Xiuli Bi
Clear Nights Ahead: Towards Multi-Weather Nighttime Image Restoration
May 22, 2025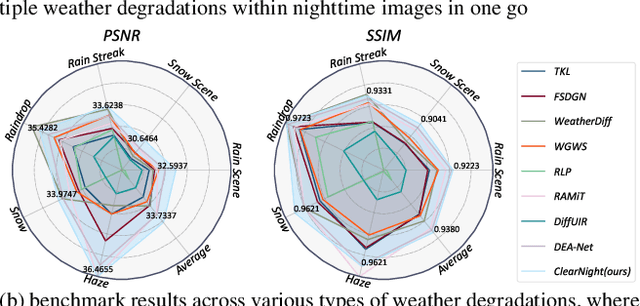
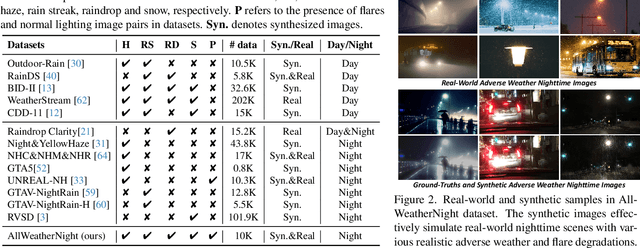

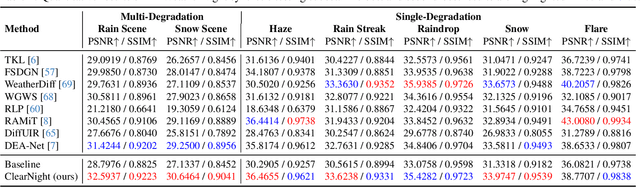
Abstract:Restoring nighttime images affected by multiple adverse weather conditions is a practical yet under-explored research problem, as multiple weather conditions often coexist in the real world alongside various lighting effects at night. This paper first explores the challenging multi-weather nighttime image restoration task, where various types of weather degradations are intertwined with flare effects. To support the research, we contribute the AllWeatherNight dataset, featuring large-scale high-quality nighttime images with diverse compositional degradations, synthesized using our introduced illumination-aware degradation generation. Moreover, we present ClearNight, a unified nighttime image restoration framework, which effectively removes complex degradations in one go. Specifically, ClearNight extracts Retinex-based dual priors and explicitly guides the network to focus on uneven illumination regions and intrinsic texture contents respectively, thereby enhancing restoration effectiveness in nighttime scenarios. In order to better represent the common and unique characters of multiple weather degradations, we introduce a weather-aware dynamic specific-commonality collaboration method, which identifies weather degradations and adaptively selects optimal candidate units associated with specific weather types. Our ClearNight achieves state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-world images. Comprehensive ablation experiments validate the necessity of AllWeatherNight dataset as well as the effectiveness of ClearNight. Project page: https://henlyta.github.io/ClearNight/mainpage.html
Mobius: Text to Seamless Looping Video Generation via Latent Shift
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:We present Mobius, a novel method to generate seamlessly looping videos from text descriptions directly without any user annotations, thereby creating new visual materials for the multi-media presentation. Our method repurposes the pre-trained video latent diffusion model for generating looping videos from text prompts without any training. During inference, we first construct a latent cycle by connecting the starting and ending noise of the videos. Given that the temporal consistency can be maintained by the context of the video diffusion model, we perform multi-frame latent denoising by gradually shifting the first-frame latent to the end in each step. As a result, the denoising context varies in each step while maintaining consistency throughout the inference process. Moreover, the latent cycle in our method can be of any length. This extends our latent-shifting approach to generate seamless looping videos beyond the scope of the video diffusion model's context. Unlike previous cinemagraphs, the proposed method does not require an image as appearance, which will restrict the motions of the generated results. Instead, our method can produce more dynamic motion and better visual quality. We conduct multiple experiments and comparisons to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, demonstrating its efficacy in different scenarios. All the code will be made available.
CustomTTT: Motion and Appearance Customized Video Generation via Test-Time Training
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Benefiting from large-scale pre-training of text-video pairs, current text-to-video (T2V) diffusion models can generate high-quality videos from the text description. Besides, given some reference images or videos, the parameter-efficient fine-tuning method, i.e. LoRA, can generate high-quality customized concepts, e.g., the specific subject or the motions from a reference video. However, combining the trained multiple concepts from different references into a single network shows obvious artifacts. To this end, we propose CustomTTT, where we can joint custom the appearance and the motion of the given video easily. In detail, we first analyze the prompt influence in the current video diffusion model and find the LoRAs are only needed for the specific layers for appearance and motion customization. Besides, since each LoRA is trained individually, we propose a novel test-time training technique to update parameters after combination utilizing the trained customized models. We conduct detailed experiments to verify the effectiveness of the proposed methods. Our method outperforms several state-of-the-art works in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
ZeroPur: Succinct Training-Free Adversarial Purification
Jun 05, 2024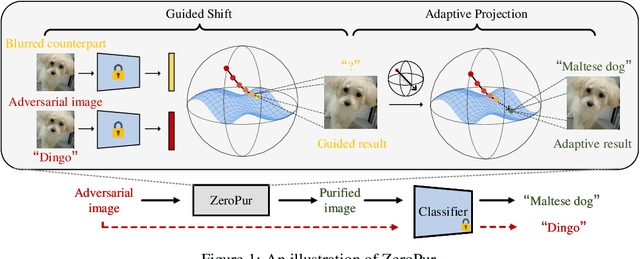

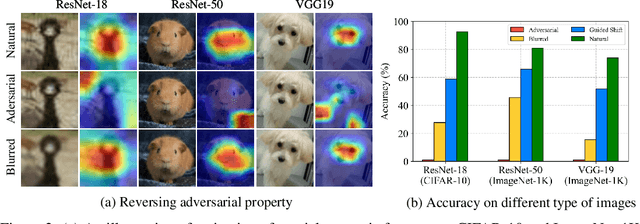

Abstract:Adversarial purification is a kind of defense technique that can defend various unseen adversarial attacks without modifying the victim classifier. Existing methods often depend on external generative models or cooperation between auxiliary functions and victim classifiers. However, retraining generative models, auxiliary functions, or victim classifiers relies on the domain of the fine-tuned dataset and is computation-consuming. In this work, we suppose that adversarial images are outliers of the natural image manifold and the purification process can be considered as returning them to this manifold. Following this assumption, we present a simple adversarial purification method without further training to purify adversarial images, called ZeroPur. ZeroPur contains two steps: given an adversarial example, Guided Shift obtains the shifted embedding of the adversarial example by the guidance of its blurred counterparts; after that, Adaptive Projection constructs a directional vector by this shifted embedding to provide momentum, projecting adversarial images onto the manifold adaptively. ZeroPur is independent of external models and requires no retraining of victim classifiers or auxiliary functions, relying solely on victim classifiers themselves to achieve purification. Extensive experiments on three datasets (CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet-1K) using various classifier architectures (ResNet, WideResNet) demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art robust performance. The code will be publicly available.
Depth-aware Test-Time Training for Zero-shot Video Object Segmentation
Mar 07, 2024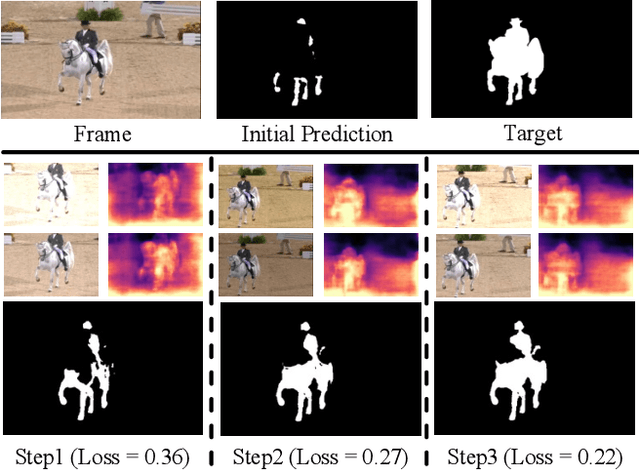
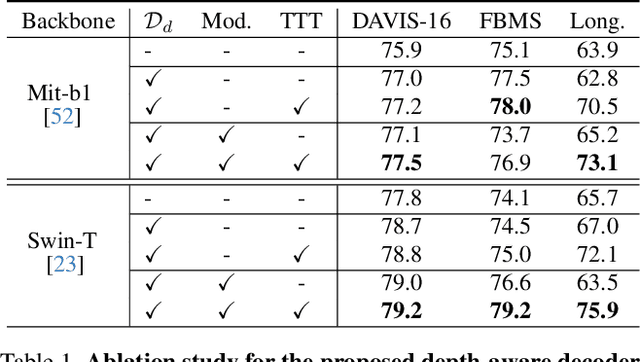
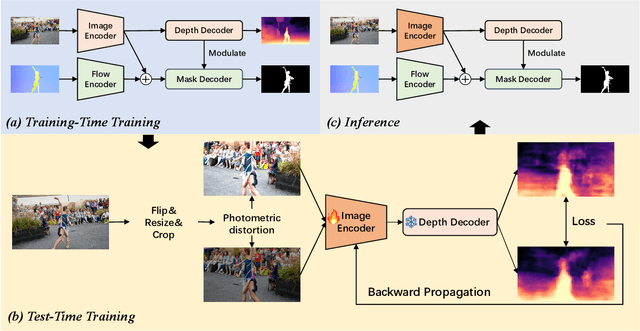
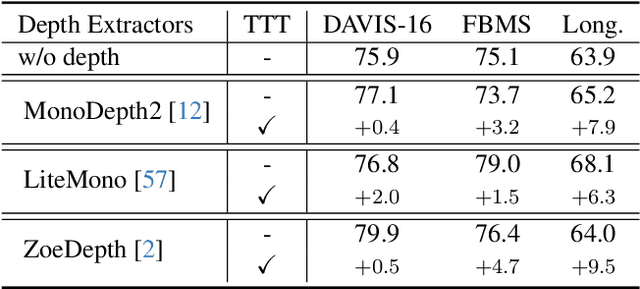
Abstract:Zero-shot Video Object Segmentation (ZSVOS) aims at segmenting the primary moving object without any human annotations. Mainstream solutions mainly focus on learning a single model on large-scale video datasets, which struggle to generalize to unseen videos. In this work, we introduce a test-time training (TTT) strategy to address the problem. Our key insight is to enforce the model to predict consistent depth during the TTT process. In detail, we first train a single network to perform both segmentation and depth prediction tasks. This can be effectively learned with our specifically designed depth modulation layer. Then, for the TTT process, the model is updated by predicting consistent depth maps for the same frame under different data augmentations. In addition, we explore different TTT weight updating strategies. Our empirical results suggest that the momentum-based weight initialization and looping-based training scheme lead to more stable improvements. Experiments show that the proposed method achieves clear improvements on ZSVOS. Our proposed video TTT strategy provides significant superiority over state-of-the-art TTT methods. Our code is available at: https://nifangbaage.github.io/DATTT.
Detecting Generated Images by Real Images Only
Nov 02, 2023



Abstract:As deep learning technology continues to evolve, the images yielded by generative models are becoming more and more realistic, triggering people to question the authenticity of images. Existing generated image detection methods detect visual artifacts in generated images or learn discriminative features from both real and generated images by massive training. This learning paradigm will result in efficiency and generalization issues, making detection methods always lag behind generation methods. This paper approaches the generated image detection problem from a new perspective: Start from real images. By finding the commonality of real images and mapping them to a dense subspace in feature space, the goal is that generated images, regardless of their generative model, are then projected outside the subspace. As a result, images from different generative models can be detected, solving some long-existing problems in the field. Experimental results show that although our method was trained only by real images and uses 99.9\% less training data than other deep learning-based methods, it can compete with state-of-the-art methods and shows excellent performance in detecting emerging generative models with high inference efficiency. Moreover, the proposed method shows robustness against various post-processing. These advantages allow the method to be used in real-world scenarios.
GreatSplicing: A Semantically Rich Splicing Dataset
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:In existing splicing forgery datasets, the insufficient semantic varieties of spliced regions cause a problem that trained detection models overfit semantic features rather than splicing traces. Meanwhile, because of the absence of a reasonable dataset, different detection methods proposed cannot reach a consensus on experimental settings. To address these urgent issues, GreatSplicing, a manually created splicing dataset with a considerable amount and high quality, is proposed in this paper. GreatSplicing comprises 5,000 spliced images and covers spliced regions with 335 distinct semantic categories, allowing neural networks to grasp splicing traces better. Extensive experiments demonstrate that models trained on GreatSplicing exhibit minimal misidentification rates and superior cross-dataset detection capabilities compared to existing datasets. Furthermore, GreatSplicing is available for all research purposes and can be downloaded from www.greatsplicing.net.
Color-related Local Binary Pattern: A Learned Local Descriptor for Color Image Recognition
Dec 11, 2020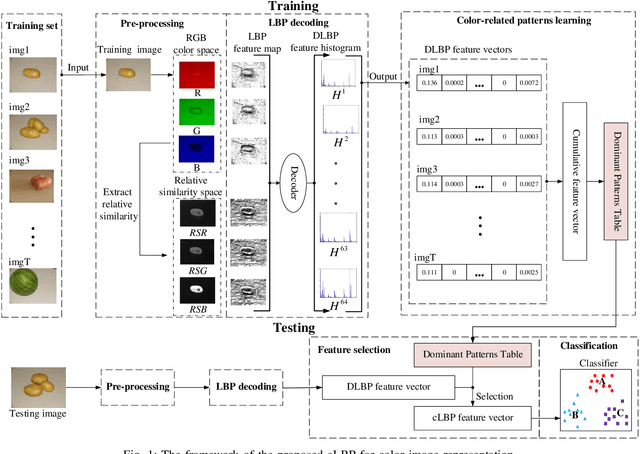
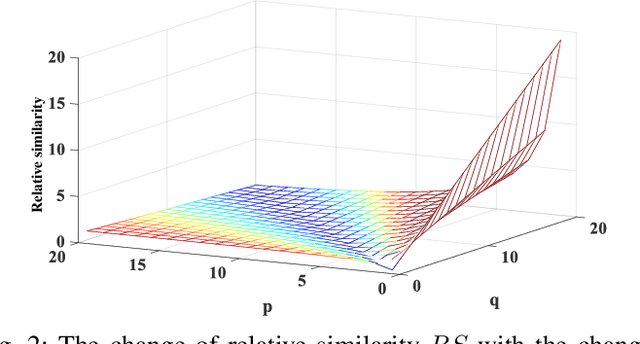
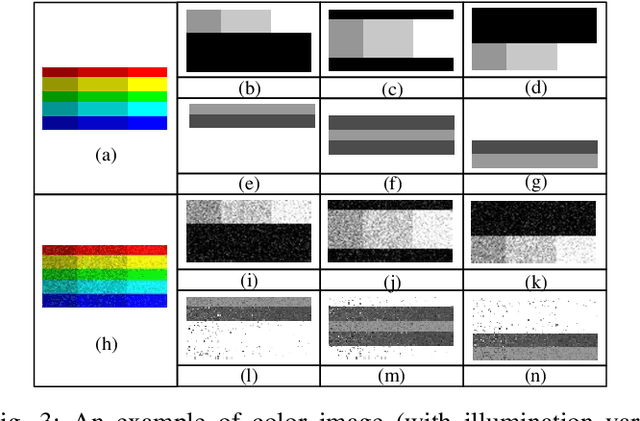
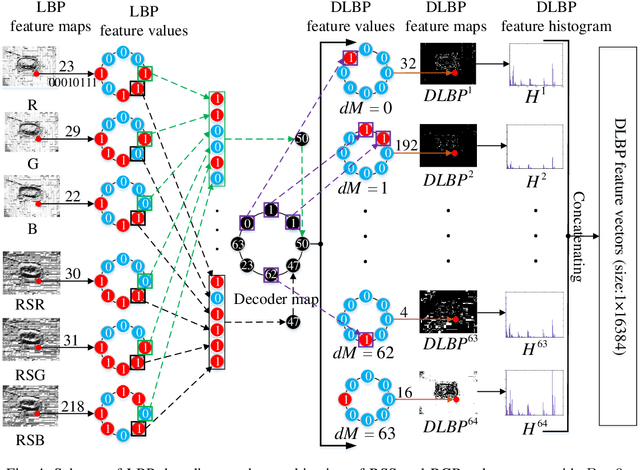
Abstract:Local binary pattern (LBP) as a kind of local feature has shown its simplicity, easy implementation and strong discriminating power in image recognition. Although some LBP variants are specifically investigated for color image recognition, the color information of images is not adequately considered and the curse of dimensionality in classification is easily caused in these methods. In this paper, a color-related local binary pattern (cLBP) which learns the dominant patterns from the decoded LBP is proposed for color images recognition. This paper first proposes a relative similarity space (RSS) that represents the color similarity between image channels for describing a color image. Then, the decoded LBP which can mine the correlation information between the LBP feature maps correspond to each color channel of RSS traditional RGB spaces, is employed for feature extraction. Finally, a feature learning strategy is employed to learn the dominant color-related patterns for reducing the dimension of feature vector and further improving the discriminatively of features. The theoretic analysis show that the proposed RSS can provide more discriminative information, and has higher noise robustness as well as higher illumination variation robustness than traditional RGB space. Experimental results on four groups, totally twelve public color image datasets show that the proposed method outperforms most of the LBP variants for color image recognition in terms of dimension of features, recognition accuracy under noise-free, noisy and illumination variation conditions.
D-Unet: A Dual-encoder U-Net for Image Splicing Forgery Detection and Localization
Dec 03, 2020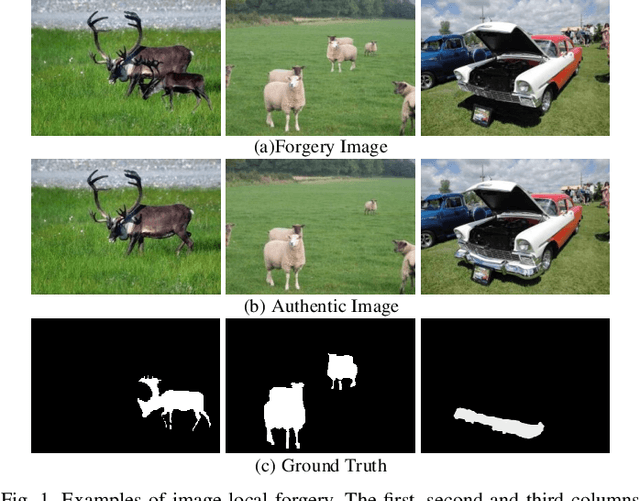

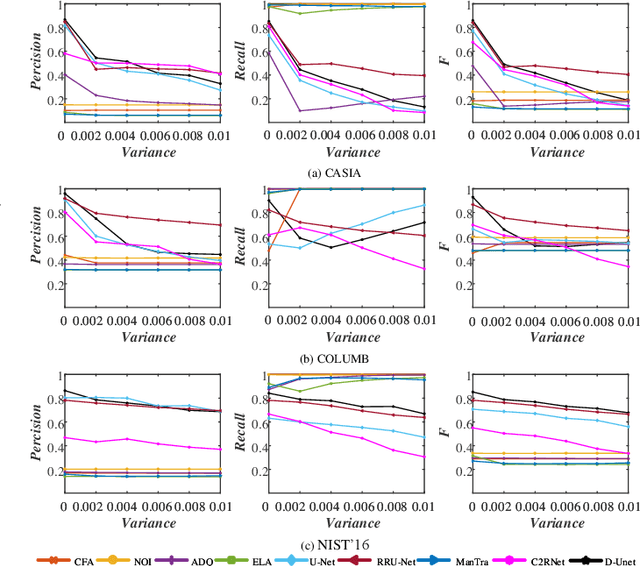
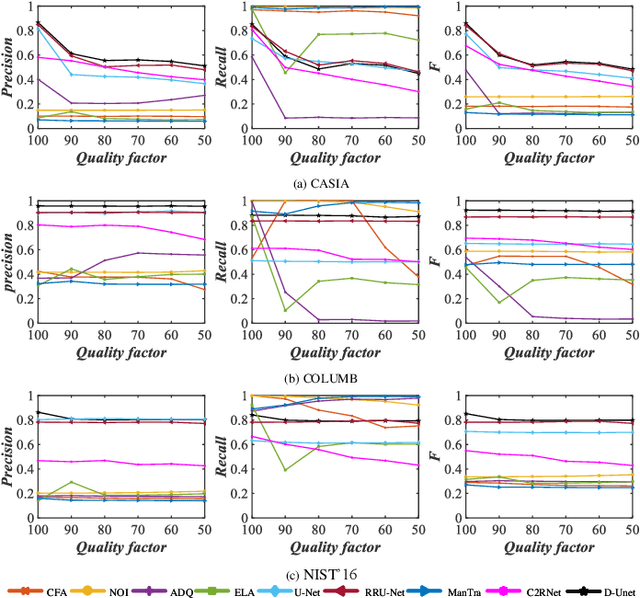
Abstract:Recently, many detection methods based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been proposed for image splicing forgery detection. Most of these detection methods focus on the local patches or local objects. In fact, image splicing forgery detection is a global binary classification task that distinguishes the tampered and non-tampered regions by image fingerprints. However, some specific image contents are hardly retained by CNN-based detection networks, but if included, would improve the detection accuracy of the networks. To resolve these issues, we propose a novel network called dual-encoder U-Net (D-Unet) for image splicing forgery detection, which employs an unfixed encoder and a fixed encoder. The unfixed encoder autonomously learns the image fingerprints that differentiate between the tampered and non-tampered regions, whereas the fixed encoder intentionally provides the direction information that assists the learning and detection of the network. This dual-encoder is followed by a spatial pyramid global-feature extraction module that expands the global insight of D-Unet for classifying the tampered and non-tampered regions more accurately. In an experimental comparison study of D-Unet and state-of-the-art methods, D-Unet outperformed the other methods in image-level and pixel-level detection, without requiring pre-training or training on a large number of forgery images. Moreover, it was stably robust to different attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge