Sashi Novitasari
Granite-speech: open-source speech-aware LLMs with strong English ASR capabilities
May 14, 2025Abstract:Granite-speech LLMs are compact and efficient speech language models specifically designed for English ASR and automatic speech translation (AST). The models were trained by modality aligning the 2B and 8B parameter variants of granite-3.3-instruct to speech on publicly available open-source corpora containing audio inputs and text targets consisting of either human transcripts for ASR or automatically generated translations for AST. Comprehensive benchmarking shows that on English ASR, which was our primary focus, they outperform several competitors' models that were trained on orders of magnitude more proprietary data, and they keep pace on English-to-X AST for major European languages, Japanese, and Chinese. The speech-specific components are: a conformer acoustic encoder using block attention and self-conditioning trained with connectionist temporal classification, a windowed query-transformer speech modality adapter used to do temporal downsampling of the acoustic embeddings and map them to the LLM text embedding space, and LoRA adapters to further fine-tune the text LLM. Granite-speech-3.3 operates in two modes: in speech mode, it performs ASR and AST by activating the encoder, projector, and LoRA adapters; in text mode, it calls the underlying granite-3.3-instruct model directly (without LoRA), essentially preserving all the text LLM capabilities and safety. Both models are freely available on HuggingFace (https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-speech-3.3-2b and https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-speech-3.3-8b) and can be used for both research and commercial purposes under a permissive Apache 2.0 license.
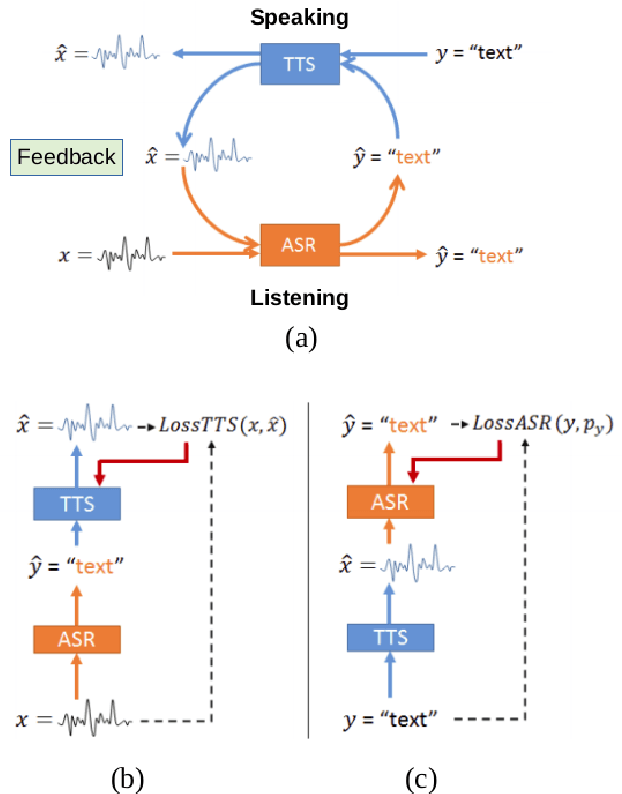
SpeeChain: A Speech Toolkit for Large-Scale Machine Speech Chain
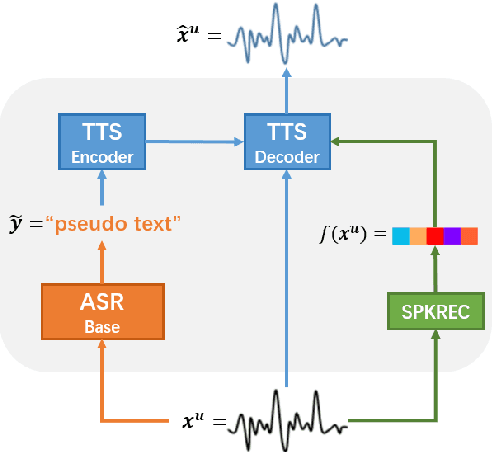
Jan 08, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces SpeeChain, an open-source Pytorch-based toolkit designed to develop the machine speech chain for large-scale use. This first release focuses on the TTS-to-ASR chain, a core component of the machine speech chain, that refers to the TTS data augmentation by unspoken text for ASR. To build an efficient pipeline for the large-scale TTS-to-ASR chain, we implement easy-to-use multi-GPU batch-level model inference, multi-dataloader batch generation, and on-the-fly data selection techniques. In this paper, we first explain the overall procedure of the TTS-to-ASR chain and the difficulties of each step. Then, we present a detailed ablation study on different types of unlabeled data, data filtering thresholds, batch composition, and real-synthetic data ratios. Our experimental results on train_clean_460 of LibriSpeech demonstrate that our TTS-to-ASR chain can significantly improve WER in a semi-supervised setting.
Improved Consistency Training for Semi-Supervised Sequence-to-Sequence ASR via Speech Chain Reconstruction and Self-Transcribing
May 14, 2022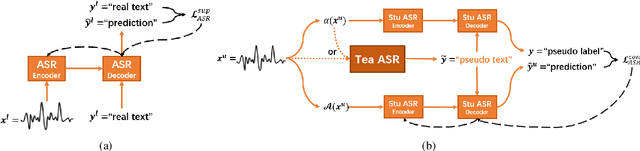
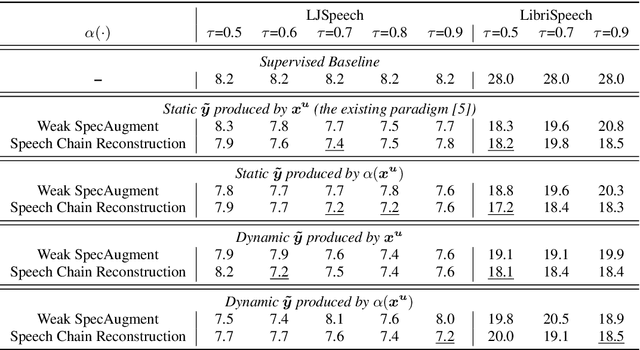
Abstract:Consistency regularization has recently been applied to semi-supervised sequence-to-sequence (S2S) automatic speech recognition (ASR). This principle encourages an ASR model to output similar predictions for the same input speech with different perturbations. The existing paradigm of semi-supervised S2S ASR utilizes SpecAugment as data augmentation and requires a static teacher model to produce pseudo transcripts for untranscribed speech. However, this paradigm fails to take full advantage of consistency regularization. First, the masking operations of SpecAugment may damage the linguistic contents of the speech, thus influencing the quality of pseudo labels. Second, S2S ASR requires both input speech and prefix tokens to make the next prediction. The static prefix tokens made by the offline teacher model cannot match dynamic pseudo labels during consistency training. In this work, we propose an improved consistency training paradigm of semi-supervised S2S ASR. We utilize speech chain reconstruction as the weak augmentation to generate high-quality pseudo labels. Moreover, we demonstrate that dynamic pseudo transcripts produced by the student ASR model benefit the consistency training. Experiments on LJSpeech and LibriSpeech corpora show that compared to supervised baselines, our improved paradigm achieves a 12.2% CER improvement in the single-speaker setting and 38.6% in the multi-speaker setting.
Simultaneous Speech-to-Speech Translation System with Neural Incremental ASR, MT, and TTS
Nov 11, 2020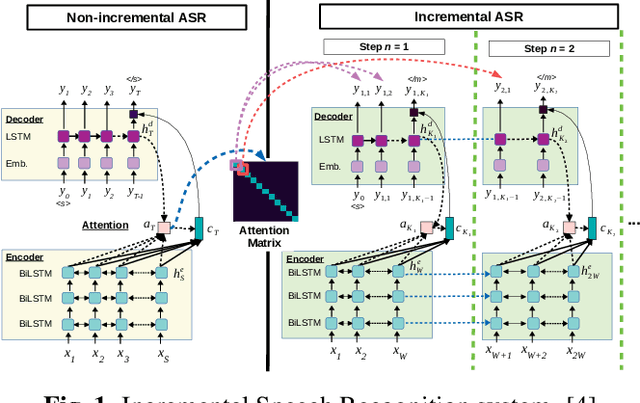
Abstract:This paper presents a newly developed, simultaneous neural speech-to-speech translation system and its evaluation. The system consists of three fully-incremental neural processing modules for automatic speech recognition (ASR), machine translation (MT), and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). We investigated its overall latency in the system's Ear-Voice Span and speaking latency along with module-level performance.
Cross-Lingual Machine Speech Chain for Javanese, Sundanese, Balinese, and Bataks Speech Recognition and Synthesis
Nov 04, 2020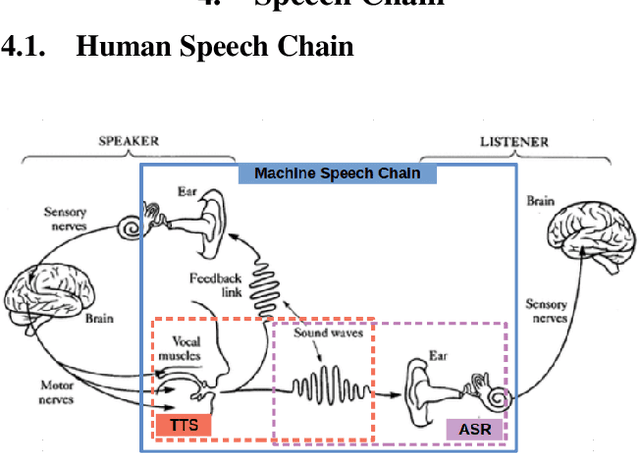
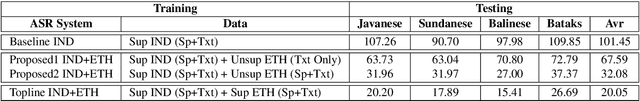

Abstract:Even though over seven hundred ethnic languages are spoken in Indonesia, the available technology remains limited that could support communication within indigenous communities as well as with people outside the villages. As a result, indigenous communities still face isolation due to cultural barriers; languages continue to disappear. To accelerate communication, speech-to-speech translation (S2ST) technology is one approach that can overcome language barriers. However, S2ST systems require machine translation (MT), speech recognition (ASR), and synthesis (TTS) that rely heavily on supervised training and a broad set of language resources that can be difficult to collect from ethnic communities. Recently, a machine speech chain mechanism was proposed to enable ASR and TTS to assist each other in semi-supervised learning. The framework was initially implemented only for monolingual languages. In this study, we focus on developing speech recognition and synthesis for these Indonesian ethnic languages: Javanese, Sundanese, Balinese, and Bataks. We first separately train ASR and TTS of standard Indonesian in supervised training. We then develop ASR and TTS of ethnic languages by utilizing Indonesian ASR and TTS in a cross-lingual machine speech chain framework with only text or only speech data removing the need for paired speech-text data of those ethnic languages.
Sequence-to-Sequence Learning via Attention Transfer for Incremental Speech Recognition
Nov 04, 2020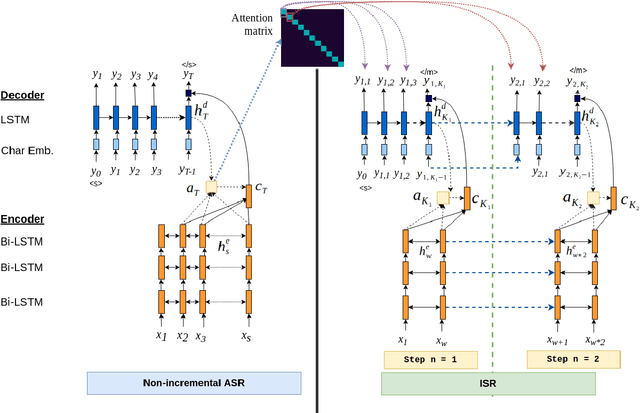
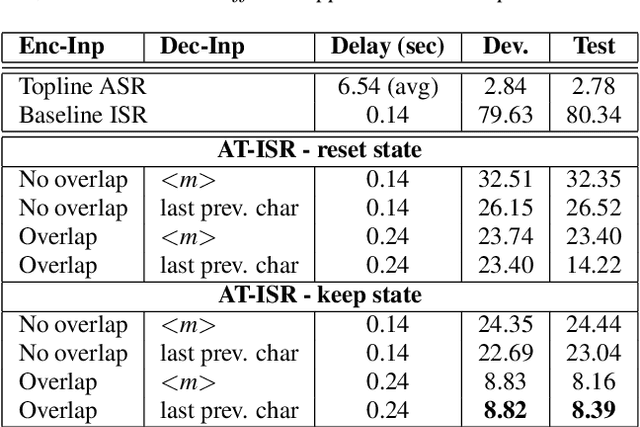
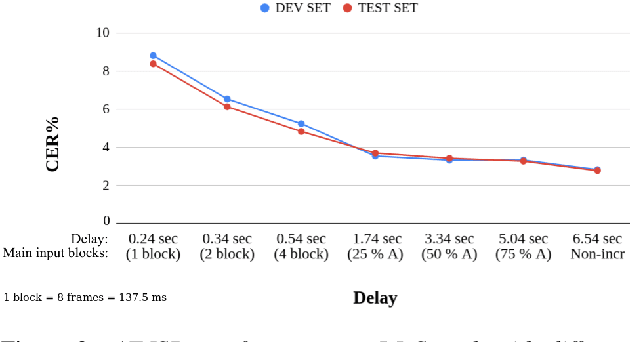
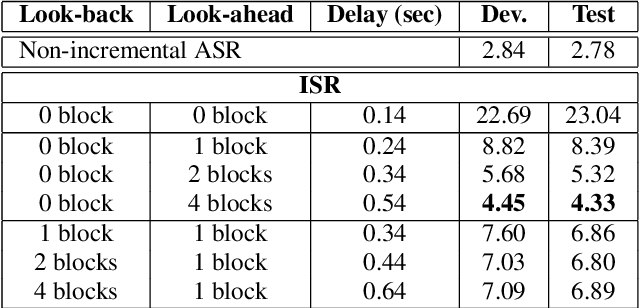
Abstract:Attention-based sequence-to-sequence automatic speech recognition (ASR) requires a significant delay to recognize long utterances because the output is generated after receiving entire input sequences. Although several studies recently proposed sequence mechanisms for incremental speech recognition (ISR), using different frameworks and learning algorithms is more complicated than the standard ASR model. One main reason is because the model needs to decide the incremental steps and learn the transcription that aligns with the current short speech segment. In this work, we investigate whether it is possible to employ the original architecture of attention-based ASR for ISR tasks by treating a full-utterance ASR as the teacher model and the ISR as the student model. We design an alternative student network that, instead of using a thinner or a shallower model, keeps the original architecture of the teacher model but with shorter sequences (few encoder and decoder states). Using attention transfer, the student network learns to mimic the same alignment between the current input short speech segments and the transcription. Our experiments show that by delaying the starting time of recognition process with about 1.7 sec, we can achieve comparable performance to one that needs to wait until the end.
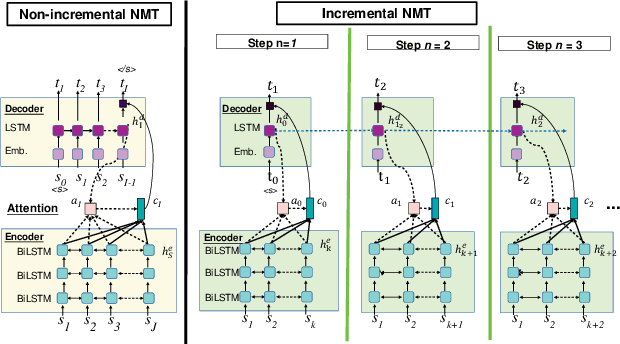
Incremental Machine Speech Chain Towards Enabling Listening while Speaking in Real-time
Nov 04, 2020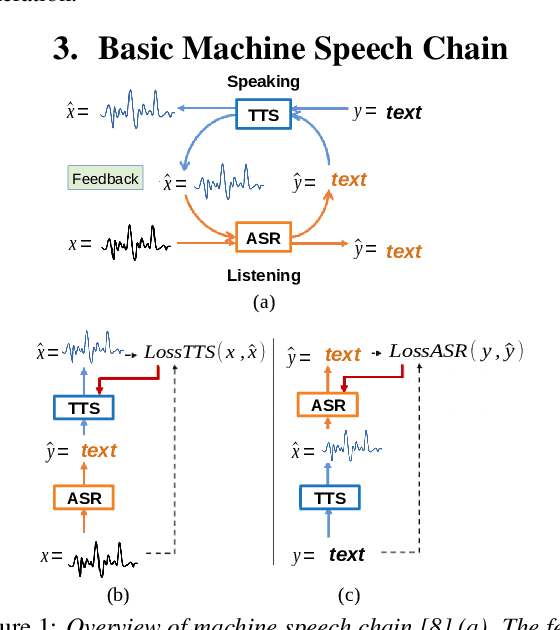
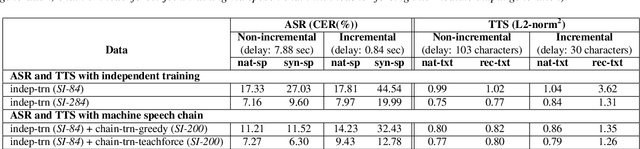
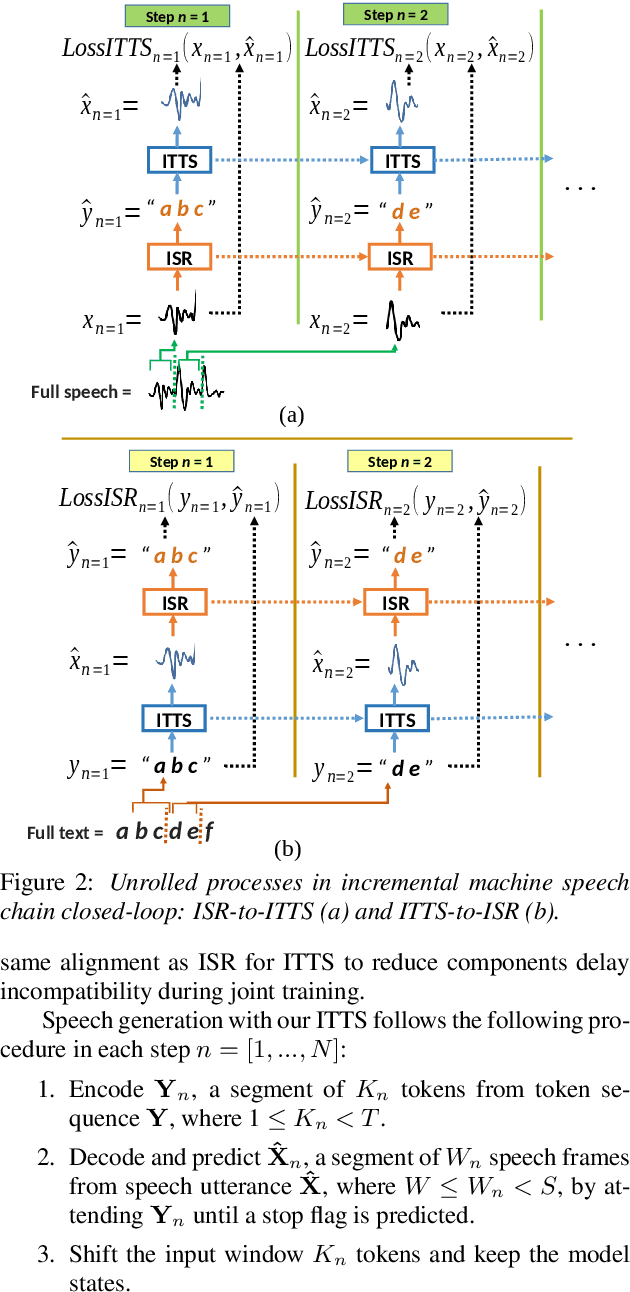
Abstract:Inspired by a human speech chain mechanism, a machine speech chain framework based on deep learning was recently proposed for the semi-supervised development of automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech synthesis TTS) systems. However, the mechanism to listen while speaking can be done only after receiving entire input sequences. Thus, there is a significant delay when encountering long utterances. By contrast, humans can listen to what hey speak in real-time, and if there is a delay in hearing, they won't be able to continue speaking. In this work, we propose an incremental machine speech chain towards enabling machine to listen while speaking in real-time. Specifically, we construct incremental ASR (ISR) and incremental TTS (ITTS) by letting both systems improve together through a short-term loop. Our experimental results reveal that our proposed framework is able to reduce delays due to long utterances while keeping a comparable performance to the non-incremental basic machine speech chain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge