Vivek Singh Bawa
Why is the winner the best?
Mar 30, 2023
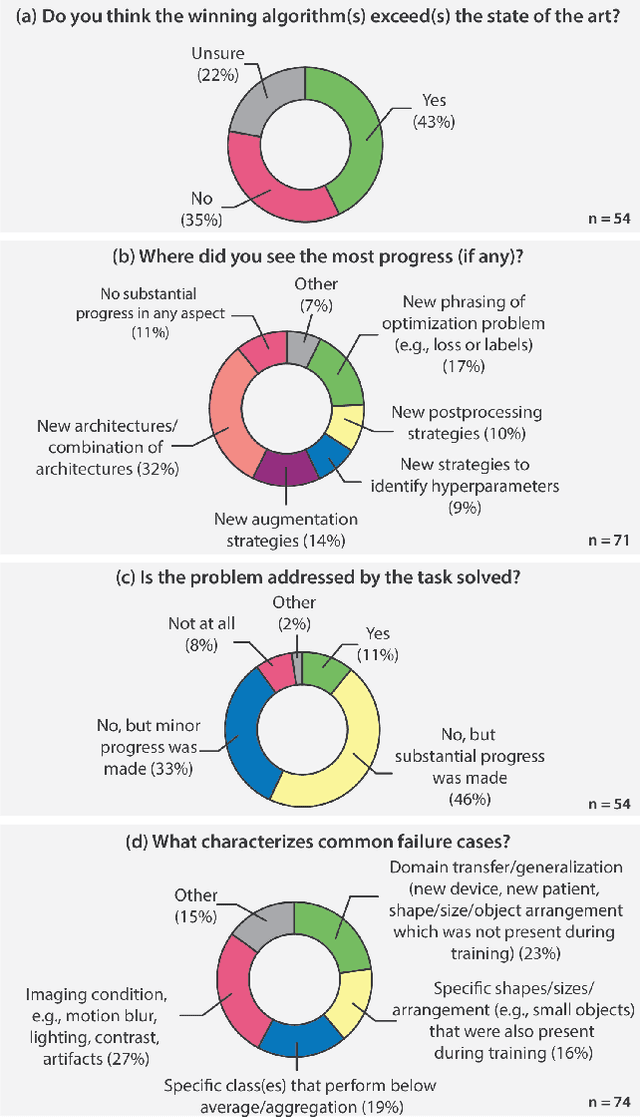
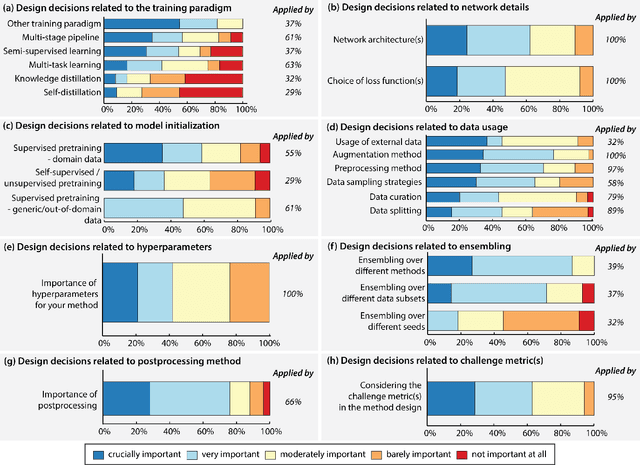
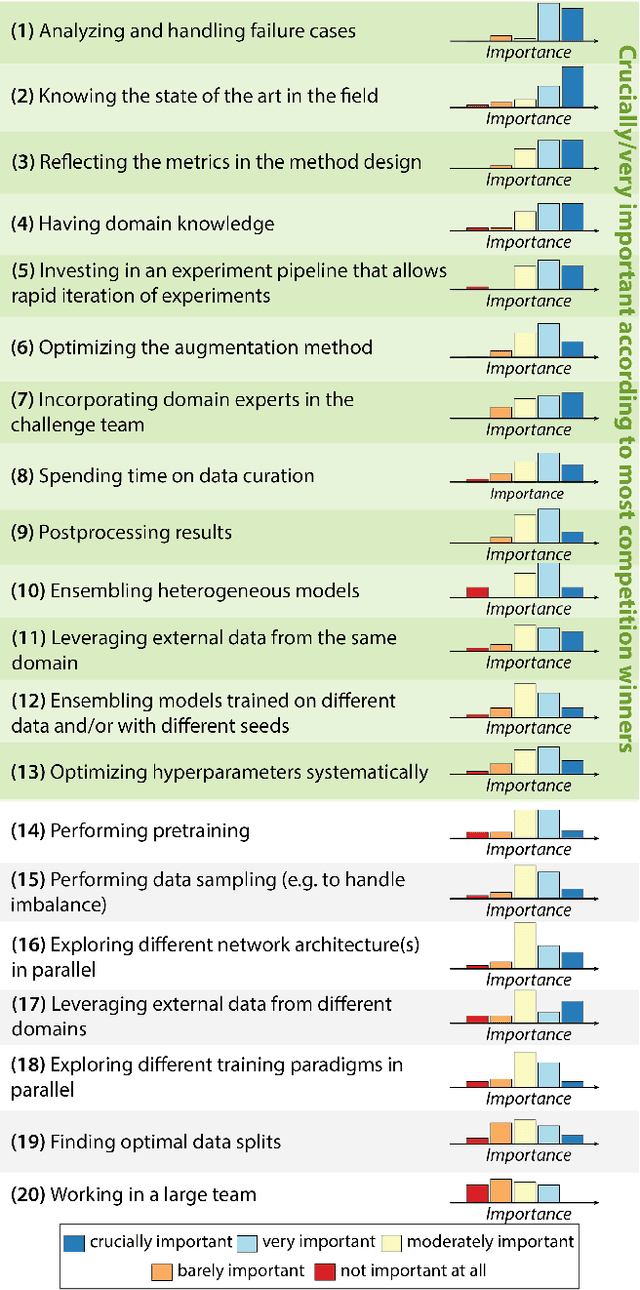
Abstract:International benchmarking competitions have become fundamental for the comparative performance assessment of image analysis methods. However, little attention has been given to investigating what can be learnt from these competitions. Do they really generate scientific progress? What are common and successful participation strategies? What makes a solution superior to a competing method? To address this gap in the literature, we performed a multi-center study with all 80 competitions that were conducted in the scope of IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021. Statistical analyses performed based on comprehensive descriptions of the submitted algorithms linked to their rank as well as the underlying participation strategies revealed common characteristics of winning solutions. These typically include the use of multi-task learning (63%) and/or multi-stage pipelines (61%), and a focus on augmentation (100%), image preprocessing (97%), data curation (79%), and postprocessing (66%). The "typical" lead of a winning team is a computer scientist with a doctoral degree, five years of experience in biomedical image analysis, and four years of experience in deep learning. Two core general development strategies stood out for highly-ranked teams: the reflection of the metrics in the method design and the focus on analyzing and handling failure cases. According to the organizers, 43% of the winning algorithms exceeded the state of the art but only 11% completely solved the respective domain problem. The insights of our study could help researchers (1) improve algorithm development strategies when approaching new problems, and (2) focus on open research questions revealed by this work.
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Audio-visual video face hallucination with frequency supervision and cross modality support by speech based lip reading loss
Nov 20, 2022



Abstract:Recently, there has been numerous breakthroughs in face hallucination tasks. However, the task remains rather challenging in videos in comparison to the images due to inherent consistency issues. The presence of extra temporal dimension in video face hallucination makes it non-trivial to learn the facial motion through out the sequence. In order to learn these fine spatio-temporal motion details, we propose a novel cross-modal audio-visual Video Face Hallucination Generative Adversarial Network (VFH-GAN). The architecture exploits the semantic correlation of between the movement of the facial structure and the associated speech signal. Another major issue in present video based approaches is the presence of blurriness around the key facial regions such as mouth and lips - where spatial displacement is much higher in comparison to other areas. The proposed approach explicitly defines a lip reading loss to learn the fine grain motion in these facial areas. During training, GANs have potential to fit frequencies from low to high, which leads to miss the hard to synthesize frequencies. Therefore, to add salient frequency features to the network we add a frequency based loss function. The visual and the quantitative comparison with state-of-the-art shows a significant improvement in performance and efficacy.
The SARAS Endoscopic Surgeon Action Detection (ESAD) dataset: Challenges and methods
Apr 07, 2021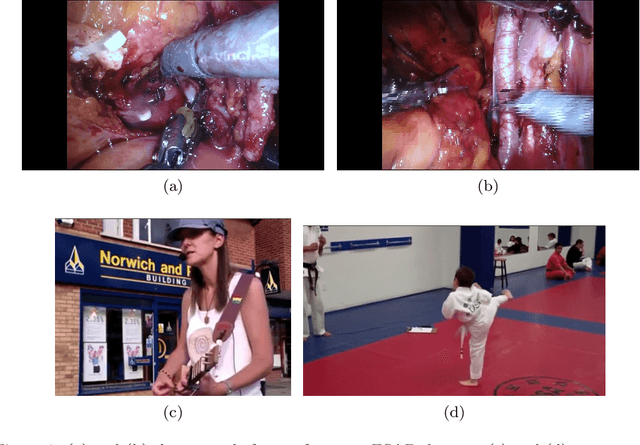
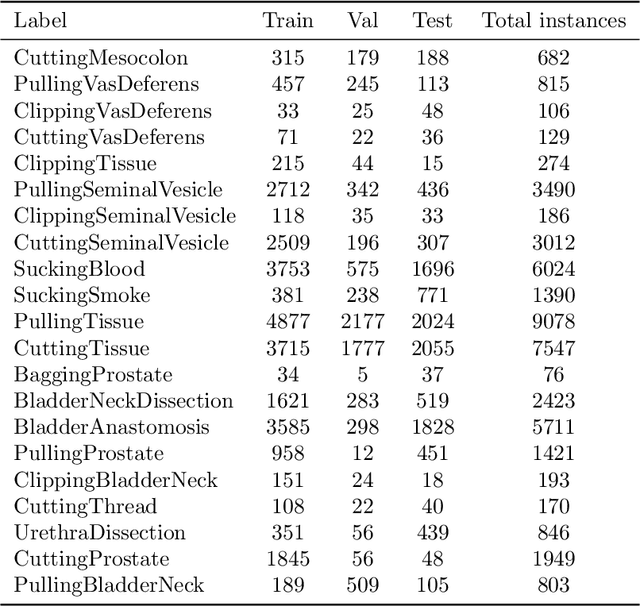
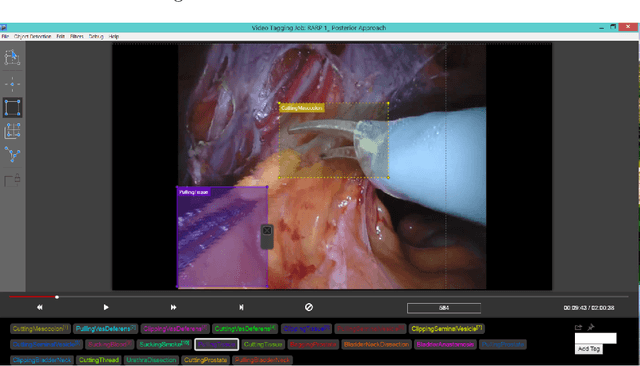

Abstract:For an autonomous robotic system, monitoring surgeon actions and assisting the main surgeon during a procedure can be very challenging. The challenges come from the peculiar structure of the surgical scene, the greater similarity in appearance of actions performed via tools in a cavity compared to, say, human actions in unconstrained environments, as well as from the motion of the endoscopic camera. This paper presents ESAD, the first large-scale dataset designed to tackle the problem of surgeon action detection in endoscopic minimally invasive surgery. ESAD aims at contributing to increase the effectiveness and reliability of surgical assistant robots by realistically testing their awareness of the actions performed by a surgeon. The dataset provides bounding box annotation for 21 action classes on real endoscopic video frames captured during prostatectomy, and was used as the basis of a recent MIDL 2020 challenge. We also present an analysis of the dataset conducted using the baseline model which was released as part of the challenge, and a description of the top performing models submitted to the challenge together with the results they obtained. This study provides significant insight into what approaches can be effective and can be extended further. We believe that ESAD will serve in the future as a useful benchmark for all researchers active in surgeon action detection and assistive robotics at large.
ESAD: Endoscopic Surgeon Action Detection Dataset
Jun 12, 2020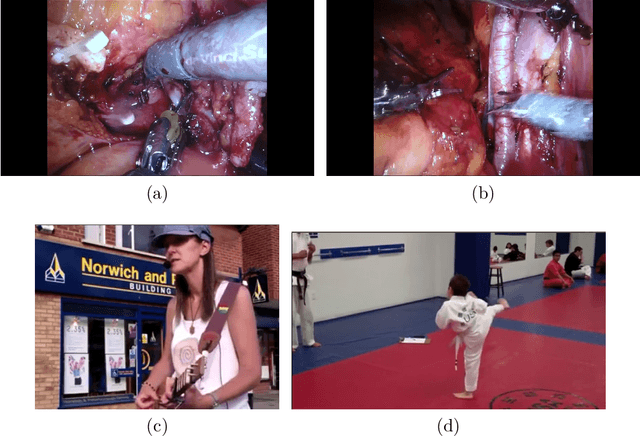



Abstract:In this work, we take aim towards increasing the effectiveness of surgical assistant robots. We intended to make assistant robots safer by making them aware about the actions of surgeon, so it can take appropriate assisting actions. In other words, we aim to solve the problem of surgeon action detection in endoscopic videos. To this, we introduce a challenging dataset for surgeon action detection in real-world endoscopic videos. Action classes are picked based on the feedback of surgeons and annotated by medical professional. Given a video frame, we draw bounding box around surgical tool which is performing action and label it with action label. Finally, we presenta frame-level action detection baseline model based on recent advances in ob-ject detection. Results on our new dataset show that our presented dataset provides enough interesting challenges for future method and it can serveas strong benchmark corresponding research in surgeon action detection in endoscopic videos.
No reference image quality assessment metric based on regional mutual information among images
Jan 17, 2019
Abstract:With the inclusion of camera in daily life, an automatic no reference image quality evaluation index is required for automatic classification of images. The present manuscripts proposes a new No Reference Regional Mutual Information based technique for evaluating the quality of an image. We use regional mutual information on subsets of the complete image. Proposed technique is tested on four benchmark natural image databases, and one benchmark synthetic database. A comparative analysis with classical and state-of-art methods indicate superiority of the present technique for high quality images and comparable for other images of the respective databases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge