Tong Hui
Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Politecnico di Milano
Channel-Aware Conditional Diffusion Model for Secure MU-MISO Communications
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While information securityis a fundamental requirement for wireless communications, conventional optimization based approaches often struggle with real-time implementation, and deep models, typically discriminative in nature, may lack the ability to cope with unforeseen scenarios. To address this challenge, this paper investigates the design of legitimate beamforming and artificial noise (AN) to achieve physical layer security by exploiting the conditional diffusion model. Specifically, we reformulate the security optimization as a conditional generative process, using a diffusion model to learn the inherent distribution of near-optimal joint beamforming and AN strategies. We employ a U-Net architecture with cross-attention to integrate channel state information, as the basis for the generative process. Moreover, we fine-tune the trained model using an objective incorporating the sum secrecy rate such that the security performance is further enhanced. Finally, simulation results validate the learning process convergence and demonstrate that the proposed generative method achieves superior secrecy performance across various scenarios as compared with the baselines.
Enhancing Tool Manipulation of An Aerial Vehicle with A Dynamically Displacing Center-of-Mass
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:As aerial robots gain traction in industrial applications, there is growing interest in enhancing their physical interaction capabilities. Pushing tasks performed by aerial manipulators have been successfully demonstrated in contact-based inspections. However, more complex industrial applications require these systems to support higher-DoF (Degree of Freedom) manipulators and generate larger forces while pushing (e.g., drilling, grinding). This paper builds on our previous work, where we introduced an aerial vehicle with a dynamically displacing CoM (Center of Mass) to improve force exertion during interactions. We propose a novel approach to further enhance this system's force generation by optimizing its CoM location during interactions. Additionally, we study the case of this aerial vehicle equipped with a 2-DoF manipulation arm to extend the system's functionality in tool-based tasks. The effectiveness of the proposed methods is validated through simulations, demonstrating the potential of this system for advanced aerial manipulation in practical settings.
AEROBULL: A Center-of-Mass Displacing Aerial Vehicle Enabling Efficient High-Force Interaction
Aug 27, 2024

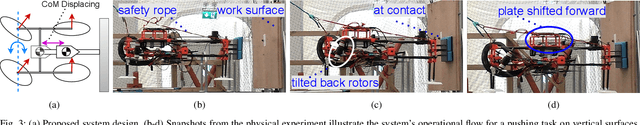

Abstract:In various industrial sectors, inspection and maintenance tasks using UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) require substantial force application to ensure effective adherence and stable contact, posing significant challenges to existing solutions. This paper addresses these industrial needs by introducing a novel lightweight aerial platform (3.12kg) designed to exert high pushing forces on non-horizontal surfaces. To increase maneuverability, the proposed platform incorporates tiltable rotors with 5-DoF (Degree of Freedom) actuation. Moreover, it has an innovative shifting-mass mechanism that dynamically adjusts the system's CoM (Center of Mass) during contact-based task execution. A compliant EE (End-Effector) is applied to ensure a smooth interaction with the work surface. We provide a detailed study of the UAV's overall system design, hardware integration of the developed physical prototype, and software architecture of the proposed control algorithm. Physical experiments were conducted to validate the control design and explore the force generation capability of the designed platform via a pushing task. With a total mass of 3.12kg, the UAV exerted a maximum pushing force of above 28N being almost equal to its gravity force. Furthermore, the experiments illustrated the benefits of having displaced CoM by benchmarking with a fixed CoM configuration.
Multi-Wheeled Passive Sliding with Fully-Actuated Aerial Robots: Tip-Over Recovery and Avoidance
May 29, 2024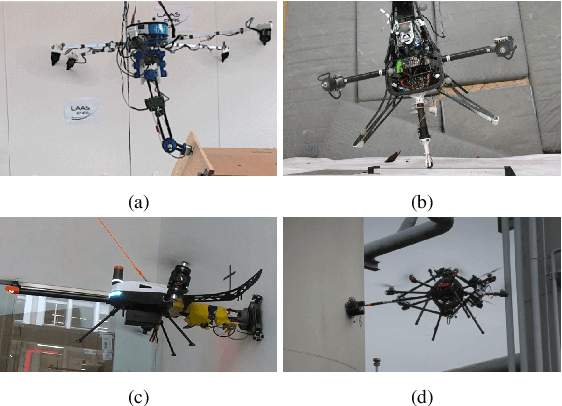

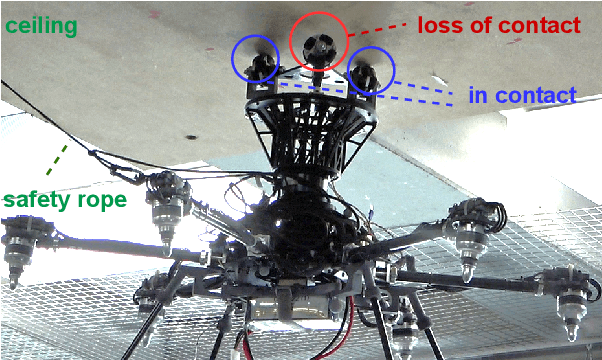
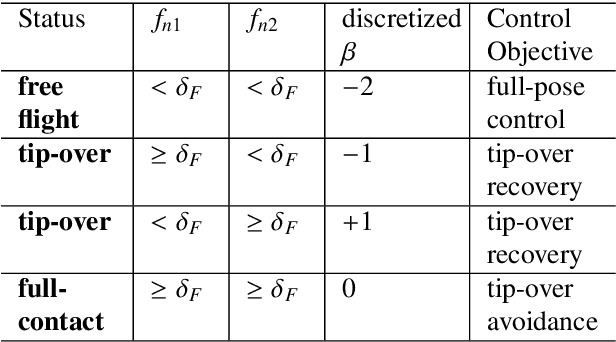
Abstract:Push-and-slide tasks carried out by fully-actuated aerial robots can be used for inspection and simple maintenance tasks at height, such as non-destructive testing and painting. Often, an end-effector based on multiple non-actuated contact wheels is used to contact the surface. This approach entails challenges in ensuring consistent wheel contact with a surface whose exact orientation and location might be uncertain due to sensor aliasing and drift. Using a standard full-pose controller dependent on the inaccurate surface position and orientation may cause wheels to lose contact during sliding, and subsequently lead to robot tip-over. To address the tip-over issue, we present two approaches: (1) tip-over avoidance guidelines for hardware design, and (2) control for tip-over recovery and avoidance. Physical experiments with a fully-actuated aerial vehicle were executed for a push-and-slide task on a flat surface. The resulting data is used in deriving tip-over avoidance guidelines and designing a simulator that closely captures real-world conditions. We then use the simulator to test the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed approaches in risky scenarios against uncertainties.
A Center-of-Mass Shifting Aerial Manipulation Platform for Heavy-Tool Handling on Non-Horizontal Surfaces
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:Aerial vehicles equipped with manipulators can serve contact-based industrial applications, where fundamental tasks like drilling and grinding often necessitate aerial platforms to handle heavy tools. Industrial environments often involve non-horizontal surfaces. Existing aerial manipulation platforms based on multirotors typically feature a fixed CoM (Center of Mass) within the rotor-defined area, leading to a considerable moment arm between the EE (End-Effector) tip and the CoM for operations on such surfaces. Carrying heavy tools at the EE tip of the manipulator with an extended moment arm can lead to system instability and potential damage to the servo actuators used in the manipulator. To tackle this issue, we present a novel aerial vehicle tailored for handling heavy tools on non-horizontal surfaces. In this work, we provide the platform's system design, modeling, and control strategies. This platform can carry heavy manipulators within the rotor-defined area during free flight. During interactions, the manipulator can shift towards the work surface outside the rotor-defined area, resulting in a displaced CoM location with a significantly shorter moment arm. Furthermore, we propose a method for automatically determining the manipulator's position to reach the maximum CoM displacement towards the work surface. Our proposed concepts are validated through simulations that closely capture the developed physical prototype of the platform.
Passive Aligning Physical Interaction of Fully-Actuated Aerial Vehicles for Pushing Tasks
Feb 27, 2024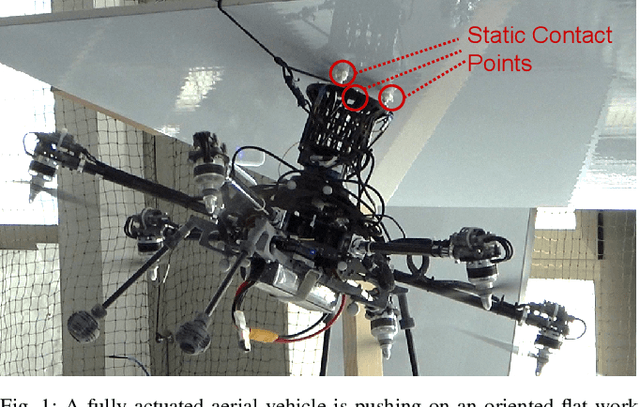
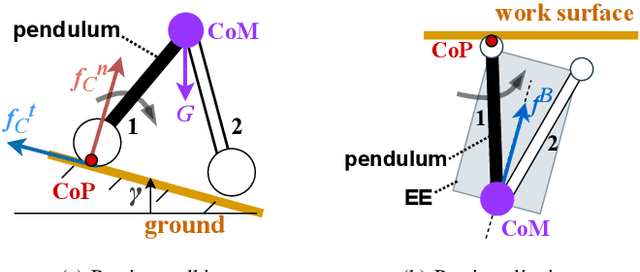
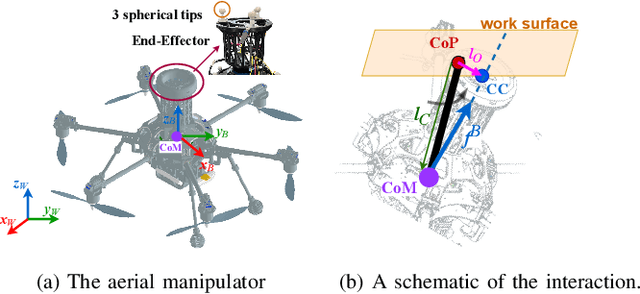
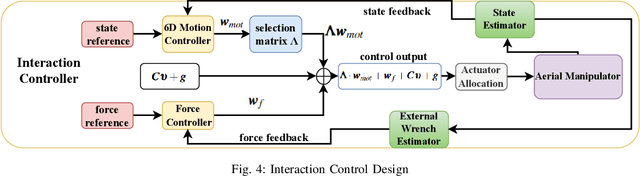
Abstract:Recently, the utilization of aerial manipulators for performing pushing tasks in non-destructive testing (NDT) applications has seen significant growth. Such operations entail physical interactions between the aerial robotic system and the environment. End-effectors with multiple contact points are often used for placing NDT sensors in contact with a surface to be inspected. Aligning the NDT sensor and the work surface while preserving contact, requires that all available contact points at the end-effector tip are in contact with the work surface. With a standard full-pose controller, attitude errors often occur due to perturbations caused by modeling uncertainties, sensor noise, and environmental uncertainties. Even small attitude errors can cause a loss of contact points between the end-effector tip and the work surface. To preserve full alignment amidst these uncertainties, we propose a control strategy which selectively deactivates angular motion control and enables direct force control in specific directions. In particular, we derive two essential conditions to be met, such that the robot can passively align with flat work surfaces achieving full alignment through the rotation along non-actively controlled axes. Additionally, these conditions serve as hardware design and control guidelines for effectively integrating the proposed control method for practical usage. Real world experiments are conducted to validate both the control design and the guidelines.
Safety-Conscious Pushing on Diverse Oriented Surfaces with Underactuated Aerial Vehicles
Feb 23, 2024Abstract:Pushing tasks performed by aerial manipulators can be used for contact-based industrial inspections. Underactuated aerial vehicles are widely employed in aerial manipulation due to their widespread availability and relatively low cost. Industrial infrastructures often consist of diverse oriented work surfaces. When interacting with such surfaces, the coupled gravity compensation and interaction force generation of underactuated aerial vehicles can present the potential challenge of near-saturation operations. The blind utilization of these platforms for such tasks can lead to instability and accidents, creating unsafe operating conditions and potentially damaging the platform. In order to ensure safe pushing on these surfaces while managing platform saturation, this work establishes a safety assessment process. This process involves the prediction of the saturation level of each actuator during pushing across variable surface orientations. Furthermore, the assessment results are used to plan and execute physical experiments, ensuring safe operations and preventing platform damage.
Versatile Airborne Ultrasonic NDT Technologies via Active Omni-Sliding with Over-Actuated Aerial Vehicles
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:This paper presents the utilization of advanced methodologies in aerial manipulation to address meaningful industrial applications and develop versatile ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) technologies with aerial robots. The primary objectives of this work are to enable multi-point measurements through sliding without re-approaching the work surface, and facilitate the representation of material thickness with B and C scans via dynamic scanning in arbitrary directions (i.e. omnidirections). To accomplish these objectives, a payload that can slide in omnidirections (here we call the omni-sliding payload) is designed for an over-actuated aerial vehicle, ensuring truly omnidirectional sliding mobility while exerting consistent forces in contact with a flat work surface. The omni-sliding payload is equipped with an omniwheel-based active end-effector and an Electro Magnetic Acoustic Transducer (EMAT). Furthermore, to ensure successful development of the designed payload and integration with the aerial vehicle, a comprehensive studying on contact conditions and system dynamics during active sliding is presented, and the derived system constraints are later used as guidelines for the hardware development and control setting. The proposed methods are validated through experiments, encompassing both the wall-sliding task and dynamic scanning for Ultrasonic Testing (UT), employing the aerial platform - Voliro T.
Static-Equilibrium Oriented Interaction Force Modeling and Control of Aerial Manipulation with Uni-Directional Thrust Multirotors
Jun 21, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a static-equilibrium oriented interaction force modeling and control approach of aerial manipulation employing uni-directional thrust (UDT) multirotors interacting with variously defined environments. First, a simplified system model for a quadrotor-based aerial manipulator is introduced considering parameterized work surfaces under assumptions, and then a range of meaningful manipulation tasks are utilized to explore the system properties in a quasi-static equilibrium state. An explicit interaction force model in relation with the aerial manipulator pose configuration and the environment parameter is derived from the static equilibrium analysis, based on which singularity is pointed out. Then a hybrid attitude/force interaction control strategy is presented to verify the proposed interaction force model, which involves high gain attitude control and feedforward plus feedback force control. This paper represents preliminary results. We study the properties of UDT-based aerial manipulators via specific tasks, and propose a novel framework for interaction force modeling and control aiming at maximizing the commercial values of UDT platforms for aerial manipulation purpose.
Centroidal Aerodynamic Modeling and Control of Flying Multibody Robots
May 17, 2022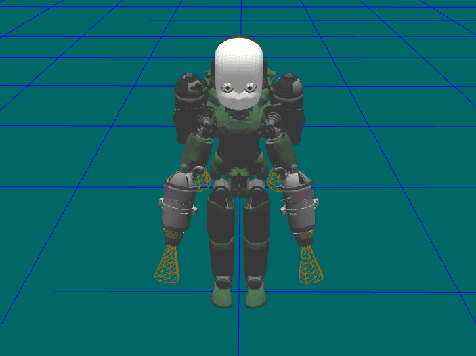
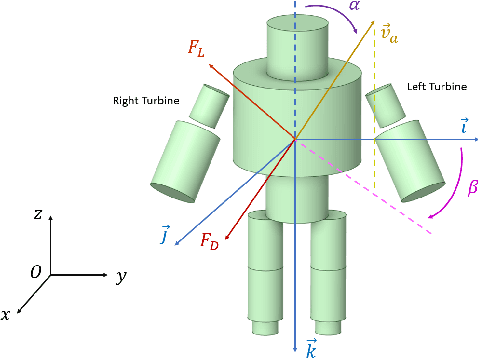
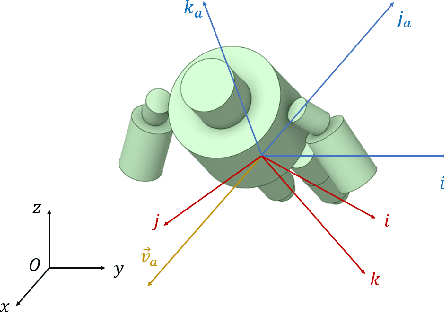
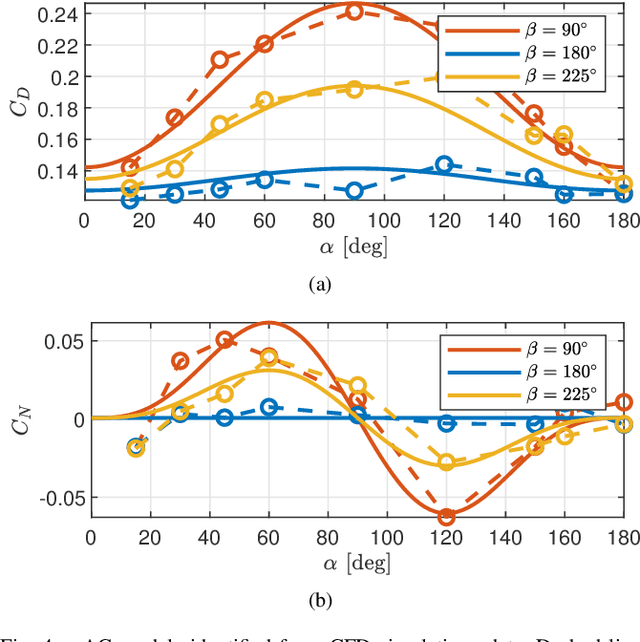
Abstract:This paper presents a modeling and control framework for multibody flying robots subject to non-negligible aerodynamic forces acting on the centroidal dynamics. First, aerodynamic forces are calculated during robot flight in different operating conditions by means of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis. Then, analytical models of the aerodynamics coefficients are generated from the dataset collected with CFD analysis. The obtained simplified aerodynamic model is also used to improve the flying robot control design. We present two control strategies: compensating for the aerodynamic effects via feedback linearization and enforcing the controller robustness with gain-scheduling. Simulation results on the jet-powered humanoid robot iRonCub validate the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge