Xiaohu Jiang
Supervised Fine-tuning in turn Improves Visual Foundation Models
Jan 18, 2024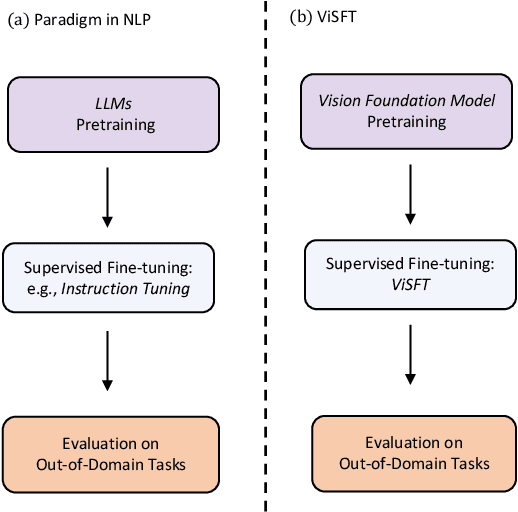
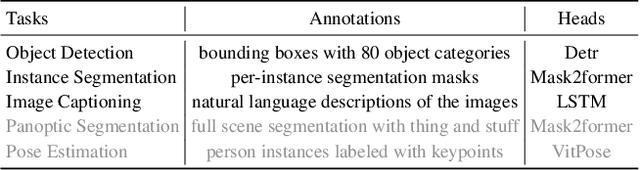

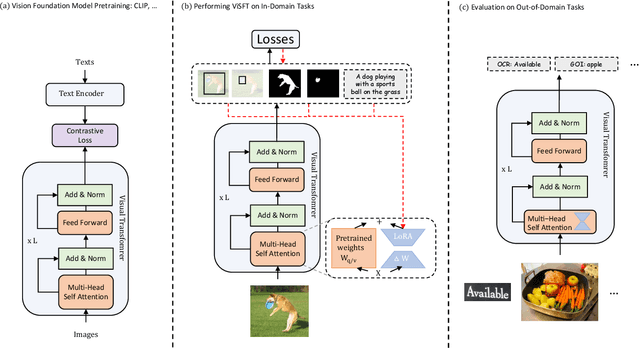
Abstract:Image-text training like CLIP has dominated the pretraining of vision foundation models in recent years. Subsequent efforts have been made to introduce region-level visual learning into CLIP's pretraining but face scalability challenges due to the lack of large-scale region-level datasets. Drawing inspiration from supervised fine-tuning (SFT) in natural language processing such as instruction tuning, we explore the potential of fine-grained SFT in enhancing the generation of vision foundation models after their pretraining. Thus a two-stage method ViSFT (Vision SFT) is proposed to unleash the fine-grained knowledge of vision foundation models. In ViSFT, the vision foundation model is enhanced by performing visual joint learning on some in-domain tasks and then tested on out-of-domain benchmarks. With updating using ViSFT on 8 V100 GPUs in less than 2 days, a vision transformer with over 4.4B parameters shows improvements across various out-of-domain benchmarks including vision and vision-linguistic scenarios.
Uni-Perceiver v2: A Generalist Model for Large-Scale Vision and Vision-Language Tasks
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Despite the remarkable success of foundation models, their task-specific fine-tuning paradigm makes them inconsistent with the goal of general perception modeling. The key to eliminating this inconsistency is to use generalist models for general task modeling. However, existing attempts at generalist models are inadequate in both versatility and performance. In this paper, we propose Uni-Perceiver v2, which is the first generalist model capable of handling major large-scale vision and vision-language tasks with competitive performance. Specifically, images are encoded as general region proposals, while texts are encoded via a Transformer-based language model. The encoded representations are transformed by a task-agnostic decoder. Different tasks are formulated as a unified maximum likelihood estimation problem. We further propose an improved optimizer to ensure stable multi-task learning with an unmixed sampling strategy, which is helpful for tasks requiring large batch-size training. After being jointly trained on various tasks, Uni-Perceiver v2 is capable of directly handling downstream tasks without any task-specific adaptation. Results show that Uni-Perceiver v2 outperforms all existing generalist models in both versatility and performance. Meanwhile, compared with the commonly-recognized strong baselines that require tasks-specific fine-tuning, Uni-Perceiver v2 achieves competitive performance on a broad range of vision and vision-language tasks.
Focal and Global Knowledge Distillation for Detectors
Nov 23, 2021



Abstract:Knowledge distillation has been applied to image classification successfully. However, object detection is much more sophisticated and most knowledge distillation methods have failed on it. In this paper, we point out that in object detection, the features of the teacher and student vary greatly in different areas, especially in the foreground and background. If we distill them equally, the uneven differences between feature maps will negatively affect the distillation. Thus, we propose Focal and Global Distillation (FGD). Focal distillation separates the foreground and background, forcing the student to focus on the teacher's critical pixels and channels. Global distillation rebuilds the relation between different pixels and transfers it from teachers to students, compensating for missing global information in focal distillation. As our method only needs to calculate the loss on the feature map, FGD can be applied to various detectors. We experiment on various detectors with different backbones and the results show that the student detector achieves excellent mAP improvement. For example, ResNet-50 based RetinaNet, Faster RCNN, RepPoints and Mask RCNN with our distillation method achieve 40.7%, 42.0%, 42.0% and 42.1% mAP on COCO2017, which are 3.3, 3.6, 3.4 and 2.9 higher than the baseline, respectively. Our codes are available at https://github.com/yzd-v/FGD.
Guiding Query Position and Performing Similar Attention for Transformer-Based Detection Heads
Aug 22, 2021



Abstract:After DETR was proposed, this novel transformer-based detection paradigm which performs several cross-attentions between object queries and feature maps for predictions has subsequently derived a series of transformer-based detection heads. These models iterate object queries after each cross-attention. However, they don't renew the query position which indicates object queries' position information. Thus model needs extra learning to figure out the newest regions that query position should express and need more attention. To fix this issue, we propose the Guided Query Position (GQPos) method to embed the latest location information of object queries to query position iteratively. Another problem of such transformer-based detection heads is the high complexity to perform attention on multi-scale feature maps, which hinders them from improving detection performance at all scales. Therefore we propose a novel fusion scheme named Similar Attention (SiA): besides the feature maps is fused, SiA also fuse the attention weights maps to accelerate the learning of high-resolution attention weight map by well-learned low-resolution attention weight map. Our experiments show that the proposed GQPos improves the performance of a series of models, including DETR, SMCA, YoloS, and HoiTransformer and SiA consistently improve the performance of multi-scale transformer-based detection heads like DETR and HoiTransformer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge