Kang Wu
When Large Vision-Language Model Meets Large Remote Sensing Imagery: Coarse-to-Fine Text-Guided Token Pruning
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Efficient vision-language understanding of large Remote Sensing Images (RSIs) is meaningful but challenging. Current Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) typically employ limited pre-defined grids to process images, leading to information loss when handling gigapixel RSIs. Conversely, using unlimited grids significantly increases computational costs. To preserve image details while reducing computational complexity, we propose a text-guided token pruning method with Dynamic Image Pyramid (DIP) integration. Our method introduces: (i) a Region Focus Module (RFM) that leverages text-aware region localization capability to identify critical vision tokens, and (ii) a coarse-to-fine image tile selection and vision token pruning strategy based on DIP, which is guided by RFM outputs and avoids directly processing the entire large imagery. Additionally, existing benchmarks for evaluating LVLMs' perception ability on large RSI suffer from limited question diversity and constrained image sizes. We construct a new benchmark named LRS-VQA, which contains 7,333 QA pairs across 8 categories, with image length up to 27,328 pixels. Our method outperforms existing high-resolution strategies on four datasets using the same data. Moreover, compared to existing token reduction methods, our approach demonstrates higher efficiency under high-resolution settings. Dataset and code are in https://github.com/VisionXLab/LRS-VQA.
Fine-Grained Scene Graph Generation via Sample-Level Bias Prediction
Jul 27, 2024



Abstract:Scene Graph Generation (SGG) aims to explore the relationships between objects in images and obtain scene summary graphs, thereby better serving downstream tasks. However, the long-tailed problem has adversely affected the scene graph's quality. The predictions are dominated by coarse-grained relationships, lacking more informative fine-grained ones. The union region of one object pair (i.e., one sample) contains rich and dedicated contextual information, enabling the prediction of the sample-specific bias for refining the original relationship prediction. Therefore, we propose a novel Sample-Level Bias Prediction (SBP) method for fine-grained SGG (SBG). Firstly, we train a classic SGG model and construct a correction bias set by calculating the margin between the ground truth label and the predicted label with one classic SGG model. Then, we devise a Bias-Oriented Generative Adversarial Network (BGAN) that learns to predict the constructed correction biases, which can be utilized to correct the original predictions from coarse-grained relationships to fine-grained ones. The extensive experimental results on VG, GQA, and VG-1800 datasets demonstrate that our SBG outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of Average@K across three mainstream SGG models: Motif, VCtree, and Transformer. Compared to dataset-level correction methods on VG, SBG shows a significant average improvement of 5.6%, 3.9%, and 3.2% on Average@K for tasks PredCls, SGCls, and SGDet, respectively. The code will be available at https://github.com/Zhuzi24/SBG.
SkySense: A Multi-Modal Remote Sensing Foundation Model Towards Universal Interpretation for Earth Observation Imagery
Dec 15, 2023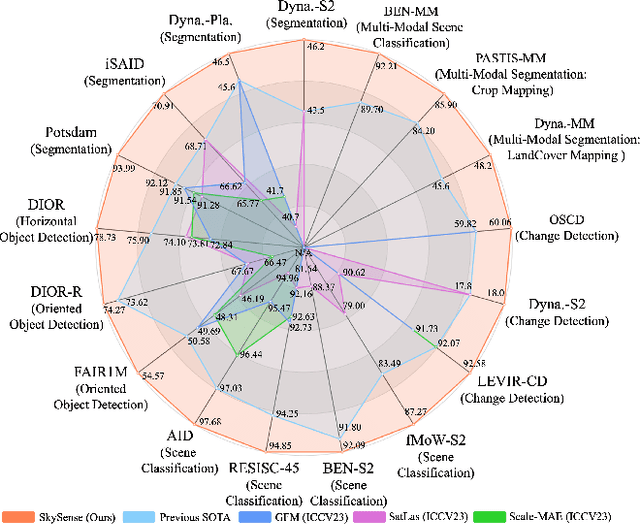
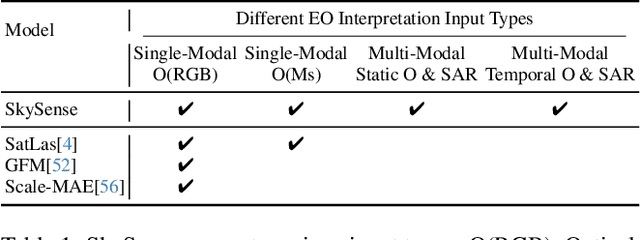
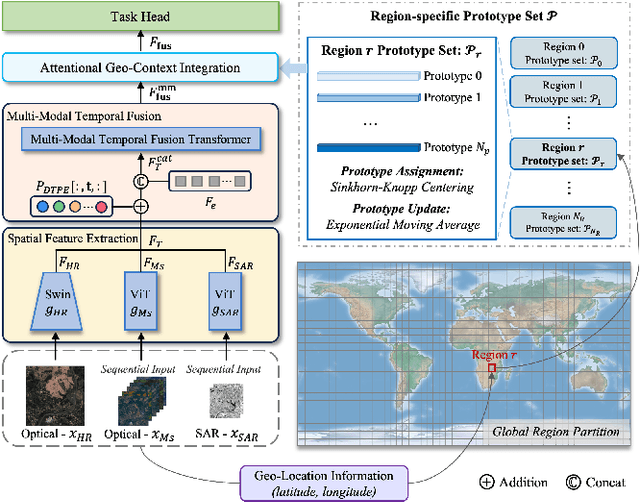
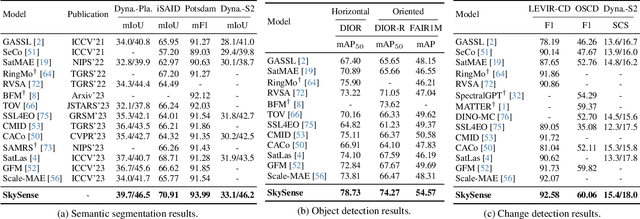
Abstract:Prior studies on Remote Sensing Foundation Model (RSFM) reveal immense potential towards a generic model for Earth Observation. Nevertheless, these works primarily focus on a single modality without temporal and geo-context modeling, hampering their capabilities for diverse tasks. In this study, we present SkySense, a generic billion-scale model, pre-trained on a curated multi-modal Remote Sensing Imagery (RSI) dataset with 21.5 million temporal sequences. SkySense incorporates a factorized multi-modal spatiotemporal encoder taking temporal sequences of optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data as input. This encoder is pre-trained by our proposed Multi-Granularity Contrastive Learning to learn representations across different modal and spatial granularities. To further enhance the RSI representations by the geo-context clue, we introduce Geo-Context Prototype Learning to learn region-aware prototypes upon RSI's multi-modal spatiotemporal features. To our best knowledge, SkySense is the largest Multi-Modal RSFM to date, whose modules can be flexibly combined or used individually to accommodate various tasks. It demonstrates remarkable generalization capabilities on a thorough evaluation encompassing 16 datasets over 7 tasks, from single- to multi-modal, static to temporal, and classification to localization. SkySense surpasses 18 recent RSFMs in all test scenarios. Specifically, it outperforms the latest models such as GFM, SatLas and Scale-MAE by a large margin, i.e., 2.76%, 3.67% and 3.61% on average respectively. We will release the pre-trained weights to facilitate future research and Earth Observation applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge