Tianzi Zang
Contrastive Self-supervised Learning in Recommender Systems: A Survey
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning-based recommender systems have achieved remarkable success in recent years. However, these methods usually heavily rely on labeled data (i.e., user-item interactions), suffering from problems such as data sparsity and cold-start. Self-supervised learning, an emerging paradigm that extracts information from unlabeled data, provides insights into addressing these problems. Specifically, contrastive self-supervised learning, due to its flexibility and promising performance, has attracted considerable interest and recently become a dominant branch in self-supervised learning-based recommendation methods. In this survey, we provide an up-to-date and comprehensive review of current contrastive self-supervised learning-based recommendation methods. Firstly, we propose a unified framework for these methods. We then introduce a taxonomy based on the key components of the framework, including view generation strategy, contrastive task, and contrastive objective. For each component, we provide detailed descriptions and discussions to guide the choice of the appropriate method. Finally, we outline open issues and promising directions for future research.
Deep Meta-learning in Recommendation Systems: A Survey
Jun 09, 2022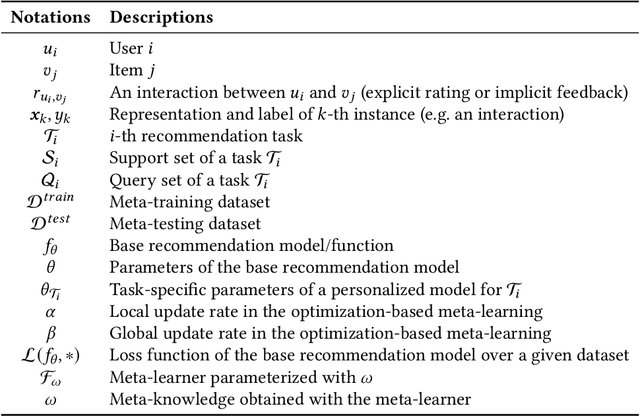
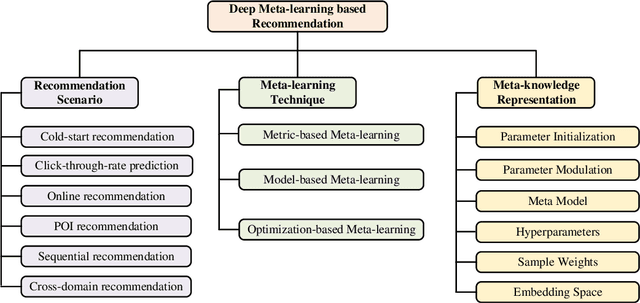
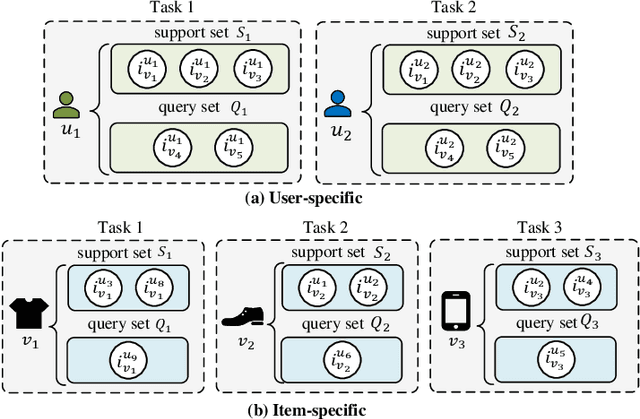
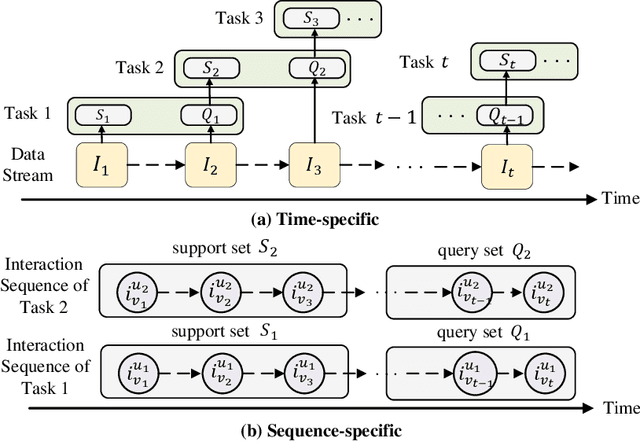
Abstract:Deep neural network based recommendation systems have achieved great success as information filtering techniques in recent years. However, since model training from scratch requires sufficient data, deep learning-based recommendation methods still face the bottlenecks of insufficient data and computational inefficiency. Meta-learning, as an emerging paradigm that learns to improve the learning efficiency and generalization ability of algorithms, has shown its strength in tackling the data sparsity issue. Recently, a growing number of studies on deep meta-learning based recommenddation systems have emerged for improving the performance under recommendation scenarios where available data is limited, e.g. user cold-start and item cold-start. Therefore, this survey provides a timely and comprehensive overview of current deep meta-learning based recommendation methods. Specifically, we propose a taxonomy to discuss existing methods according to recommendation scenarios, meta-learning techniques, and meta-knowledge representations, which could provide the design space for meta-learning based recommendation methods. For each recommendation scenario, we further discuss technical details about how existing methods apply meta-learning to improve the generalization ability of recommendation models. Finally, we also point out several limitations in current research and highlight some promising directions for future research in this area.
A Survey on Cross-domain Recommendation: Taxonomies, Methods, and Future Directions
Aug 07, 2021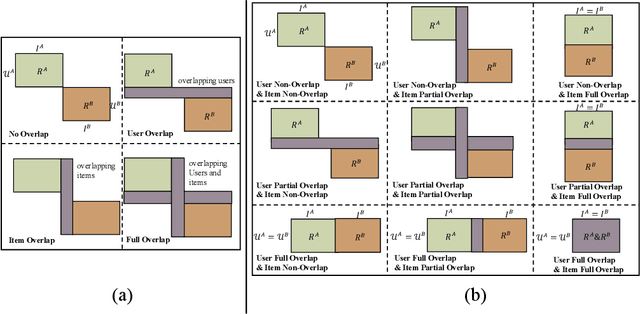
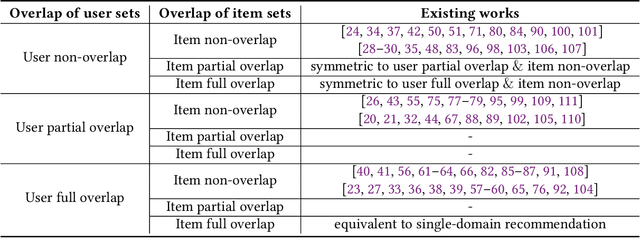
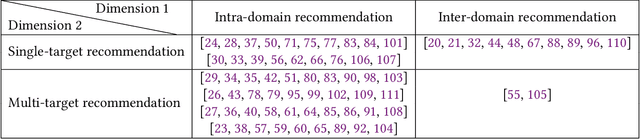
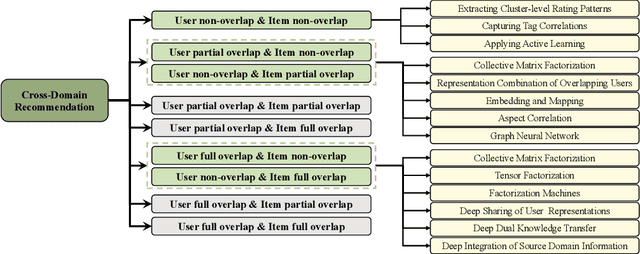
Abstract:Traditional recommendation systems are faced with two long-standing obstacles, namely, data sparsity and cold-start problems, which promote the emergence and development of Cross-Domain Recommendation (CDR). The core idea of CDR is to leverage information collected from other domains to alleviate the two problems in one domain. Over the last decade, many efforts have been engaged for cross-domain recommendation. Recently, with the development of deep learning and neural networks, a large number of methods have emerged. However, there is a limited number of systematic surveys on CDR, especially regarding the latest proposed methods as well as the recommendation scenarios and recommendation tasks they address. In this survey paper, we first proposed a two-level taxonomy of cross-domain recommendation which classifies different recommendation scenarios and recommendation tasks. We then introduce and summarize existing cross-domain recommendation approaches under different recommendation scenarios in a structured manner. We also organize datasets commonly used. We conclude this survey by providing several potential research directions about this field.
Jointly Modeling Heterogeneous Student Behaviors and Interactions Among Multiple Prediction Tasks
Mar 25, 2021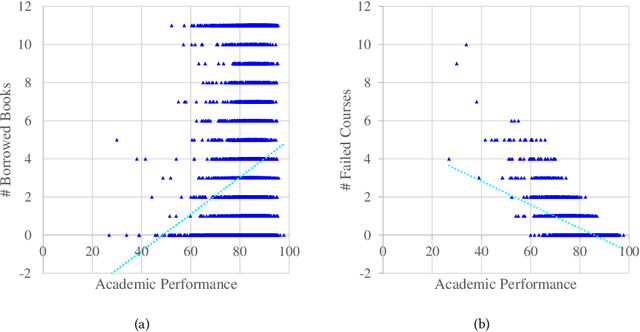
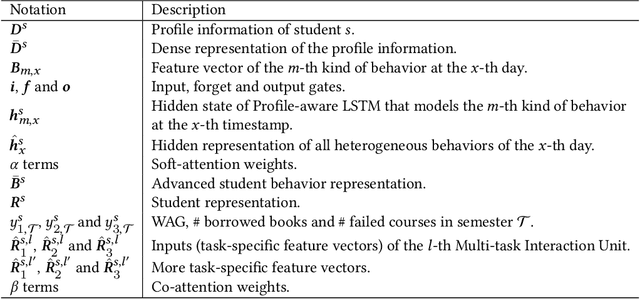
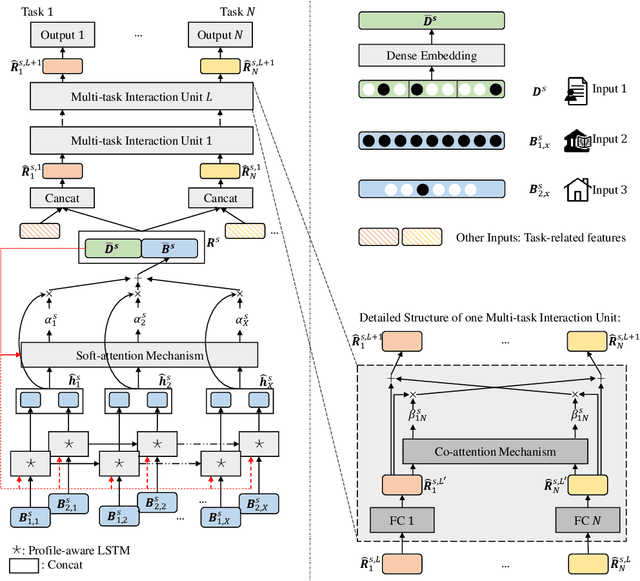
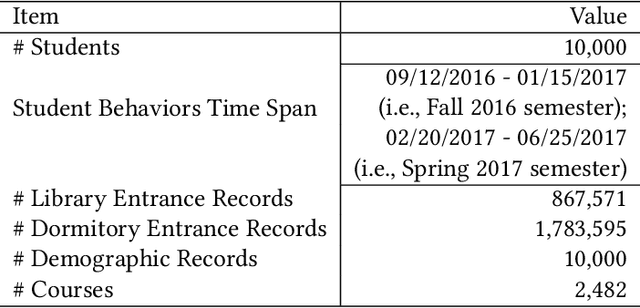
Abstract:Prediction tasks about students have practical significance for both student and college. Making multiple predictions about students is an important part of a smart campus. For instance, predicting whether a student will fail to graduate can alert the student affairs office to take predictive measures to help the student improve his/her academic performance. With the development of information technology in colleges, we can collect digital footprints which encode heterogeneous behaviors continuously. In this paper, we focus on modeling heterogeneous behaviors and making multiple predictions together, since some prediction tasks are related and learning the model for a specific task may have the data sparsity problem. To this end, we propose a variant of LSTM and a soft-attention mechanism. The proposed LSTM is able to learn the student profile-aware representation from heterogeneous behavior sequences. The proposed soft-attention mechanism can dynamically learn different importance degrees of different days for every student. In this way, heterogeneous behaviors can be well modeled. In order to model interactions among multiple prediction tasks, we propose a co-attention mechanism based unit. With the help of the stacked units, we can explicitly control the knowledge transfer among multiple tasks. We design three motivating behavior prediction tasks based on a real-world dataset collected from a college. Qualitative and quantitative experiments on the three prediction tasks have demonstrated the effectiveness of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge