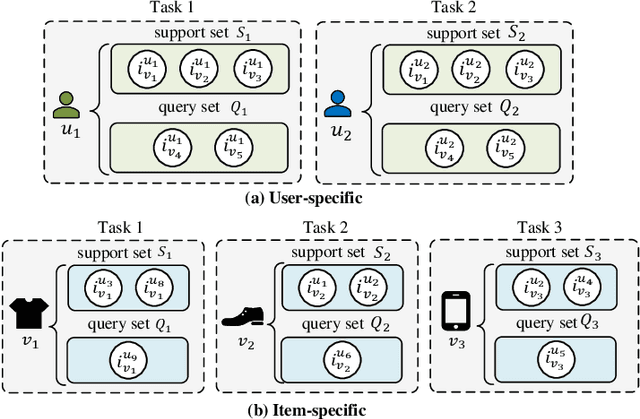
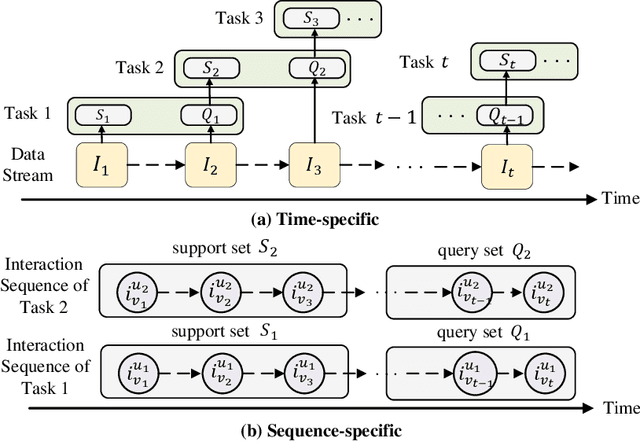
Abstract:Deep neural network based recommendation systems have achieved great success as information filtering techniques in recent years. However, since model training from scratch requires sufficient data, deep learning-based recommendation methods still face the bottlenecks of insufficient data and computational inefficiency. Meta-learning, as an emerging paradigm that learns to improve the learning efficiency and generalization ability of algorithms, has shown its strength in tackling the data sparsity issue. Recently, a growing number of studies on deep meta-learning based recommenddation systems have emerged for improving the performance under recommendation scenarios where available data is limited, e.g. user cold-start and item cold-start. Therefore, this survey provides a timely and comprehensive overview of current deep meta-learning based recommendation methods. Specifically, we propose a taxonomy to discuss existing methods according to recommendation scenarios, meta-learning techniques, and meta-knowledge representations, which could provide the design space for meta-learning based recommendation methods. For each recommendation scenario, we further discuss technical details about how existing methods apply meta-learning to improve the generalization ability of recommendation models. Finally, we also point out several limitations in current research and highlight some promising directions for future research in this area.
A Survey on Cross-domain Recommendation: Taxonomies, Methods, and Future Directions
Aug 07, 2021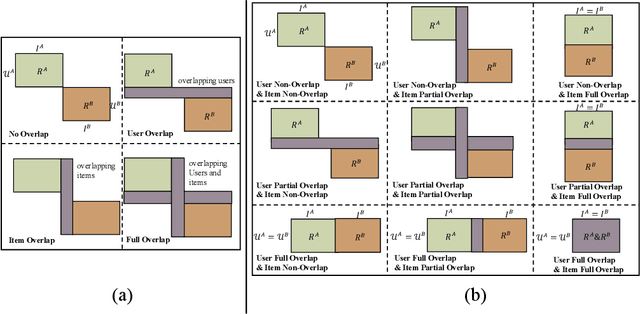
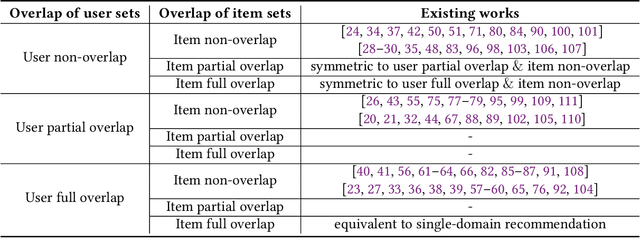
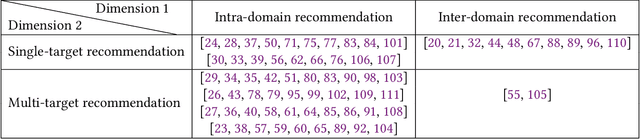
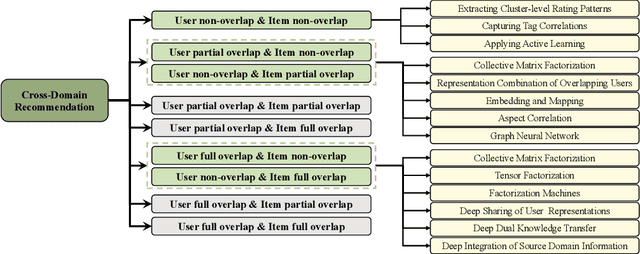
Abstract:Traditional recommendation systems are faced with two long-standing obstacles, namely, data sparsity and cold-start problems, which promote the emergence and development of Cross-Domain Recommendation (CDR). The core idea of CDR is to leverage information collected from other domains to alleviate the two problems in one domain. Over the last decade, many efforts have been engaged for cross-domain recommendation. Recently, with the development of deep learning and neural networks, a large number of methods have emerged. However, there is a limited number of systematic surveys on CDR, especially regarding the latest proposed methods as well as the recommendation scenarios and recommendation tasks they address. In this survey paper, we first proposed a two-level taxonomy of cross-domain recommendation which classifies different recommendation scenarios and recommendation tasks. We then introduce and summarize existing cross-domain recommendation approaches under different recommendation scenarios in a structured manner. We also organize datasets commonly used. We conclude this survey by providing several potential research directions about this field.
Jointly Modeling Heterogeneous Student Behaviors and Interactions Among Multiple Prediction Tasks
Mar 25, 2021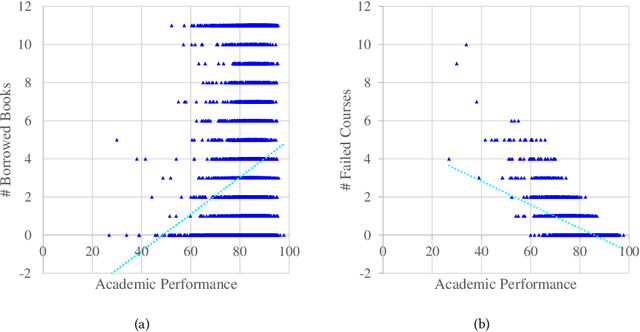
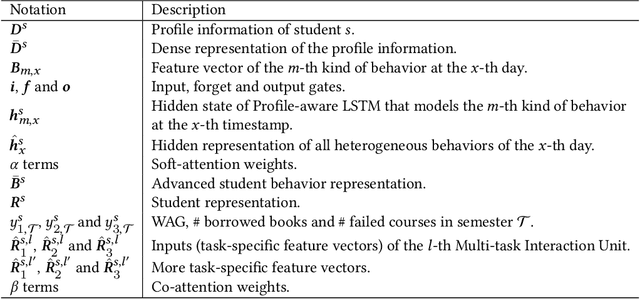
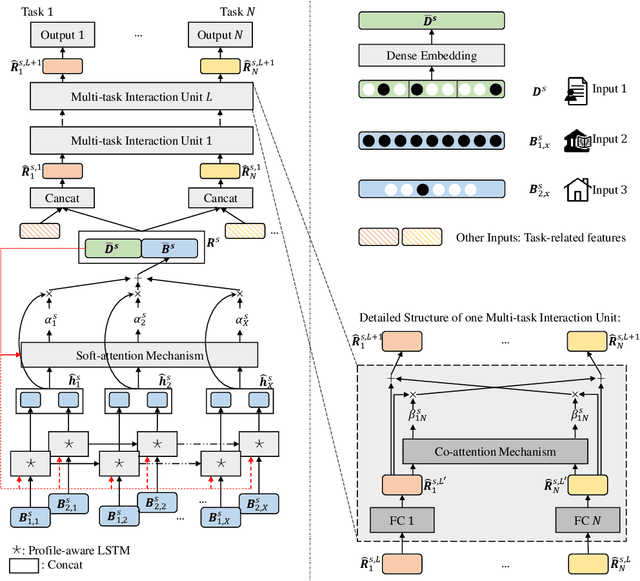
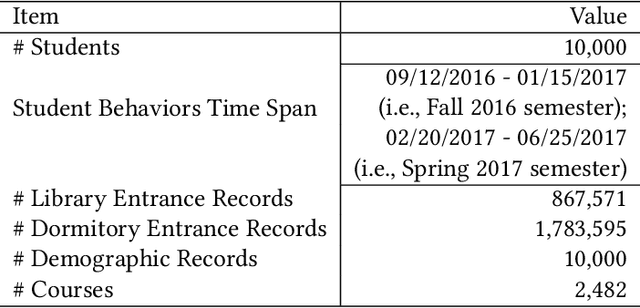
Abstract:Prediction tasks about students have practical significance for both student and college. Making multiple predictions about students is an important part of a smart campus. For instance, predicting whether a student will fail to graduate can alert the student affairs office to take predictive measures to help the student improve his/her academic performance. With the development of information technology in colleges, we can collect digital footprints which encode heterogeneous behaviors continuously. In this paper, we focus on modeling heterogeneous behaviors and making multiple predictions together, since some prediction tasks are related and learning the model for a specific task may have the data sparsity problem. To this end, we propose a variant of LSTM and a soft-attention mechanism. The proposed LSTM is able to learn the student profile-aware representation from heterogeneous behavior sequences. The proposed soft-attention mechanism can dynamically learn different importance degrees of different days for every student. In this way, heterogeneous behaviors can be well modeled. In order to model interactions among multiple prediction tasks, we propose a co-attention mechanism based unit. With the help of the stacked units, we can explicitly control the knowledge transfer among multiple tasks. We design three motivating behavior prediction tasks based on a real-world dataset collected from a college. Qualitative and quantitative experiments on the three prediction tasks have demonstrated the effectiveness of our model.
Modeling Long-Term and Short-Term Interests with Parallel Attentions for Session-based Recommendation
Jun 27, 2020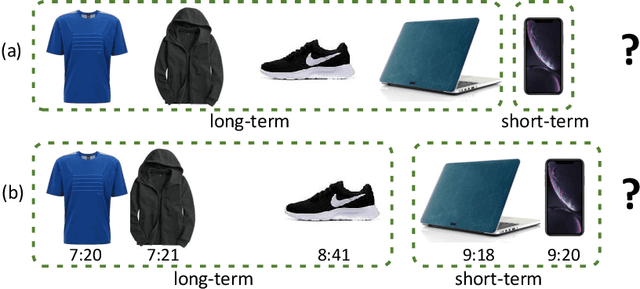
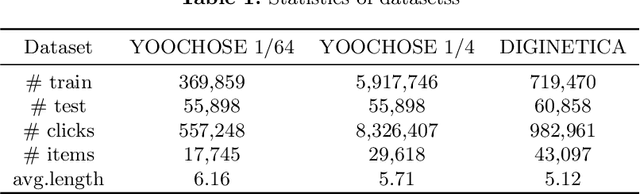
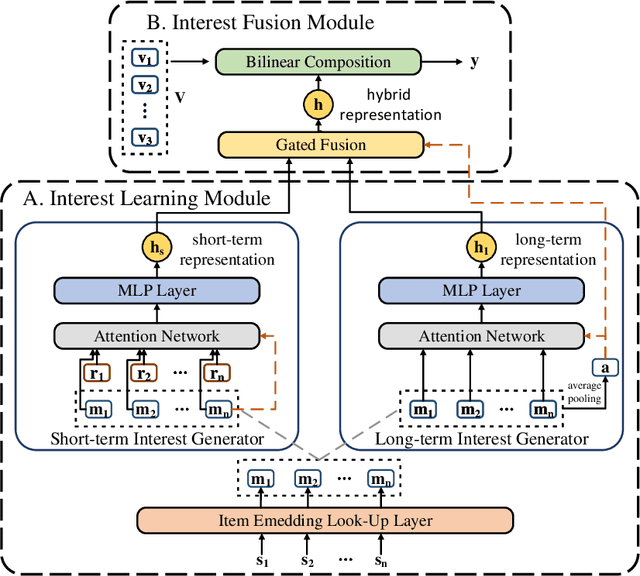
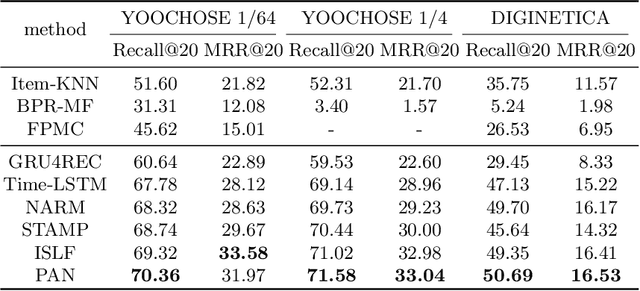
Abstract:The aim of session-based recommendation is to predict the users' next clicked item, which is a challenging task due to the inherent uncertainty in user behaviors and anonymous implicit feedback information. A powerful session-based recommender can typically explore the users' evolving interests (i.e., a combination of his/her long-term and short-term interests). Recent advances in attention mechanisms have led to state-of-the-art methods for solving this task. However, there are two main drawbacks. First, most of the attention-based methods only simply utilize the last clicked item to represent the user's short-term interest ignoring the temporal information and behavior context, which may fail to capture the recent preference of users comprehensively. Second, current studies typically think long-term and short-term interests as equally important, but the importance of them should be user-specific. Therefore, we propose a novel Parallel Attention Network model (PAN) for Session-based Recommendation. Specifically, we propose a novel time-aware attention mechanism to learn user's short-term interest by taking into account the contextual information and temporal signals simultaneously. Besides, we introduce a gated fusion method that adaptively integrates the user's long-term and short-term preferences to generate the hybrid interest representation. Experiments on the three real-world datasets show that PAN achieves obvious improvements than the state-of-the-art methods.
ALCNN: Attention-based Model for Fine-grained Demand Inference of Dock-less Shared Bike in New Cities
Sep 25, 2019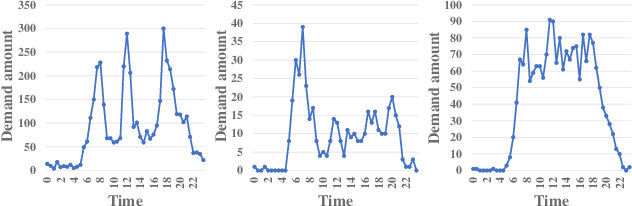
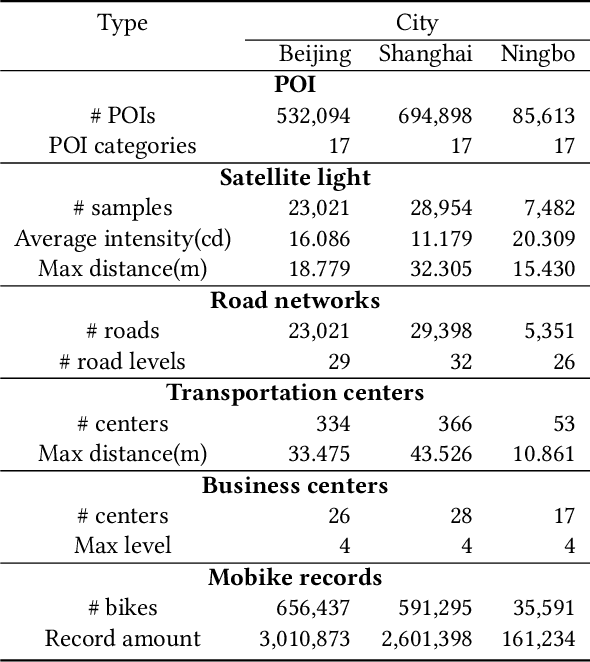
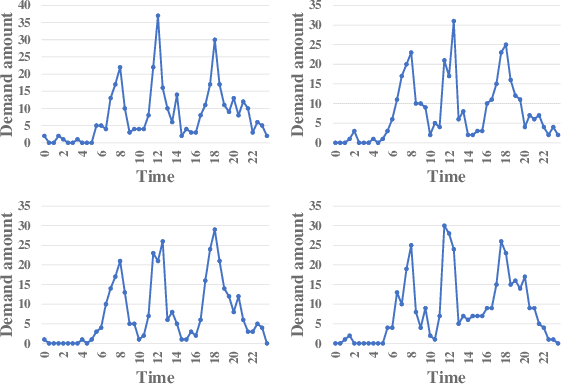
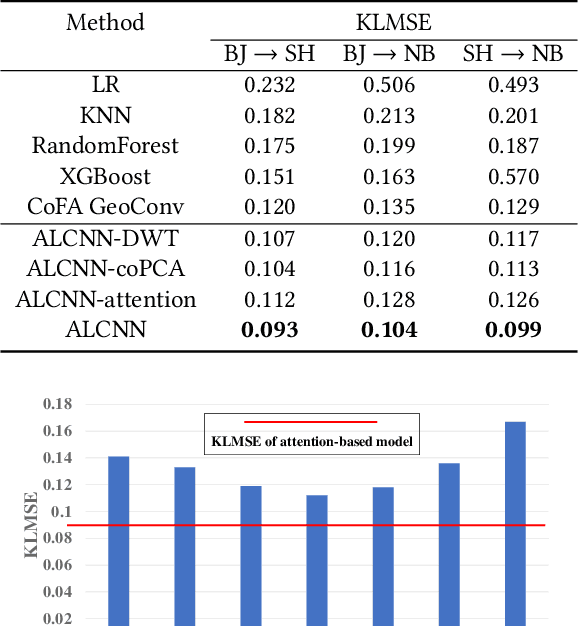
Abstract:In recent years, dock-less shared bikes have been widely spread across many cities in China and facilitate people's lives. However, at the same time, it also raises many problems about dock-less shared bike management due to the mismatching between demands and real distribution of bikes. Before deploying dock-less shared bikes in a city, companies need to make a plan for dispatching bikes from places having excessive bikes to locations with high demands for providing better services. In this paper, we study the problem of inferring fine-grained bike demands anywhere in a new city before the deployment of bikes. This problem is challenging because new city lacks training data and bike demands vary by both places and time. To solve the problem, we provide various methods to extract discriminative features from multi-source geographic data, such as POI, road networks and nighttime light, for each place. We utilize correlation Principle Component Analysis (coPCA) to deal with extracted features of both old city and new city to realize distribution adaption. Then, we adopt a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) based model to mine daily patterns for each place from fine-grained bike demand. We propose an attention based local CNN model, \textbf{ALCNN}, to infer the daily patterns with latent features from coPCA with multiple CNNs for modeling the influence of neighbor places. In addition, ALCNN merges latent features from multiple CNNs and can select a suitable size of influenced regions. The extensive experiments on real-life datasets show that the proposed approach outperforms competitive methods.
CoLight: Learning Network-level Cooperation for Traffic Signal Control
May 11, 2019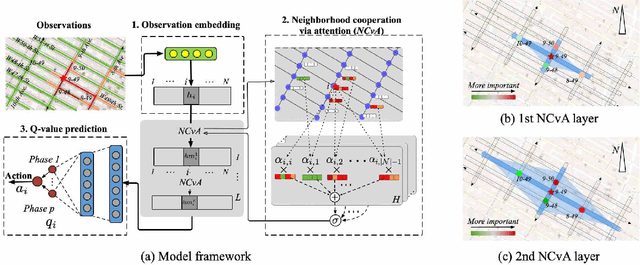
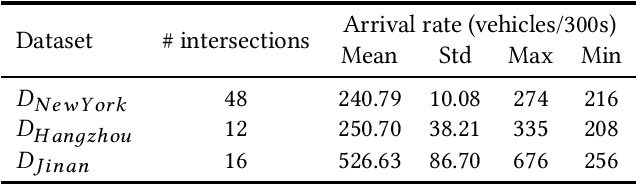
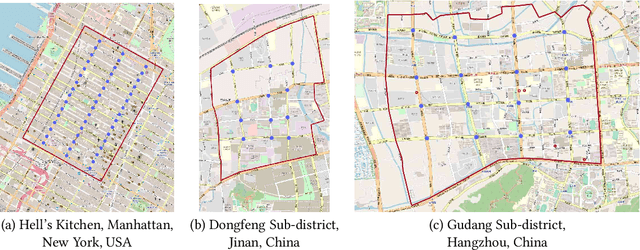
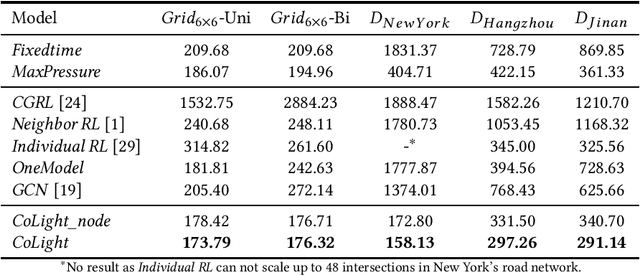
Abstract:Cooperation is critical in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). In the context of traffic signal control, good cooperation among the traffic signal agents enables the vehicles to move through intersections more smoothly. Conventional transportation approaches implement cooperation by pre-calculating the offsets between two intersections. Such pre-calculated offsets are not suitable for dynamic traffic environments. To incorporate cooperation in reinforcement learning (RL), two typical approaches are proposed to take the influence of other agents into consideration: (1) learning the communications (i.e., the representation of influences between agents) and (2) learning joint actions for agents. While joint modeling of actions has shown a preferred trend in recent studies, an in-depth study of improving the learning of communications between agents has not been systematically studied in the context of traffic signal control. To learn the communications between agents, in this paper, we propose to use graph attentional network to facilitate cooperation. Specifically, for a target intersection in a network, our proposed model, CoLight, cannot only incorporate the influences of neighboring intersections but learn to differentiate their impacts to the target intersection. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to use graph attentional network in the setting of reinforcement learning for traffic signal control. In experiments, we demonstrate that by learning the communication, the proposed model can achieve surprisingly good performance, whereas the existing approaches based on joint action modeling fail to learn well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge