Tomoya Yanagita
NAIST Simultaneous Speech Translation System for IWSLT 2024
Jun 30, 2024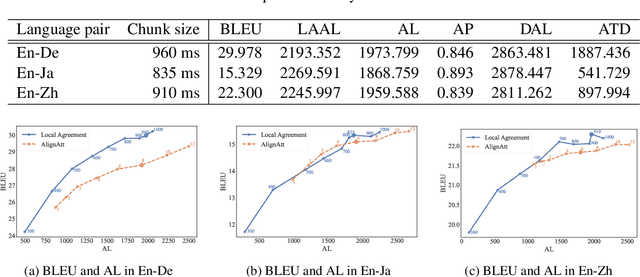
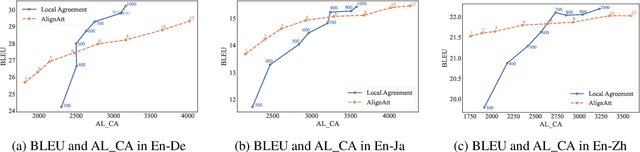


Abstract:This paper describes NAIST's submission to the simultaneous track of the IWSLT 2024 Evaluation Campaign: English-to-{German, Japanese, Chinese} speech-to-text translation and English-to-Japanese speech-to-speech translation. We develop a multilingual end-to-end speech-to-text translation model combining two pre-trained language models, HuBERT and mBART. We trained this model with two decoding policies, Local Agreement (LA) and AlignAtt. The submitted models employ the LA policy because it outperformed the AlignAtt policy in previous models. Our speech-to-speech translation method is a cascade of the above speech-to-text model and an incremental text-to-speech (TTS) module that incorporates a phoneme estimation model, a parallel acoustic model, and a parallel WaveGAN vocoder. We improved our incremental TTS by applying the Transformer architecture with the AlignAtt policy for the estimation model. The results show that our upgraded TTS module contributed to improving the system performance.
Simultaneous Speech-to-Speech Translation System with Neural Incremental ASR, MT, and TTS
Nov 11, 2020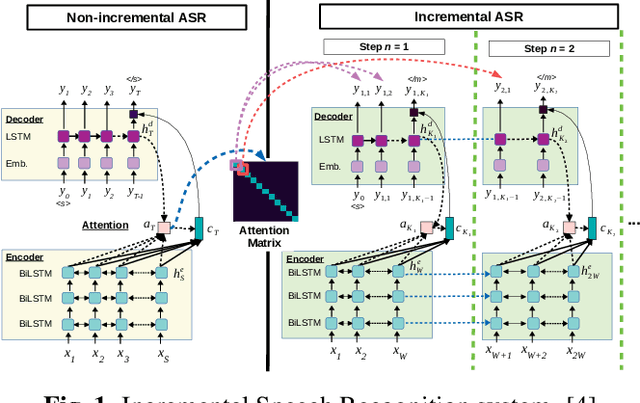
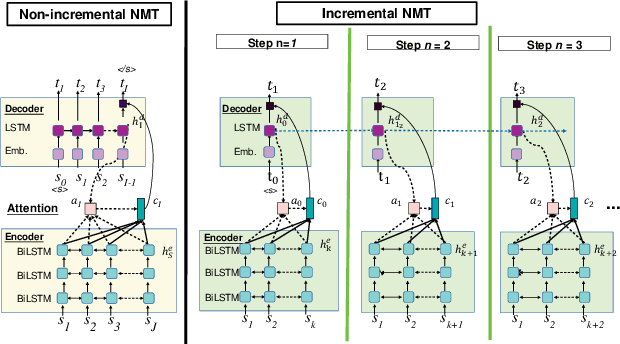
Abstract:This paper presents a newly developed, simultaneous neural speech-to-speech translation system and its evaluation. The system consists of three fully-incremental neural processing modules for automatic speech recognition (ASR), machine translation (MT), and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). We investigated its overall latency in the system's Ear-Voice Span and speaking latency along with module-level performance.
Incremental Machine Speech Chain Towards Enabling Listening while Speaking in Real-time
Nov 04, 2020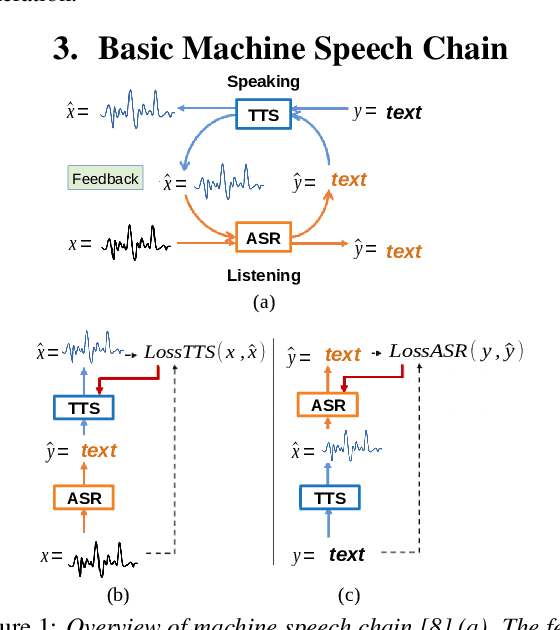
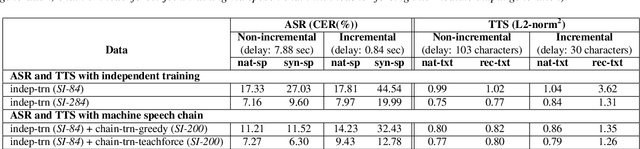
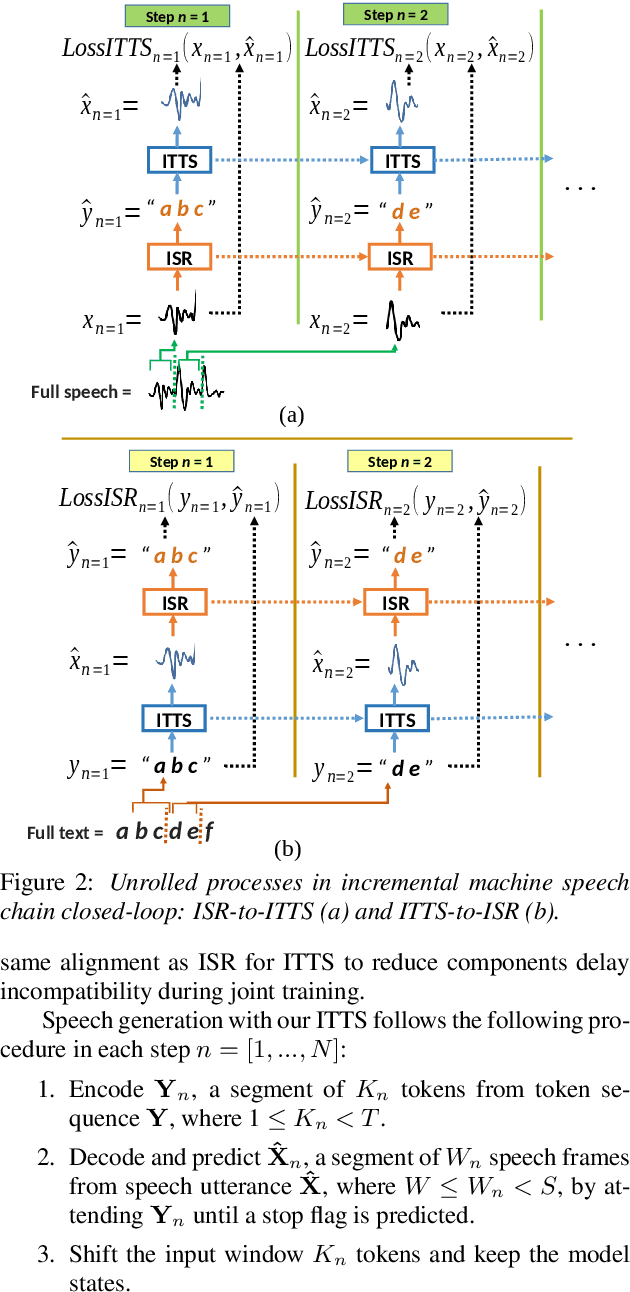
Abstract:Inspired by a human speech chain mechanism, a machine speech chain framework based on deep learning was recently proposed for the semi-supervised development of automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech synthesis TTS) systems. However, the mechanism to listen while speaking can be done only after receiving entire input sequences. Thus, there is a significant delay when encountering long utterances. By contrast, humans can listen to what hey speak in real-time, and if there is a delay in hearing, they won't be able to continue speaking. In this work, we propose an incremental machine speech chain towards enabling machine to listen while speaking in real-time. Specifically, we construct incremental ASR (ISR) and incremental TTS (ITTS) by letting both systems improve together through a short-term loop. Our experimental results reveal that our proposed framework is able to reduce delays due to long utterances while keeping a comparable performance to the non-incremental basic machine speech chain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge