Weikang Qiu
Efficient Long-Horizon Vision-Language-Action Models via Static-Dynamic Disentanglement
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for generalist robotic control. Built upon vision-language model (VLM) architectures, VLAs predict actions conditioned on visual observations and language instructions, achieving strong performance and generalization across tasks. However, VLAs face two major challenges: limited long-horizon context and inefficient inference due to the quadratic attention complexity and large parameter counts. Our work is motivated by the observation that much of the visual information in a trajectory remains static across timesteps (e.g., the background). Leveraging this property, we propose SD-VLA, a framework that disentangles visual inputs into multi-level static and dynamic tokens, which enables (1) retaining a single copy of static tokens across frames to significantly reduce context length, and (2) reusing the key-value (KV) cache of static tokens through a lightweight recache gate that updates only when necessary. This design enables efficient multi-frame integration and efficient inference. In addition, we introduce a new benchmark that more effectively evaluates the long-horizon temporal dependency modeling ability of VLAs. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms baselines on this benchmark by 39.8% absolute improvement in success rate, and achieves a 3.9% gain on the SimplerEnv benchmark. Moreover, SD-VLA delivers a 2.26x inference speedup over the base VLA model on the same benchmark, enabling faster and more practical real-world deployment.
Mixture-of-Personas Language Models for Population Simulation
Apr 07, 2025


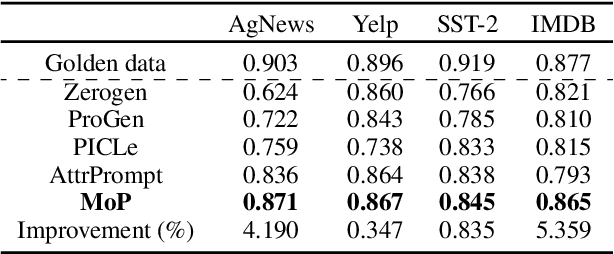
Abstract:Advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) paved the way for their emerging applications in various domains, such as human behavior simulations, where LLMs could augment human-generated data in social science research and machine learning model training. However, pretrained LLMs often fail to capture the behavioral diversity of target populations due to the inherent variability across individuals and groups. To address this, we propose \textit{Mixture of Personas} (MoP), a \textit{probabilistic} prompting method that aligns the LLM responses with the target population. MoP is a contextual mixture model, where each component is an LM agent characterized by a persona and an exemplar representing subpopulation behaviors. The persona and exemplar are randomly chosen according to the learned mixing weights to elicit diverse LLM responses during simulation. MoP is flexible, requires no model finetuning, and is transferable across base models. Experiments for synthetic data generation show that MoP outperforms competing methods in alignment and diversity metrics.
An Item is Worth a Prompt: Versatile Image Editing with Disentangled Control
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Building on the success of text-to-image diffusion models (DPMs), image editing is an important application to enable human interaction with AI-generated content. Among various editing methods, editing within the prompt space gains more attention due to its capacity and simplicity of controlling semantics. However, since diffusion models are commonly pretrained on descriptive text captions, direct editing of words in text prompts usually leads to completely different generated images, violating the requirements for image editing. On the other hand, existing editing methods usually consider introducing spatial masks to preserve the identity of unedited regions, which are usually ignored by DPMs and therefore lead to inharmonic editing results. Targeting these two challenges, in this work, we propose to disentangle the comprehensive image-prompt interaction into several item-prompt interactions, with each item linked to a special learned prompt. The resulting framework, named D-Edit, is based on pretrained diffusion models with cross-attention layers disentangled and adopts a two-step optimization to build item-prompt associations. Versatile image editing can then be applied to specific items by manipulating the corresponding prompts. We demonstrate state-of-the-art results in four types of editing operations including image-based, text-based, mask-based editing, and item removal, covering most types of editing applications, all within a single unified framework. Notably, D-Edit is the first framework that can (1) achieve item editing through mask editing and (2) combine image and text-based editing. We demonstrate the quality and versatility of the editing results for a diverse collection of images through both qualitative and quantitative evaluations.
Learning High-Order Relationships of Brain Regions
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:Discovering reliable and informative interactions among brain regions from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) signals is essential in neuroscientific predictions of cognition. Most of the current methods fail to accurately characterize those interactions because they only focus on pairwise connections and overlook the high-order relationships of brain regions. We delve into this problem and argue that these high-order relationships should be maximally informative and minimally redundant (MIMR). However, identifying such high-order relationships is challenging and highly under-explored. Methods that can be tailored to our context are also non-existent. In response to this gap, we propose a novel method named HyBRiD that aims to extract MIMR high-order relationships from fMRI data. HyBRiD employs a Constructor to identify hyperedge structures, and a Weighter to compute a weight for each hyperedge. HyBRiD achieves the MIMR objective through an innovative information bottleneck framework named multi-head drop-bottleneck with theoretical guarantees. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model. Our model outperforms the state-of-the-art predictive model by an average of 12.1%, regarding the quality of hyperedges measured by CPM, a standard protocol for studying brain connections.
Revisiting the Knowledge Injection Frameworks
Nov 02, 2023Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs), such as GPTs, have attained great impact worldwide. However, how to adapt these LLMs to better suit the vertical domain-specific tasks by utilizing external knowledge remains not completely solved. Indeed, there have emerged a few works on this line where most of them rely on an alignment heuristic that is built to inject the corresponding knowledge tuple into the associated text sample. However, despite the promise, we identify a pivotal problem in this work ubiquitously. Simply put, we find that injecting unaligned (i.e., random) knowledge tuple into the LLMs achieves comparable (and sometimes better) results than the aligned knowledge being injected. We therefore take a thorough investigation of this frustrating finding on a variety of related prior work and further provide a chain of potential interpretations for the phenomenon. Based on all that, we offer a simple remediated technique. Briefly, the core of this technique is rooted in an ideological emphasis on the pruning and purification of the external knowledge base to be injected into LLMs. At last, we show that by integrating this technique into most (if not all) knowledge injection frameworks and recent LLMs, it manages to overcome the aforementioned sanity problem and further pushes the boundary of the performance of the domain-adaptive LLMs.
Learning Graph Search Heuristics
Dec 07, 2022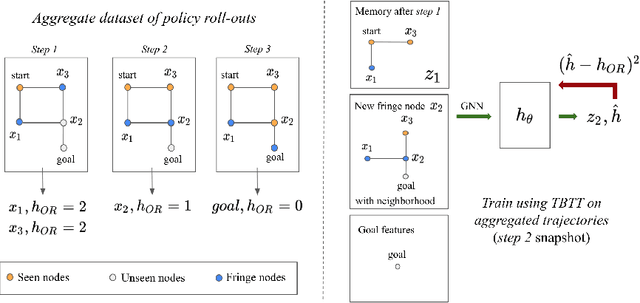
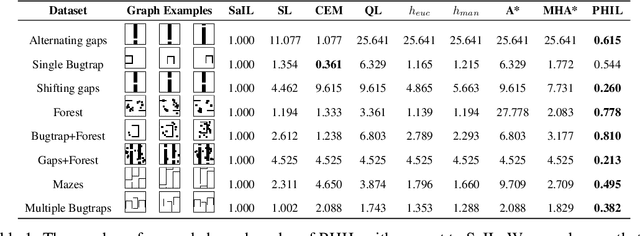
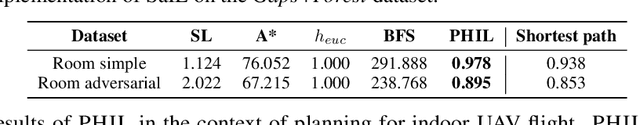
Abstract:Searching for a path between two nodes in a graph is one of the most well-studied and fundamental problems in computer science. In numerous domains such as robotics, AI, or biology, practitioners develop search heuristics to accelerate their pathfinding algorithms. However, it is a laborious and complex process to hand-design heuristics based on the problem and the structure of a given use case. Here we present PHIL (Path Heuristic with Imitation Learning), a novel neural architecture and a training algorithm for discovering graph search and navigation heuristics from data by leveraging recent advances in imitation learning and graph representation learning. At training time, we aggregate datasets of search trajectories and ground-truth shortest path distances, which we use to train a specialized graph neural network-based heuristic function using backpropagation through steps of the pathfinding process. Our heuristic function learns graph embeddings useful for inferring node distances, runs in constant time independent of graph sizes, and can be easily incorporated in an algorithm such as A* at test time. Experiments show that PHIL reduces the number of explored nodes compared to state-of-the-art methods on benchmark datasets by 58.5\% on average, can be directly applied in diverse graphs ranging from biological networks to road networks, and allows for fast planning in time-critical robotics domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge