Tingzhu Wang
Fine-Grained Scene Graph Generation via Sample-Level Bias Prediction
Jul 27, 2024



Abstract:Scene Graph Generation (SGG) aims to explore the relationships between objects in images and obtain scene summary graphs, thereby better serving downstream tasks. However, the long-tailed problem has adversely affected the scene graph's quality. The predictions are dominated by coarse-grained relationships, lacking more informative fine-grained ones. The union region of one object pair (i.e., one sample) contains rich and dedicated contextual information, enabling the prediction of the sample-specific bias for refining the original relationship prediction. Therefore, we propose a novel Sample-Level Bias Prediction (SBP) method for fine-grained SGG (SBG). Firstly, we train a classic SGG model and construct a correction bias set by calculating the margin between the ground truth label and the predicted label with one classic SGG model. Then, we devise a Bias-Oriented Generative Adversarial Network (BGAN) that learns to predict the constructed correction biases, which can be utilized to correct the original predictions from coarse-grained relationships to fine-grained ones. The extensive experimental results on VG, GQA, and VG-1800 datasets demonstrate that our SBG outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of Average@K across three mainstream SGG models: Motif, VCtree, and Transformer. Compared to dataset-level correction methods on VG, SBG shows a significant average improvement of 5.6%, 3.9%, and 3.2% on Average@K for tasks PredCls, SGCls, and SGDet, respectively. The code will be available at https://github.com/Zhuzi24/SBG.
SkySenseGPT: A Fine-Grained Instruction Tuning Dataset and Model for Remote Sensing Vision-Language Understanding
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:Remote Sensing Large Multi-Modal Models (RSLMMs) are developing rapidly and showcase significant capabilities in remote sensing imagery (RSI) comprehension. However, due to the limitations of existing datasets, RSLMMs have shortcomings in understanding the rich semantic relations among objects in complex remote sensing scenes. To unlock RSLMMs' complex comprehension ability, we propose a large-scale instruction tuning dataset FIT-RS, containing 1,800,851 instruction samples. FIT-RS covers common interpretation tasks and innovatively introduces several complex comprehension tasks of escalating difficulty, ranging from relation reasoning to image-level scene graph generation. Based on FIT-RS, we build the FIT-RSFG benchmark. Furthermore, we establish a new benchmark to evaluate the fine-grained relation comprehension capabilities of LMMs, named FIT-RSRC. Based on combined instruction data, we propose SkySenseGPT, which achieves outstanding performance on both public datasets and FIT-RSFG, surpassing existing RSLMMs. We hope the FIT-RS dataset can enhance the relation comprehension capability of RSLMMs and provide a large-scale fine-grained data source for the remote sensing community. The dataset will be available at https://github.com/Luo-Z13/SkySenseGPT
Scene Graph Generation in Large-Size VHR Satellite Imagery: A Large-Scale Dataset and A Context-Aware Approach
Jun 13, 2024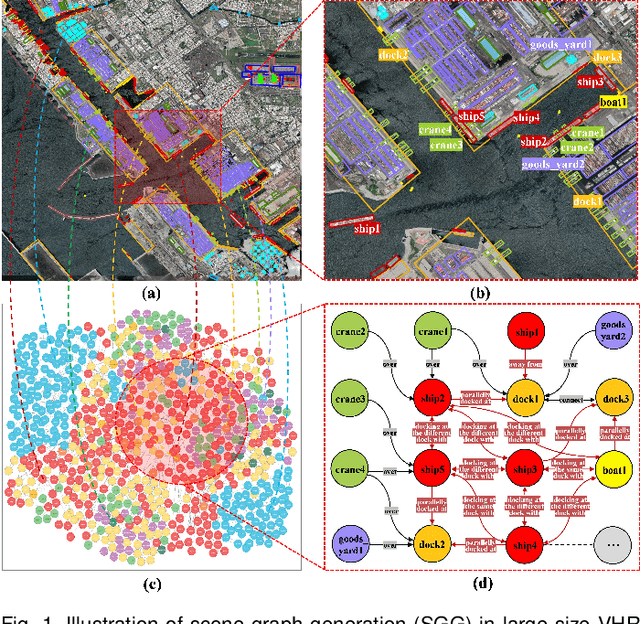
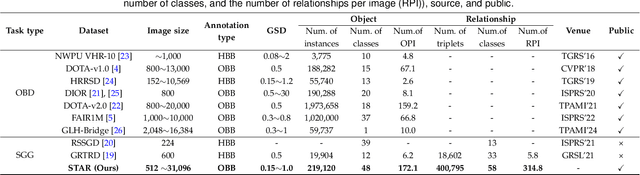
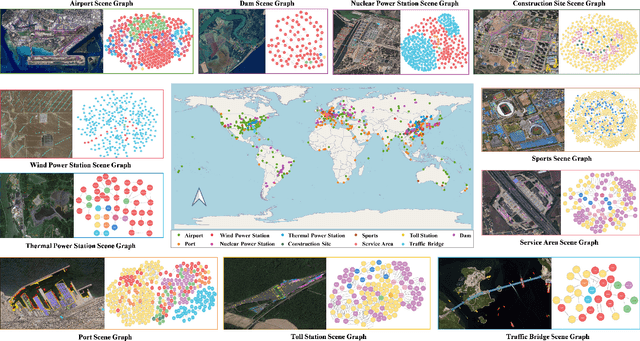
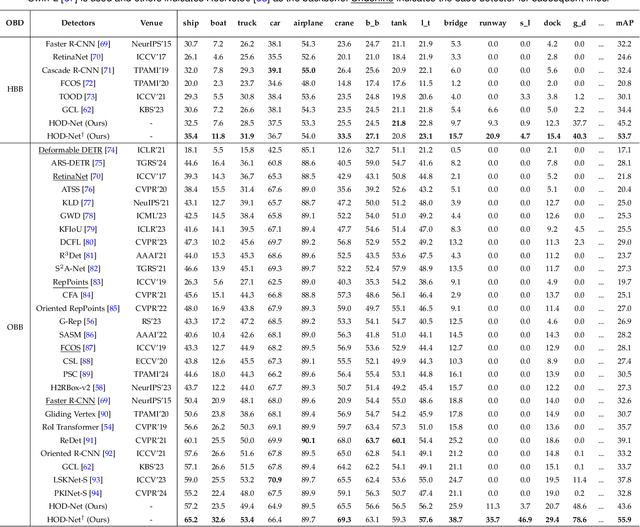
Abstract:Scene graph generation (SGG) in satellite imagery (SAI) benefits promoting intelligent understanding of geospatial scenarios from perception to cognition. In SAI, objects exhibit great variations in scales and aspect ratios, and there exist rich relationships between objects (even between spatially disjoint objects), which makes it necessary to holistically conduct SGG in large-size very-high-resolution (VHR) SAI. However, the lack of SGG datasets with large-size VHR SAI has constrained the advancement of SGG in SAI. Due to the complexity of large-size VHR SAI, mining triplets <subject, relationship, object> in large-size VHR SAI heavily relies on long-range contextual reasoning. Consequently, SGG models designed for small-size natural imagery are not directly applicable to large-size VHR SAI. To address the scarcity of datasets, this paper constructs a large-scale dataset for SGG in large-size VHR SAI with image sizes ranging from 512 x 768 to 27,860 x 31,096 pixels, named RSG, encompassing over 210,000 objects and more than 400,000 triplets. To realize SGG in large-size VHR SAI, we propose a context-aware cascade cognition (CAC) framework to understand SAI at three levels: object detection (OBD), pair pruning and relationship prediction. As a fundamental prerequisite for SGG in large-size SAI, a holistic multi-class object detection network (HOD-Net) that can flexibly integrate multi-scale contexts is proposed. With the consideration that there exist a huge amount of object pairs in large-size SAI but only a minority of object pairs contain meaningful relationships, we design a pair proposal generation (PPG) network via adversarial reconstruction to select high-value pairs. Furthermore, a relationship prediction network with context-aware messaging (RPCM) is proposed to predict the relationship types of these pairs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge