Victor Letzelter
LTCI, S2A, IDS, IP Paris
Test-Time Conditioning with Representation-Aligned Visual Features
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While representation alignment with self-supervised models has been shown to improve diffusion model training, its potential for enhancing inference-time conditioning remains largely unexplored. We introduce Representation-Aligned Guidance (REPA-G), a framework that leverages these aligned representations, with rich semantic properties, to enable test-time conditioning from features in generation. By optimizing a similarity objective (the potential) at inference, we steer the denoising process toward a conditioned representation extracted from a pre-trained feature extractor. Our method provides versatile control at multiple scales, ranging from fine-grained texture matching via single patches to broad semantic guidance using global image feature tokens. We further extend this to multi-concept composition, allowing for the faithful combination of distinct concepts. REPA-G operates entirely at inference time, offering a flexible and precise alternative to often ambiguous text prompts or coarse class labels. We theoretically justify how this guidance enables sampling from the potential-induced tilted distribution. Quantitative results on ImageNet and COCO demonstrate that our approach achieves high-quality, diverse generations. Code is available at https://github.com/valeoai/REPA-G.
Winner-takes-all for Multivariate Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting
Jun 05, 2025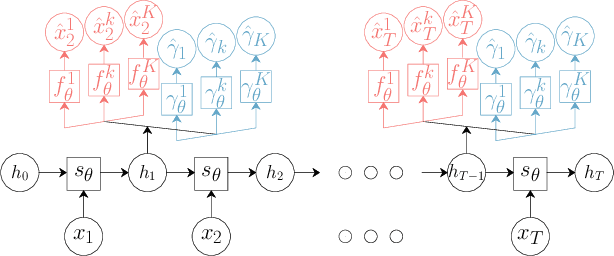
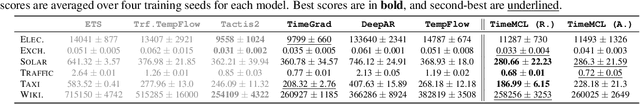
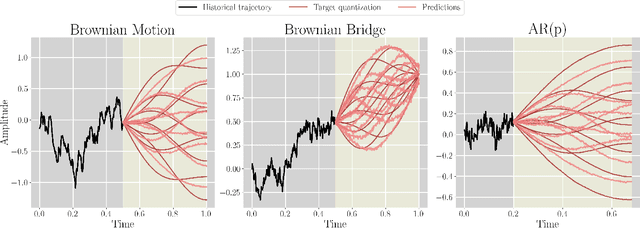

Abstract:We introduce TimeMCL, a method leveraging the Multiple Choice Learning (MCL) paradigm to forecast multiple plausible time series futures. Our approach employs a neural network with multiple heads and utilizes the Winner-Takes-All (WTA) loss to promote diversity among predictions. MCL has recently gained attention due to its simplicity and ability to address ill-posed and ambiguous tasks. We propose an adaptation of this framework for time-series forecasting, presenting it as an efficient method to predict diverse futures, which we relate to its implicit quantization objective. We provide insights into our approach using synthetic data and evaluate it on real-world time series, demonstrating its promising performance at a light computational cost.
Annealed Winner-Takes-All for Motion Forecasting
Sep 18, 2024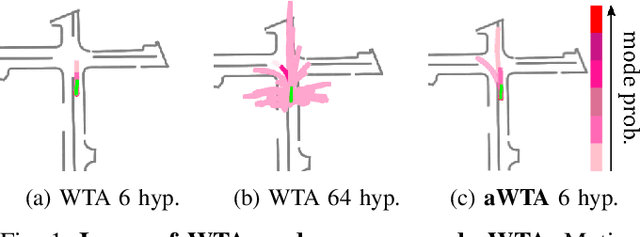
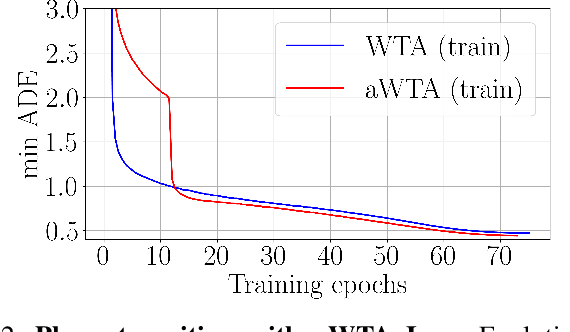
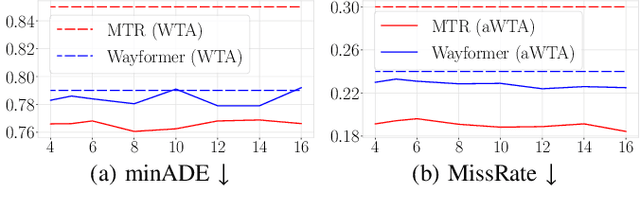
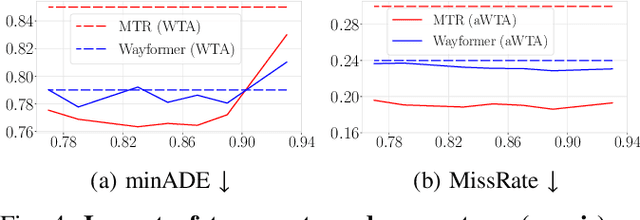
Abstract:In autonomous driving, motion prediction aims at forecasting the future trajectories of nearby agents, helping the ego vehicle to anticipate behaviors and drive safely. A key challenge is generating a diverse set of future predictions, commonly addressed using data-driven models with Multiple Choice Learning (MCL) architectures and Winner-Takes-All (WTA) training objectives. However, these methods face initialization sensitivity and training instabilities. Additionally, to compensate for limited performance, some approaches rely on training with a large set of hypotheses, requiring a post-selection step during inference to significantly reduce the number of predictions. To tackle these issues, we take inspiration from annealed MCL, a recently introduced technique that improves the convergence properties of MCL methods through an annealed Winner-Takes-All loss (aWTA). In this paper, we demonstrate how the aWTA loss can be integrated with state-of-the-art motion forecasting models to enhance their performance using only a minimal set of hypotheses, eliminating the need for the cumbersome post-selection step. Our approach can be easily incorporated into any trajectory prediction model normally trained using WTA and yields significant improvements. To facilitate the application of our approach to future motion forecasting models, the code will be made publicly available upon acceptance: https://github.com/valeoai/MF_aWTA.
Annealed Multiple Choice Learning: Overcoming limitations of Winner-takes-all with annealing
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Annealed Multiple Choice Learning (aMCL) which combines simulated annealing with MCL. MCL is a learning framework handling ambiguous tasks by predicting a small set of plausible hypotheses. These hypotheses are trained using the Winner-takes-all (WTA) scheme, which promotes the diversity of the predictions. However, this scheme may converge toward an arbitrarily suboptimal local minimum, due to the greedy nature of WTA. We overcome this limitation using annealing, which enhances the exploration of the hypothesis space during training. We leverage insights from statistical physics and information theory to provide a detailed description of the model training trajectory. Additionally, we validate our algorithm by extensive experiments on synthetic datasets, on the standard UCI benchmark, and on speech separation.
Winner-takes-all learners are geometry-aware conditional density estimators
Jun 07, 2024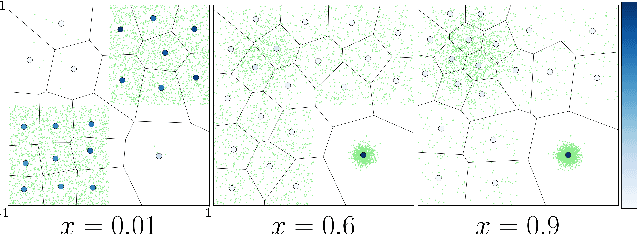
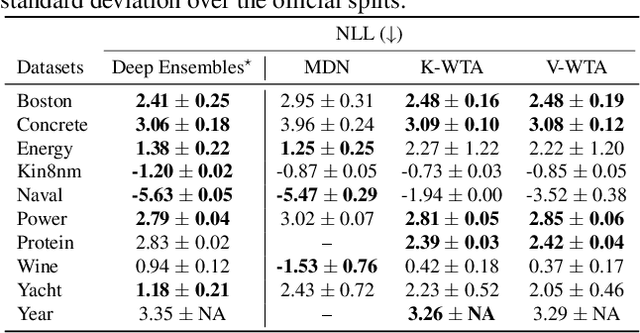
Abstract:Winner-takes-all training is a simple learning paradigm, which handles ambiguous tasks by predicting a set of plausible hypotheses. Recently, a connection was established between Winner-takes-all training and centroidal Voronoi tessellations, showing that, once trained, hypotheses should quantize optimally the shape of the conditional distribution to predict. However, the best use of these hypotheses for uncertainty quantification is still an open question.In this work, we show how to leverage the appealing geometric properties of the Winner-takes-all learners for conditional density estimation, without modifying its original training scheme. We theoretically establish the advantages of our novel estimator both in terms of quantization and density estimation, and we demonstrate its competitiveness on synthetic and real-world datasets, including audio data.
ManiPose: Manifold-Constrained Multi-Hypothesis 3D Human Pose Estimation
Dec 11, 2023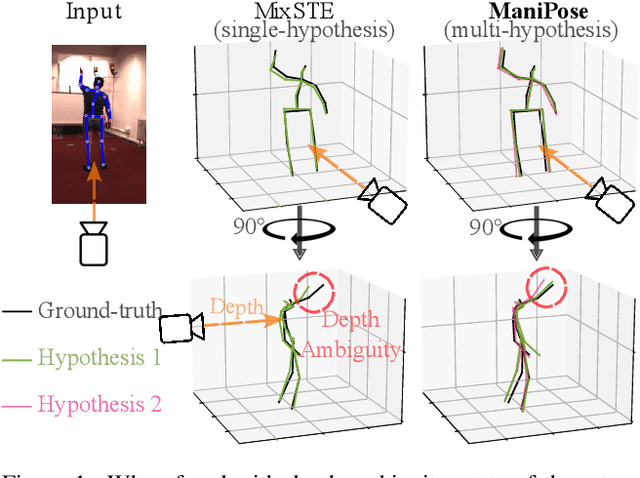
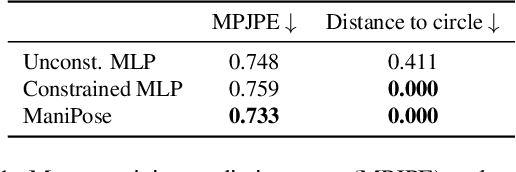
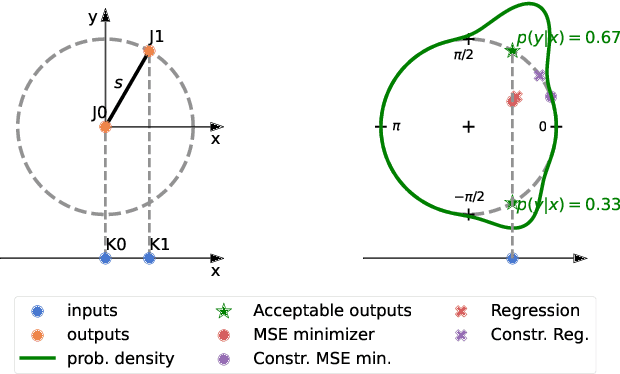
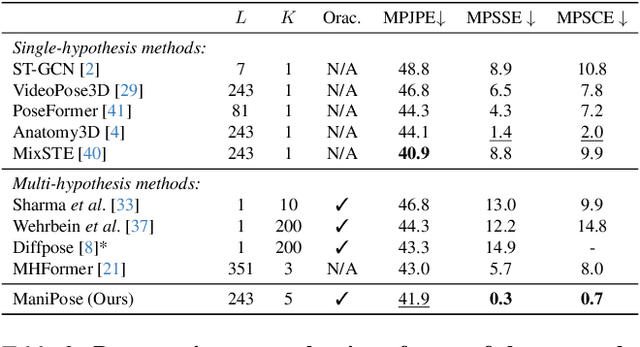
Abstract:Monocular 3D human pose estimation (3D-HPE) is an inherently ambiguous task, as a 2D pose in an image might originate from different possible 3D poses. Yet, most 3D-HPE methods rely on regression models, which assume a one-to-one mapping between inputs and outputs. In this work, we provide theoretical and empirical evidence that, because of this ambiguity, common regression models are bound to predict topologically inconsistent poses, and that traditional evaluation metrics, such as the MPJPE, P-MPJPE and PCK, are insufficient to assess this aspect. As a solution, we propose ManiPose, a novel manifold-constrained multi-hypothesis model capable of proposing multiple candidate 3D poses for each 2D input, together with their corresponding plausibility. Unlike previous multi-hypothesis approaches, our solution is completely supervised and does not rely on complex generative models, thus greatly facilitating its training and usage. Furthermore, by constraining our model to lie within the human pose manifold, we can guarantee the consistency of all hypothetical poses predicted with our approach, which was not possible in previous works. We illustrate the usefulness of ManiPose in a synthetic 1D-to-2D lifting setting and demonstrate on real-world datasets that it outperforms state-of-the-art models in pose consistency by a large margin, while still reaching competitive MPJPE performance.
Resilient Multiple Choice Learning: A learned scoring scheme with application to audio scene analysis
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:We introduce Resilient Multiple Choice Learning (rMCL), an extension of the MCL approach for conditional distribution estimation in regression settings where multiple targets may be sampled for each training input. Multiple Choice Learning is a simple framework to tackle multimodal density estimation, using the Winner-Takes-All (WTA) loss for a set of hypotheses. In regression settings, the existing MCL variants focus on merging the hypotheses, thereby eventually sacrificing the diversity of the predictions. In contrast, our method relies on a novel learned scoring scheme underpinned by a mathematical framework based on Voronoi tessellations of the output space, from which we can derive a probabilistic interpretation. After empirically validating rMCL with experiments on synthetic data, we further assess its merits on the sound source localization problem, demonstrating its practical usefulness and the relevance of its interpretation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge