Venelin Kovatchev
Fairly Accurate: Optimizing Accuracy Parity in Fair Target-Group Detection
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:In algorithmic toxicity detection pipelines, it is important to identify which demographic group(s) are the subject of a post, a task commonly known as \textit{target (group) detection}. While accurate detection is clearly important, we further advocate a fairness objective: to provide equal protection to all groups who may be targeted. To this end, we adopt \textit{Accuracy Parity} (AP) -- balanced detection accuracy across groups -- as our fairness objective. However, in order to align model training with our AP fairness objective, we require an equivalent loss function. Moreover, for gradient-based models such as neural networks, this loss function needs to be differentiable. Because no such loss function exists today for AP, we propose \emph{Group Accuracy Parity} (GAP): the first differentiable loss function having a one-on-one mapping to AP. We empirically show that GAP addresses disparate impact on groups for target detection. Furthermore, because a single post often targets multiple groups in practice, we also provide a mathematical extension of GAP to larger multi-group settings, something typically requiring heuristics in prior work. Our findings show that by optimizing AP, GAP better mitigates bias in comparison with other commonly employed loss functions.
Benchmark Transparency: Measuring the Impact of Data on Evaluation
Mar 31, 2024Abstract:In this paper we present an exploratory research on quantifying the impact that data distribution has on the performance and evaluation of NLP models. We propose an automated framework that measures the data point distribution across 6 different dimensions: ambiguity, difficulty, discriminability, length, noise, and perplexity. We use disproportional stratified sampling to measure how much the data distribution affects absolute (Acc/F1) and relative (Rank) model performance. We experiment on 2 different datasets (SQUAD and MNLI) and test a total of 135 different models (125 on SQUAD and 10 on MNLI). We demonstrate that without explicit control of the data distribution, standard evaluation frameworks are inconsistent and unreliable. We find that the impact of the data is statistically significant and is often larger than the impact of changing the metric. In a second set of experiments, we demonstrate that the impact of data on evaluation is not just observable, but also predictable. We propose to use benchmark transparency as a method for comparing datasets and quantifying the similarity between them. We find that the ``dataset similarity vector'' can be used to predict how well a model generalizes out of distribution.
The State of Human-centered NLP Technology for Fact-checking
Jan 08, 2023

Abstract:Misinformation threatens modern society by promoting distrust in science, changing narratives in public health, heightening social polarization, and disrupting democratic elections and financial markets, among a myriad of other societal harms. To address this, a growing cadre of professional fact-checkers and journalists provide high-quality investigations into purported facts. However, these largely manual efforts have struggled to match the enormous scale of the problem. In response, a growing body of Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies have been proposed for more scalable fact-checking. Despite tremendous growth in such research, however, practical adoption of NLP technologies for fact-checking still remains in its infancy today. In this work, we review the capabilities and limitations of the current NLP technologies for fact-checking. Our particular focus is to further chart the design space for how these technologies can be harnessed and refined in order to better meet the needs of human fact-checkers. To do so, we review key aspects of NLP-based fact-checking: task formulation, dataset construction, modeling, and human-centered strategies, such as explainable models and human-in-the-loop approaches. Next, we review the efficacy of applying NLP-based fact-checking tools to assist human fact-checkers. We recommend that future research include collaboration with fact-checker stakeholders early on in NLP research, as well as incorporation of human-centered design practices in model development, in order to further guide technology development for human use and practical adoption. Finally, we advocate for more research on benchmark development supporting extrinsic evaluation of human-centered fact-checking technologies.
* Published in Machine and Human Factors in Misinformation Management -- a special issue of Information Processing and Management
InferES : A Natural Language Inference Corpus for Spanish Featuring Negation-Based Contrastive and Adversarial Examples
Oct 06, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we present InferES - an original corpus for Natural Language Inference (NLI) in European Spanish. We propose, implement, and analyze a variety of corpus-creating strategies utilizing expert linguists and crowd workers. The objectives behind InferES are to provide high-quality data, and, at the same time to facilitate the systematic evaluation of automated systems. Specifically, we focus on measuring and improving the performance of machine learning systems on negation-based adversarial examples and their ability to generalize across out-of-distribution topics. We train two transformer models on InferES (8,055 gold examples) in a variety of scenarios. Our best model obtains 72.8% accuracy, leaving a lot of room for improvement. The "hypothesis-only" baseline performs only 2%-5% higher than majority, indicating much fewer annotation artifacts than prior work. We find that models trained on InferES generalize very well across topics (both in- and out-of-distribution) and perform moderately well on negation-based adversarial examples.
Paraphrasing, textual entailment, and semantic similarity above word level
Aug 10, 2022Abstract:This dissertation explores the linguistic and computational aspects of the meaning relations that can hold between two or more complex linguistic expressions (phrases, clauses, sentences, paragraphs). In particular, it focuses on Paraphrasing, Textual Entailment, Contradiction, and Semantic Similarity. In Part I: "Similarity at the Level of Words and Phrases", I study the Distributional Hypothesis (DH) and explore several different methodologies for quantifying semantic similarity at the levels of words and short phrases. In Part II: "Paraphrase Typology and Paraphrase Identification", I focus on the meaning relation of paraphrasing and the empirical task of automated Paraphrase Identification (PI). In Part III: "Paraphrasing, Textual Entailment, and Semantic Similarity", I present a novel direction in the research on textual meaning relations, resulting from joint research carried out on on paraphrasing, textual entailment, contradiction, and semantic similarity.
longhorns at DADC 2022: How many linguists does it take to fool a Question Answering model? A systematic approach to adversarial attacks
Jun 29, 2022



Abstract:Developing methods to adversarially challenge NLP systems is a promising avenue for improving both model performance and interpretability. Here, we describe the approach of the team "longhorns" on Task 1 of the The First Workshop on Dynamic Adversarial Data Collection (DADC), which asked teams to manually fool a model on an Extractive Question Answering task. Our team finished first, with a model error rate of 62%. We advocate for a systematic, linguistically informed approach to formulating adversarial questions, and we describe the results of our pilot experiments, as well as our official submission.
Fairly Accurate: Learning Optimal Accuracy vs. Fairness Tradeoffs for Hate Speech Detection
Apr 15, 2022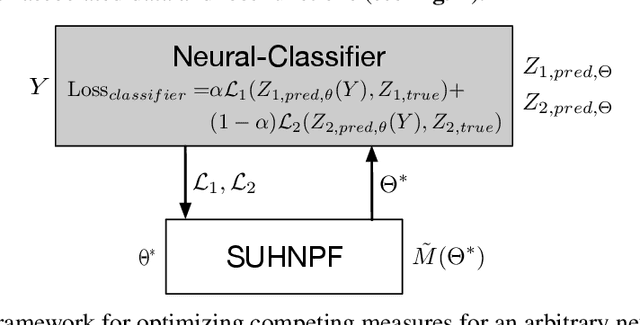
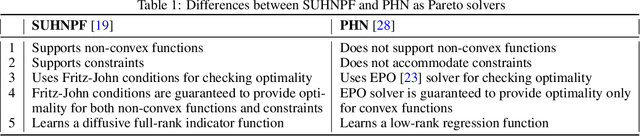

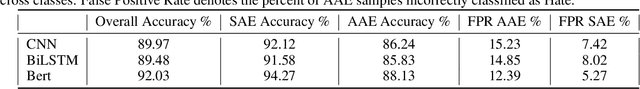
Abstract:Recent work has emphasized the importance of balancing competing objectives in model training (e.g., accuracy vs. fairness, or competing measures of fairness). Such trade-offs reflect a broader class of multi-objective optimization (MOO) problems in which optimization methods seek Pareto optimal trade-offs between competing goals. In this work, we first introduce a differentiable measure that enables direct optimization of group fairness (specifically, balancing accuracy across groups) in model training. Next, we demonstrate two model-agnostic MOO frameworks for learning Pareto optimal parameterizations over different groups of neural classification models. We evaluate our methods on the specific task of hate speech detection, in which prior work has shown lack of group fairness across speakers of different English dialects. Empirical results across convolutional, sequential, and transformer-based neural architectures show superior empirical accuracy vs. fairness trade-offs over prior work. More significantly, our measure enables the Pareto machinery to ensure that each architecture achieves the best possible trade-off between fairness and accuracy w.r.t. the dataset, given user-prescribed error tolerance bounds.
ProtoTEx: Explaining Model Decisions with Prototype Tensors
Apr 11, 2022



Abstract:We present ProtoTEx, a novel white-box NLP classification architecture based on prototype networks. ProtoTEx faithfully explains model decisions based on prototype tensors that encode latent clusters of training examples. At inference time, classification decisions are based on the distances between the input text and the prototype tensors, explained via the training examples most similar to the most influential prototypes. We also describe a novel interleaved training algorithm that effectively handles classes characterized by the absence of indicative features. On a propaganda detection task, ProtoTEx accuracy matches BART-large and exceeds BERT-large with the added benefit of providing faithful explanations. A user study also shows that prototype-based explanations help non-experts to better recognize propaganda in online news.
NL-Augmenter: A Framework for Task-Sensitive Natural Language Augmentation
Dec 06, 2021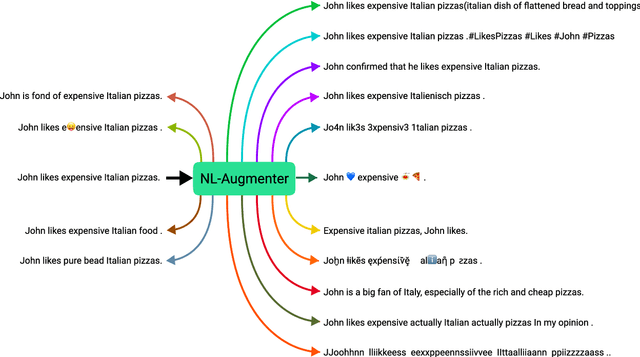
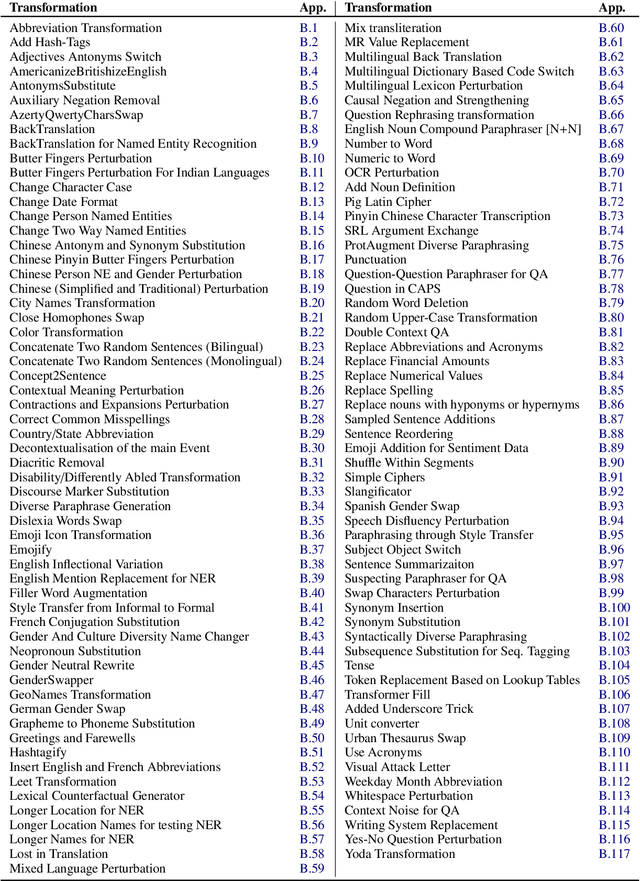
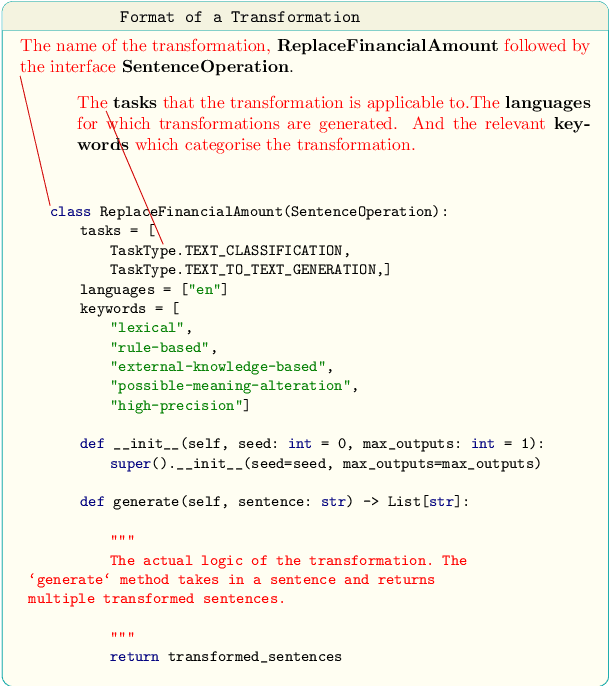
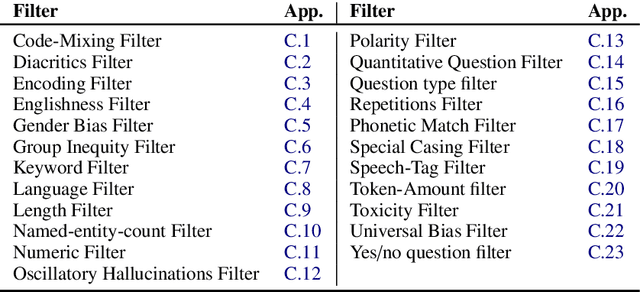
Abstract:Data augmentation is an important component in the robustness evaluation of models in natural language processing (NLP) and in enhancing the diversity of the data they are trained on. In this paper, we present NL-Augmenter, a new participatory Python-based natural language augmentation framework which supports the creation of both transformations (modifications to the data) and filters (data splits according to specific features). We describe the framework and an initial set of 117 transformations and 23 filters for a variety of natural language tasks. We demonstrate the efficacy of NL-Augmenter by using several of its transformations to analyze the robustness of popular natural language models. The infrastructure, datacards and robustness analysis results are available publicly on the NL-Augmenter repository (\url{https://github.com/GEM-benchmark/NL-Augmenter}).
Can vectors read minds better than experts? Comparing data augmentation strategies for the automated scoring of children's mindreading ability
Jun 03, 2021



Abstract:In this paper we implement and compare 7 different data augmentation strategies for the task of automatic scoring of children's ability to understand others' thoughts, feelings, and desires (or "mindreading"). We recruit in-domain experts to re-annotate augmented samples and determine to what extent each strategy preserves the original rating. We also carry out multiple experiments to measure how much each augmentation strategy improves the performance of automatic scoring systems. To determine the capabilities of automatic systems to generalize to unseen data, we create UK-MIND-20 - a new corpus of children's performance on tests of mindreading, consisting of 10,320 question-answer pairs. We obtain a new state-of-the-art performance on the MIND-CA corpus, improving macro-F1-score by 6 points. Results indicate that both the number of training examples and the quality of the augmentation strategies affect the performance of the systems. The task-specific augmentations generally outperform task-agnostic augmentations. Automatic augmentations based on vectors (GloVe, FastText) perform the worst. We find that systems trained on MIND-CA generalize well to UK-MIND-20. We demonstrate that data augmentation strategies also improve the performance on unseen data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge