Xinyi Zou
EasyAnimate: A High-Performance Long Video Generation Method based on Transformer Architecture
May 29, 2024Abstract:This paper presents EasyAnimate, an advanced method for video generation that leverages the power of transformer architecture for high-performance outcomes. We have expanded the DiT framework originally designed for 2D image synthesis to accommodate the complexities of 3D video generation by incorporating a motion module block. It is used to capture temporal dynamics, thereby ensuring the production of consistent frames and seamless motion transitions. The motion module can be adapted to various DiT baseline methods to generate video with different styles. It can also generate videos with different frame rates and resolutions during both training and inference phases, suitable for both images and videos. Moreover, we introduce slice VAE, a novel approach to condense the temporal axis, facilitating the generation of long duration videos. Currently, EasyAnimate exhibits the proficiency to generate videos with 144 frames. We provide a holistic ecosystem for video production based on DiT, encompassing aspects such as data pre-processing, VAE training, DiT models training (both the baseline model and LoRA model), and end-to-end video inference. Code is available at: https://github.com/aigc-apps/EasyAnimate. We are continuously working to enhance the performance of our method.
EasyPhoto: Your Smart AI Photo Generator
Oct 07, 2023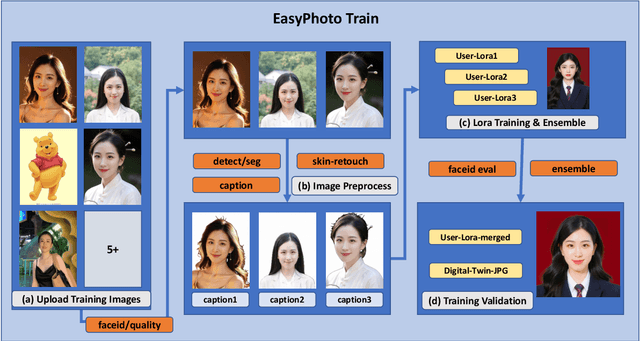
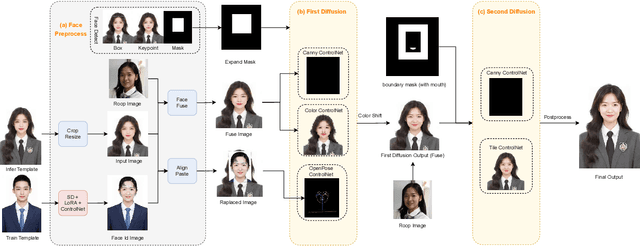
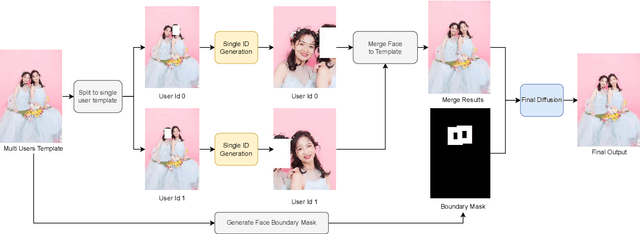

Abstract:Stable Diffusion web UI (SD-WebUI) is a comprehensive project that provides a browser interface based on Gradio library for Stable Diffusion models. In this paper, We propose a novel WebUI plugin called EasyPhoto, which enables the generation of AI portraits. By training a digital doppelganger of a specific user ID using 5 to 20 relevant images, the finetuned model (according to the trained LoRA model) allows for the generation of AI photos using arbitrary templates. Our current implementation supports the modification of multiple persons and different photo styles. Furthermore, we allow users to generate fantastic template image with the strong SDXL model, enhancing EasyPhoto's capabilities to deliver more diverse and satisfactory results. The source code for EasyPhoto is available at: https://github.com/aigc-apps/sd-webui-EasyPhoto. We also support a webui-free version by using diffusers: https://github.com/aigc-apps/EasyPhoto. We are continuously enhancing our efforts to expand the EasyPhoto pipeline, making it suitable for any identification (not limited to just the face), and we enthusiastically welcome any intriguing ideas or suggestions.
PAI-Diffusion: Constructing and Serving a Family of Open Chinese Diffusion Models for Text-to-image Synthesis on the Cloud
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:Text-to-image synthesis for the Chinese language poses unique challenges due to its large vocabulary size, and intricate character relationships. While existing diffusion models have shown promise in generating images from textual descriptions, they often neglect domain-specific contexts and lack robustness in handling the Chinese language. This paper introduces PAI-Diffusion, a comprehensive framework that addresses these limitations. PAI-Diffusion incorporates both general and domain-specific Chinese diffusion models, enabling the generation of contextually relevant images. It explores the potential of using LoRA and ControlNet for fine-grained image style transfer and image editing, empowering users with enhanced control over image generation. Moreover, PAI-Diffusion seamlessly integrates with Alibaba Cloud's Machine Learning Platform for AI, providing accessible and scalable solutions. All the Chinese diffusion model checkpoints, LoRAs, and ControlNets, including domain-specific ones, are publicly available. A user-friendly Chinese WebUI and the diffusers-api elastic inference toolkit, also open-sourced, further facilitate the easy deployment of PAI-Diffusion models in various environments, making it a valuable resource for Chinese text-to-image synthesis.
YOLOX-PAI: An Improved YOLOX Version by PAI
Aug 27, 2022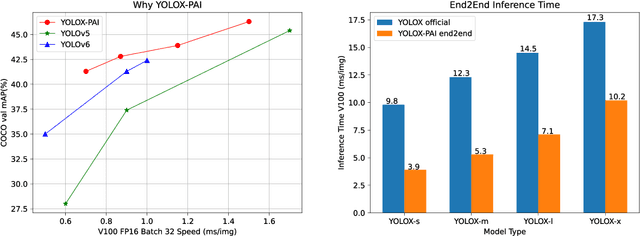
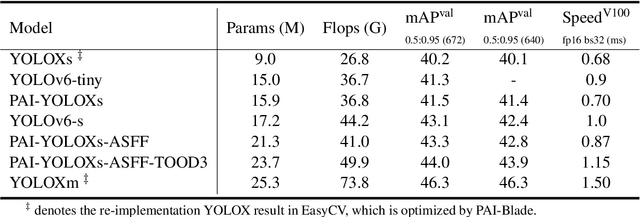
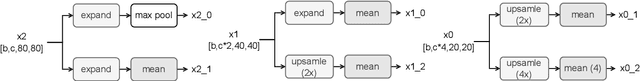
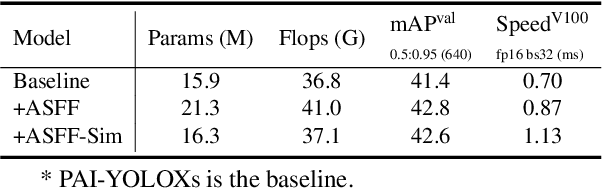
Abstract:We develop an all-in-one computer vision toolbox named EasyCV to facilitate the use of various SOTA computer vision methods. Recently, we add YOLOX-PAI, an improved version of YOLOX, into EasyCV. We conduct ablation studies to investigate the influence of some detection methods on YOLOX. We also provide an easy use for PAI-Blade which is used to accelerate the inference process based on BladeDISC and TensorRT. Finally, we receive 42.8 mAP on COCO dateset within 1.0 ms on a single NVIDIA V100 GPU, which is a bit faster than YOLOv6. A simple but efficient predictor api is also designed in EasyCV to conduct end2end object detection. Codes and models are now available at: https://github.com/alibaba/EasyCV.
Learn-to-Decompose: Cascaded Decomposition Network for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Facial Expression Recognition
Jul 16, 2022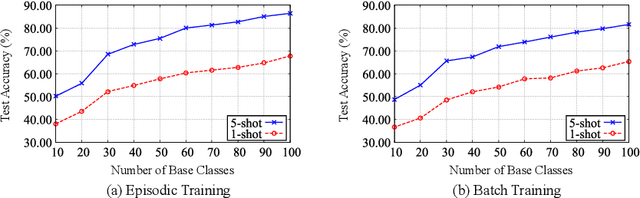
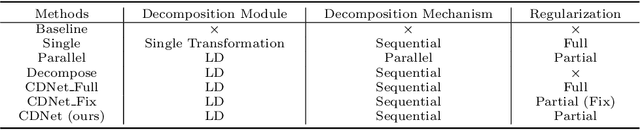
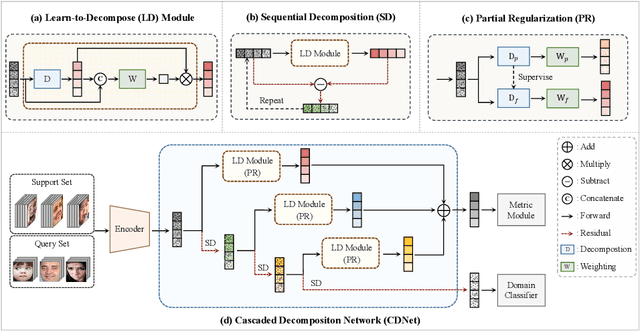
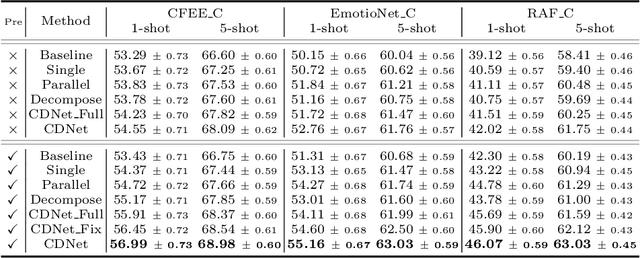
Abstract:Most existing compound facial expression recognition (FER) methods rely on large-scale labeled compound expression data for training. However, collecting such data is labor-intensive and time-consuming. In this paper, we address the compound FER task in the cross-domain few-shot learning (FSL) setting, which requires only a few samples of compound expressions in the target domain. Specifically, we propose a novel cascaded decomposition network (CDNet), which cascades several learn-to-decompose modules with shared parameters based on a sequential decomposition mechanism, to obtain a transferable feature space. To alleviate the overfitting problem caused by limited base classes in our task, a partial regularization strategy is designed to effectively exploit the best of both episodic training and batch training. By training across similar tasks on multiple basic expression datasets, CDNet learns the ability of learn-to-decompose that can be easily adapted to identify unseen compound expressions. Extensive experiments on both in-the-lab and in-the-wild compound expression datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed CDNet against several state-of-the-art FSL methods. Code is available at: https://github.com/zouxinyi0625/CDNet.
When Facial Expression Recognition Meets Few-Shot Learning: A Joint and Alternate Learning Framework
Jan 18, 2022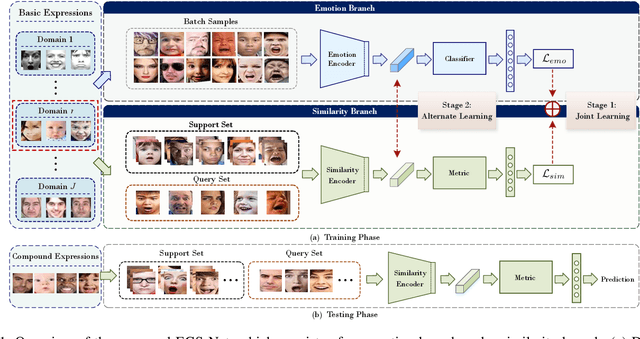

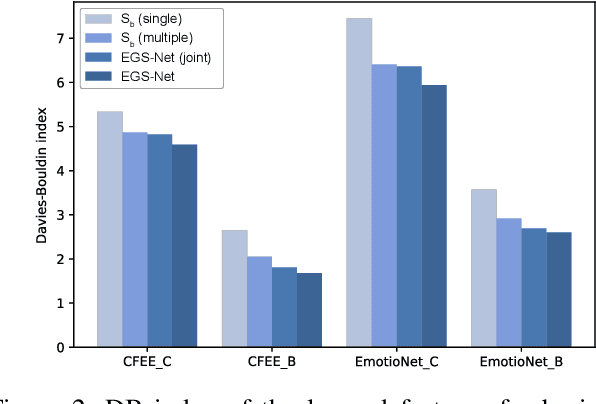

Abstract:Human emotions involve basic and compound facial expressions. However, current research on facial expression recognition (FER) mainly focuses on basic expressions, and thus fails to address the diversity of human emotions in practical scenarios. Meanwhile, existing work on compound FER relies heavily on abundant labeled compound expression training data, which are often laboriously collected under the professional instruction of psychology. In this paper, we study compound FER in the cross-domain few-shot learning setting, where only a few images of novel classes from the target domain are required as a reference. In particular, we aim to identify unseen compound expressions with the model trained on easily accessible basic expression datasets. To alleviate the problem of limited base classes in our FER task, we propose a novel Emotion Guided Similarity Network (EGS-Net), consisting of an emotion branch and a similarity branch, based on a two-stage learning framework. Specifically, in the first stage, the similarity branch is jointly trained with the emotion branch in a multi-task fashion. With the regularization of the emotion branch, we prevent the similarity branch from overfitting to sampled base classes that are highly overlapped across different episodes. In the second stage, the emotion branch and the similarity branch play a "two-student game" to alternately learn from each other, thereby further improving the inference ability of the similarity branch on unseen compound expressions. Experimental results on both in-the-lab and in-the-wild compound expression datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method against several state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge