Xuyang Ge
Attention Layers Add Into Low-Dimensional Residual Subspaces
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:While transformer models are widely believed to operate in high-dimensional hidden spaces, we show that attention outputs are confined to a surprisingly low-dimensional subspace, where about 60\% of the directions account for 99\% of the variance--a phenomenon that is induced by the attention output projection matrix and consistently observed across diverse model families and datasets. Critically, we find this low-rank structure as a fundamental cause of the prevalent dead feature problem in sparse dictionary learning, where it creates a mismatch between randomly initialized features and the intrinsic geometry of the activation space. Building on this insight, we propose a subspace-constrained training method for sparse autoencoders (SAEs), initializing feature directions into the active subspace of activations. Our approach reduces dead features from 87\% to below 1\% in Attention Output SAEs with 1M features, and can further extend to other sparse dictionary learning methods. Our findings provide both new insights into the geometry of attention and practical tools for improving sparse dictionary learning in large language models.
Towards Understanding the Nature of Attention with Low-Rank Sparse Decomposition
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:We propose Low-Rank Sparse Attention (Lorsa), a sparse replacement model of Transformer attention layers to disentangle original Multi Head Self Attention (MHSA) into individually comprehensible components. Lorsa is designed to address the challenge of attention superposition to understand attention-mediated interaction between features in different token positions. We show that Lorsa heads find cleaner and finer-grained versions of previously discovered MHSA behaviors like induction heads, successor heads and attention sink behavior (i.e., heavily attending to the first token). Lorsa and Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) are both sparse dictionary learning methods applied to different Transformer components, and lead to consistent findings in many ways. For instance, we discover a comprehensive family of arithmetic-specific Lorsa heads, each corresponding to an atomic operation in Llama-3.1-8B. Automated interpretability analysis indicates that Lorsa achieves parity with SAE in interpretability while Lorsa exhibits superior circuit discovery properties, especially for features computed collectively by multiple MHSA heads. We also conduct extensive experiments on architectural design ablation, Lorsa scaling law and error analysis.
Llama Scope: Extracting Millions of Features from Llama-3.1-8B with Sparse Autoencoders
Oct 27, 2024



Abstract:Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) have emerged as a powerful unsupervised method for extracting sparse representations from language models, yet scalable training remains a significant challenge. We introduce a suite of 256 SAEs, trained on each layer and sublayer of the Llama-3.1-8B-Base model, with 32K and 128K features. Modifications to a state-of-the-art SAE variant, Top-K SAEs, are evaluated across multiple dimensions. In particular, we assess the generalizability of SAEs trained on base models to longer contexts and fine-tuned models. Additionally, we analyze the geometry of learned SAE latents, confirming that \emph{feature splitting} enables the discovery of new features. The Llama Scope SAE checkpoints are publicly available at~\url{https://huggingface.co/fnlp/Llama-Scope}, alongside our scalable training, interpretation, and visualization tools at \url{https://github.com/OpenMOSS/Language-Model-SAEs}. These contributions aim to advance the open-source Sparse Autoencoder ecosystem and support mechanistic interpretability research by reducing the need for redundant SAE training.
Towards Universality: Studying Mechanistic Similarity Across Language Model Architectures
Oct 10, 2024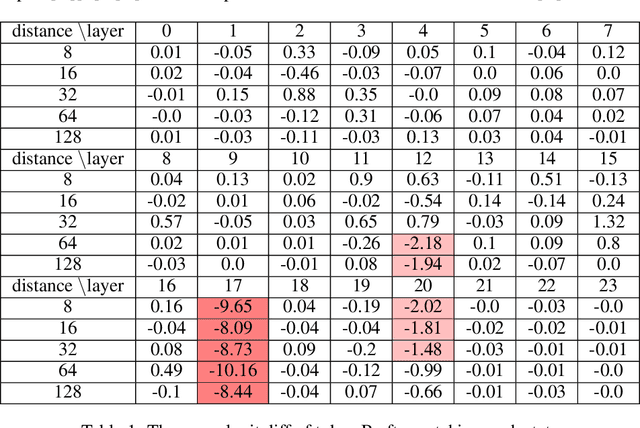
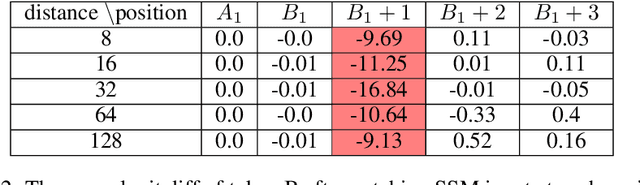

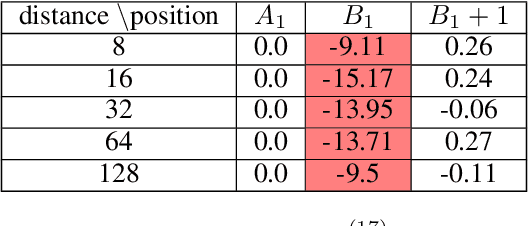
Abstract:The hypothesis of Universality in interpretability suggests that different neural networks may converge to implement similar algorithms on similar tasks. In this work, we investigate two mainstream architectures for language modeling, namely Transformers and Mambas, to explore the extent of their mechanistic similarity. We propose to use Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) to isolate interpretable features from these models and show that most features are similar in these two models. We also validate the correlation between feature similarity and Universality. We then delve into the circuit-level analysis of Mamba models and find that the induction circuits in Mamba are structurally analogous to those in Transformers. We also identify a nuanced difference we call \emph{Off-by-One motif}: The information of one token is written into the SSM state in its next position. Whilst interaction between tokens in Transformers does not exhibit such trend.
TravelAgent: An AI Assistant for Personalized Travel Planning
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:As global tourism expands and artificial intelligence technology advances, intelligent travel planning services have emerged as a significant research focus. Within dynamic real-world travel scenarios with multi-dimensional constraints, services that support users in automatically creating practical and customized travel itineraries must address three key objectives: Rationality, Comprehensiveness, and Personalization. However, existing systems with rule-based combinations or LLM-based planning methods struggle to fully satisfy these criteria. To overcome the challenges, we introduce TravelAgent, a travel planning system powered by large language models (LLMs) designed to provide reasonable, comprehensive, and personalized travel itineraries grounded in dynamic scenarios. TravelAgent comprises four modules: Tool-usage, Recommendation, Planning, and Memory Module. We evaluate TravelAgent's performance with human and simulated users, demonstrating its overall effectiveness in three criteria and confirming the accuracy of personalized recommendations.
Automatically Identifying Local and Global Circuits with Linear Computation Graphs
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Circuit analysis of any certain model behavior is a central task in mechanistic interpretability. We introduce our circuit discovery pipeline with sparse autoencoders (SAEs) and a variant called skip SAEs. With these two modules inserted into the model, the model's computation graph with respect to OV and MLP circuits becomes strictly linear. Our methods do not require linear approximation to compute the causal effect of each node. This fine-grained graph enables identifying both end-to-end and local circuits accounting for either logits or intermediate features. We can scalably apply this pipeline with a technique called Hierarchical Attribution. We analyze three kind of circuits in GPT2-Small, namely bracket, induction and Indirect Object Identification circuits. Our results reveal new findings underlying existing discoveries.
SurveyAgent: A Conversational System for Personalized and Efficient Research Survey
Apr 09, 2024Abstract:In the rapidly advancing research fields such as AI, managing and staying abreast of the latest scientific literature has become a significant challenge for researchers. Although previous efforts have leveraged AI to assist with literature searches, paper recommendations, and question-answering, a comprehensive support system that addresses the holistic needs of researchers has been lacking. This paper introduces SurveyAgent, a novel conversational system designed to provide personalized and efficient research survey assistance to researchers. SurveyAgent integrates three key modules: Knowledge Management for organizing papers, Recommendation for discovering relevant literature, and Query Answering for engaging with content on a deeper level. This system stands out by offering a unified platform that supports researchers through various stages of their literature review process, facilitated by a conversational interface that prioritizes user interaction and personalization. Our evaluation demonstrates SurveyAgent's effectiveness in streamlining research activities, showcasing its capability to facilitate how researchers interact with scientific literature.
Dictionary Learning Improves Patch-Free Circuit Discovery in Mechanistic Interpretability: A Case Study on Othello-GPT
Feb 19, 2024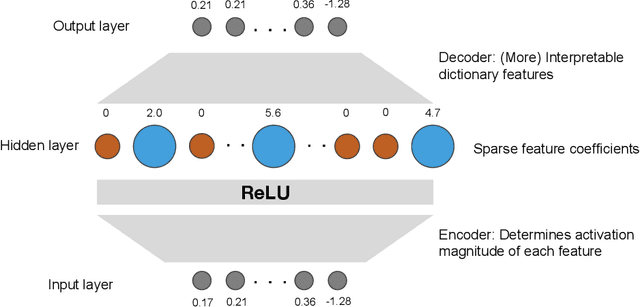
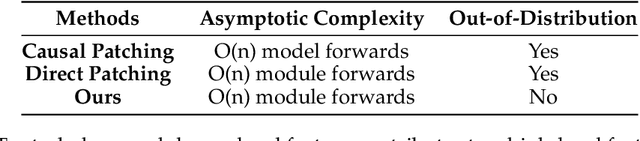
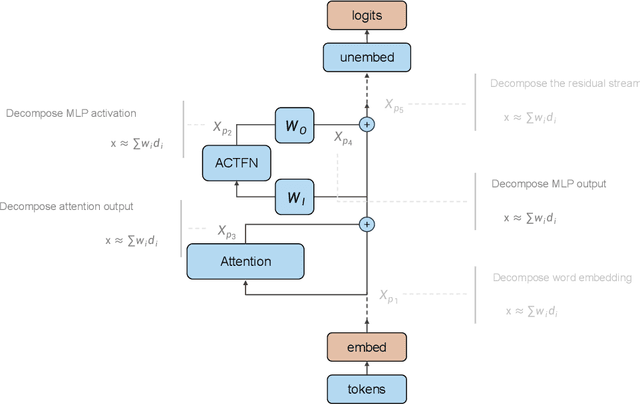
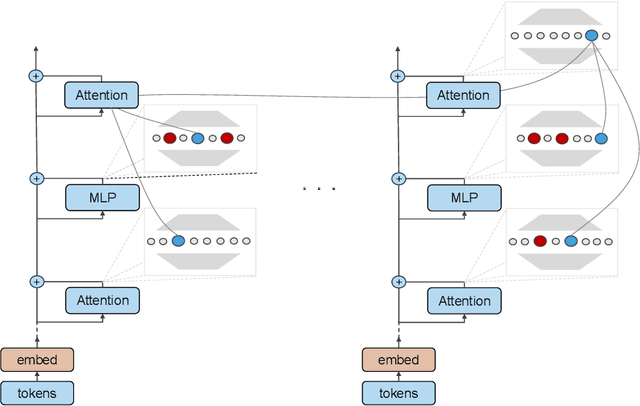
Abstract:Sparse dictionary learning has been a rapidly growing technique in mechanistic interpretability to attack superposition and extract more human-understandable features from model activations. We ask a further question based on the extracted more monosemantic features: How do we recognize circuits connecting the enormous amount of dictionary features? We propose a circuit discovery framework alternative to activation patching. Our framework suffers less from out-of-distribution and proves to be more efficient in terms of asymptotic complexity. The basic unit in our framework is dictionary features decomposed from all modules writing to the residual stream, including embedding, attention output and MLP output. Starting from any logit, dictionary feature or attention score, we manage to trace down to lower-level dictionary features of all tokens and compute their contribution to these more interpretable and local model behaviors. We dig in a small transformer trained on a synthetic task named Othello and find a number of human-understandable fine-grained circuits inside of it.
Beneath Surface Similarity: Large Language Models Make Reasonable Scientific Analogies after Structure Abduction
May 22, 2023


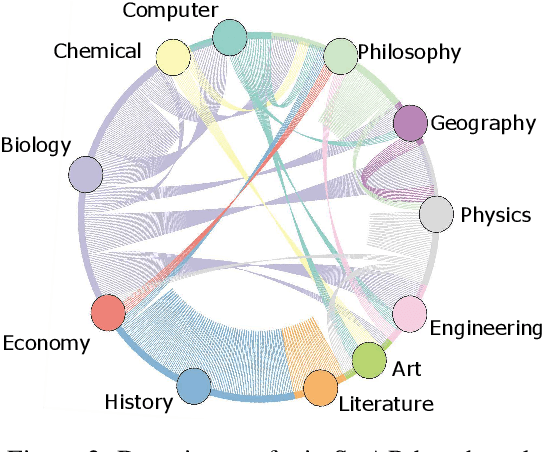
Abstract:Analogical reasoning is essential for human cognition, allowing us to comprehend new concepts by relating them to familiar ones based on common relational structures. Previous work mainly focuses on word analogies, which do not fully represent the analogical reasoning ability of language models (LMs) aligning with humans. This paper first examines analogy prompting for large language models (LLMs) in scientific question-answering tasks. Then we discover that LLMs tend to ignore relational structures when performing word analogies, casting doubt on their utility for evaluating analogical reasoning. For better evaluation aligning with humans, we propose an analogical structure abduction task based on cognitive psychology, which aims to abduct structures between two systems to establish an analogy. Then we create a benchmark of scientific analogical reasoning with structure abduction, SCAR, consisting of 400 scientific analogies across 13 domains for this task. Empirical results reveal that LLMs struggle with this task, but the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) method with background knowledge and explanations can improve their capability.
Distilling Script Knowledge from Large Language Models for Constrained Language Planning
May 22, 2023



Abstract:In everyday life, humans often plan their actions by following step-by-step instructions in the form of goal-oriented scripts. Previous work has exploited language models (LMs) to plan for abstract goals of stereotypical activities (e.g., "make a cake"), but leaves more specific goals with multi-facet constraints understudied (e.g., "make a cake for diabetics"). In this paper, we define the task of constrained language planning for the first time. We propose an overgenerate-then-filter approach to improve large language models (LLMs) on this task, and use it to distill a novel constrained language planning dataset, CoScript, which consists of 55,000 scripts. Empirical results demonstrate that our method significantly improves the constrained language planning ability of LLMs, especially on constraint faithfulness. Furthermore, CoScript is demonstrated to be quite effective in endowing smaller LMs with constrained language planning ability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge