Tin A. Tun
3D Structural Phenotype of the Optic Nerve Head at the Intersection of Glaucoma and Myopia - A Key to Improving Glaucoma Diagnosis in Myopic Populations
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Purpose: To characterize the 3D structural phenotypes of the optic nerve head (ONH) in patients with glaucoma, high myopia, and concurrent high myopia and glaucoma, and to evaluate their variations across these conditions. Participants: A total of 685 optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans from 754 subjects of Singapore-Chinese ethnicity, including 256 healthy (H), 94 highly myopic (HM), 227 glaucomatous (G), and 108 highly myopic with glaucoma (HMG) cases. Methods: We segmented the retinal and connective tissues from OCT volumes and their boundary edges were converted into 3D point clouds. To classify the 3D point clouds into four ONH conditions, i.e., H, HM, G, and HMG, a specialized ensemble network was developed, consisting of an encoder to transform high-dimensional input data into a compressed latent vector, a decoder to reconstruct point clouds from the latent vector, and a classifier to categorize the point clouds into the four ONH conditions. Results: The classification network achieved high accuracy, distinguishing H, HM, G, and HMG classes with a micro-average AUC of 0.92 $\pm$ 0.03 on an independent test set. The decoder effectively reconstructed point clouds, achieving a Chamfer loss of 0.013 $\pm$ 0.002. Dimensionality reduction clustered ONHs into four distinct groups, revealing structural variations such as changes in retinal and connective tissue thickness, tilting and stretching of the disc and scleral canal opening, and alterations in optic cup morphology, including shallow or deep excavation, across the four conditions. Conclusions: This study demonstrated that ONHs exhibit distinct structural signatures across H, HM, G, and HMG conditions. The findings further indicate that ONH morphology provides sufficient information for classification into distinct clusters, with principal components capturing unique structural patterns within each group.
Introducing the Biomechanics-Function Relationship in Glaucoma: Improved Visual Field Loss Predictions from intraocular pressure-induced Neural Tissue Strains
Jun 21, 2024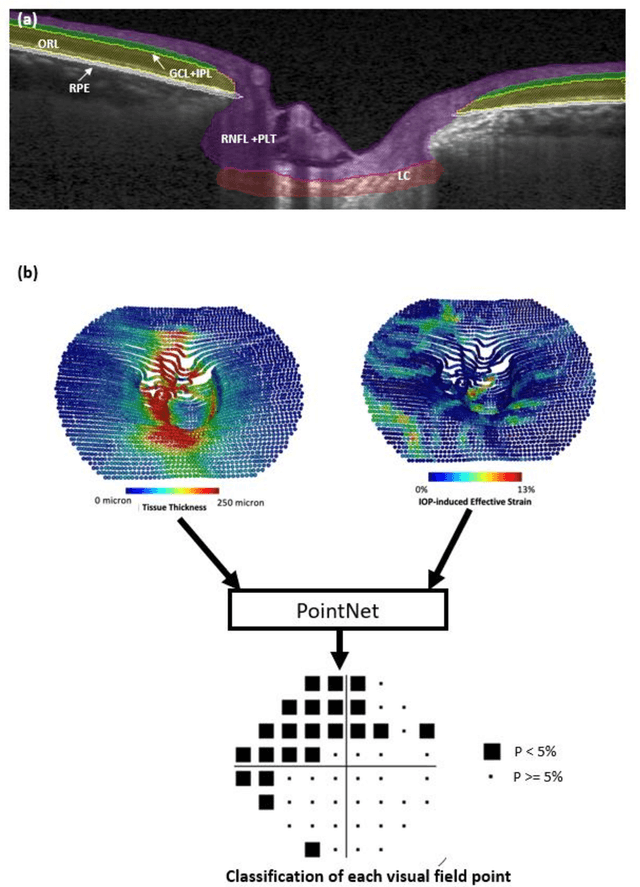

Abstract:Objective. (1) To assess whether neural tissue structure and biomechanics could predict functional loss in glaucoma; (2) To evaluate the importance of biomechanics in making such predictions. Design, Setting and Participants. We recruited 238 glaucoma subjects. For one eye of each subject, we imaged the optic nerve head (ONH) using spectral-domain OCT under the following conditions: (1) primary gaze and (2) primary gaze with acute IOP elevation. Main Outcomes: We utilized automatic segmentation of optic nerve head (ONH) tissues and digital volume correlation (DVC) analysis to compute intraocular pressure (IOP)-induced neural tissue strains. A robust geometric deep learning approach, known as Point-Net, was employed to predict the full Humphrey 24-2 pattern standard deviation (PSD) maps from ONH structural and biomechanical information. For each point in each PSD map, we predicted whether it exhibited no defect or a PSD value of less than 5%. Predictive performance was evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation and the F1-score. We compared the model's performance with and without the inclusion of IOP-induced strains to assess the impact of biomechanics on prediction accuracy. Results: Integrating biomechanical (IOP-induced neural tissue strains) and structural (tissue morphology and neural tissues thickness) information yielded a significantly better predictive model (F1-score: 0.76+-0.02) across validation subjects, as opposed to relying only on structural information, which resulted in a significantly lower F1-score of 0.71+-0.02 (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Our study has shown that the integration of biomechanical data can significantly improve the accuracy of visual field loss predictions. This highlights the importance of the biomechanics-function relationship in glaucoma, and suggests that biomechanics may serve as a crucial indicator for the development and progression of glaucoma.
The 3D Structural Phenotype of the Glaucomatous Optic Nerve Head and its Relationship with The Severity of Visual Field Damage
Jan 07, 2023Abstract:$\bf{Purpose}$: To describe the 3D structural changes in both connective and neural tissues of the optic nerve head (ONH) that occur concurrently at different stages of glaucoma using traditional and AI-driven approaches. $\bf{Methods}$: We included 213 normal, 204 mild glaucoma (mean deviation [MD] $\ge$ -6.00 dB), 118 moderate glaucoma (MD of -6.01 to -12.00 dB), and 118 advanced glaucoma patients (MD < -12.00 dB). All subjects had their ONHs imaged in 3D with Spectralis optical coherence tomography. To describe the 3D structural phenotype of glaucoma as a function of severity, we used two different approaches: (1) We extracted human-defined 3D structural parameters of the ONH including retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness, lamina cribrosa (LC) shape and depth at different stages of glaucoma; (2) we also employed a geometric deep learning method (i.e. PointNet) to identify the most important 3D structural features that differentiate ONHs from different glaucoma severity groups without any human input. $\bf{Results}$: We observed that the majority of ONH structural changes occurred in the early glaucoma stage, followed by a plateau effect in the later stages. Using PointNet, we also found that 3D ONH structural changes were present in both neural and connective tissues. In both approaches, we observed that structural changes were more prominent in the superior and inferior quadrant of the ONH, particularly in the RNFL, the prelamina, and the LC. As the severity of glaucoma increased, these changes became more diffuse (i.e. widespread), particularly in the LC. $\bf{Conclusions}$: In this study, we were able to uncover complex 3D structural changes of the ONH in both neural and connective tissues as a function of glaucoma severity. We hope to provide new insights into the complex pathophysiology of glaucoma that might help clinicians in their daily clinical care.
AI-based Clinical Assessment of Optic Nerve Head Robustness Superseding Biomechanical Testing
Jun 09, 2022
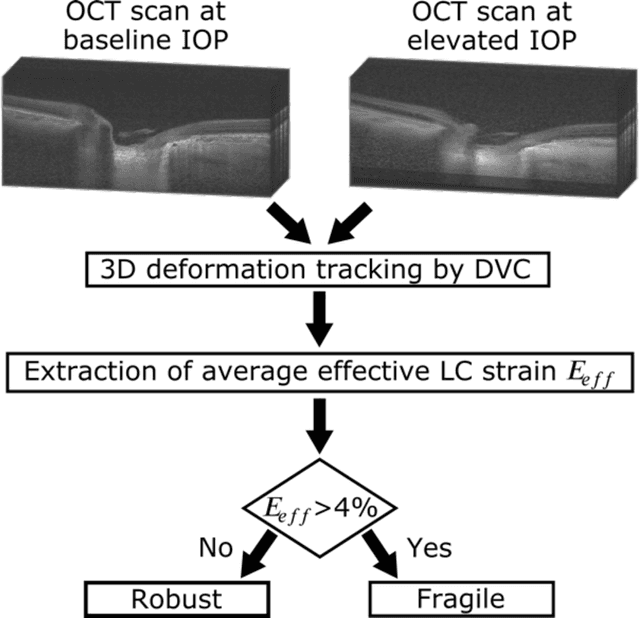
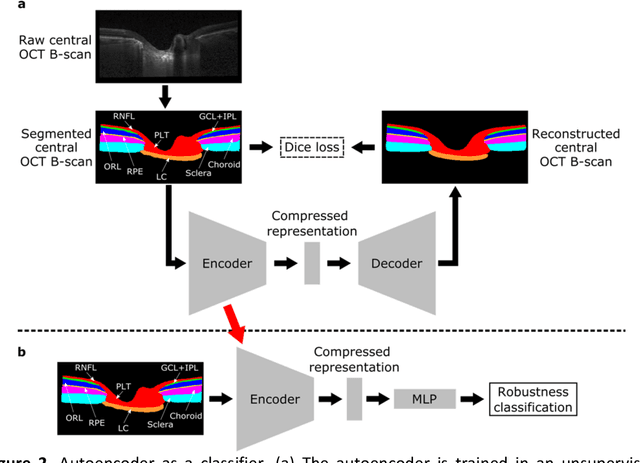
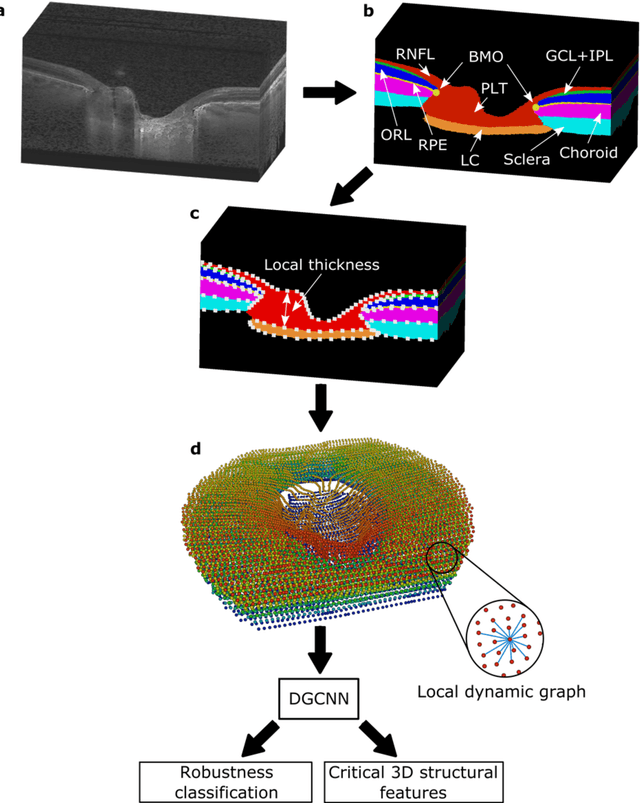
Abstract:$\mathbf{Purpose}$: To use artificial intelligence (AI) to: (1) exploit biomechanical knowledge of the optic nerve head (ONH) from a relatively large population; (2) assess ONH robustness from a single optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan of the ONH; (3) identify what critical three-dimensional (3D) structural features make a given ONH robust. $\mathbf{Design}$: Retrospective cross-sectional study. $\mathbf{Methods}$: 316 subjects had their ONHs imaged with OCT before and after acute intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation through ophthalmo-dynamometry. IOP-induced lamina-cribrosa deformations were then mapped in 3D and used to classify ONHs. Those with LC deformations superior to 4% were considered fragile, while those with deformations inferior to 4% robust. Learning from these data, we compared three AI algorithms to predict ONH robustness strictly from a baseline (undeformed) OCT volume: (1) a random forest classifier; (2) an autoencoder; and (3) a dynamic graph CNN (DGCNN). The latter algorithm also allowed us to identify what critical 3D structural features make a given ONH robust. $\mathbf{Results}$: All 3 methods were able to predict ONH robustness from 3D structural information alone and without the need to perform biomechanical testing. The DGCNN (area under the receiver operating curve [AUC]: 0.76 $\pm$ 0.08) outperformed the autoencoder (AUC: 0.70 $\pm$ 0.07) and the random forest classifier (AUC: 0.69 $\pm$ 0.05). Interestingly, to assess ONH robustness, the DGCNN mainly used information from the scleral canal and the LC insertion sites. $\mathbf{Conclusions}$: We propose an AI-driven approach that can assess the robustness of a given ONH solely from a single OCT scan of the ONH, and without the need to perform biomechanical testing. Longitudinal studies should establish whether ONH robustness could help us identify fast visual field loss progressors.
Geometric Deep Learning to Identify the Critical 3D Structural Features of the Optic Nerve Head for Glaucoma Diagnosis
Apr 20, 2022

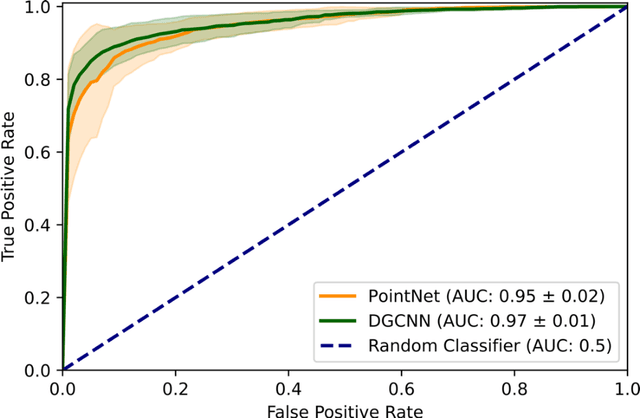

Abstract:Purpose: The optic nerve head (ONH) undergoes complex and deep 3D morphological changes during the development and progression of glaucoma. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is the current gold standard to visualize and quantify these changes, however the resulting 3D deep-tissue information has not yet been fully exploited for the diagnosis and prognosis of glaucoma. To this end, we aimed: (1) To compare the performance of two relatively recent geometric deep learning techniques in diagnosing glaucoma from a single OCT scan of the ONH; and (2) To identify the 3D structural features of the ONH that are critical for the diagnosis of glaucoma. Methods: In this study, we included a total of 2,247 non-glaucoma and 2,259 glaucoma scans from 1,725 subjects. All subjects had their ONHs imaged in 3D with Spectralis OCT. All OCT scans were automatically segmented using deep learning to identify major neural and connective tissues. Each ONH was then represented as a 3D point cloud. We used PointNet and dynamic graph convolutional neural network (DGCNN) to diagnose glaucoma from such 3D ONH point clouds and to identify the critical 3D structural features of the ONH for glaucoma diagnosis. Results: Both the DGCNN (AUC: 0.97$\pm$0.01) and PointNet (AUC: 0.95$\pm$0.02) were able to accurately detect glaucoma from 3D ONH point clouds. The critical points formed an hourglass pattern with most of them located in the inferior and superior quadrant of the ONH. Discussion: The diagnostic accuracy of both geometric deep learning approaches was excellent. Moreover, we were able to identify the critical 3D structural features of the ONH for glaucoma diagnosis that tremendously improved the transparency and interpretability of our method. Consequently, our approach may have strong potential to be used in clinical applications for the diagnosis and prognosis of a wide range of ophthalmic disorders.
Medical Application of Geometric Deep Learning for the Diagnosis of Glaucoma
Apr 14, 2022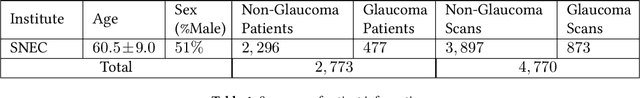
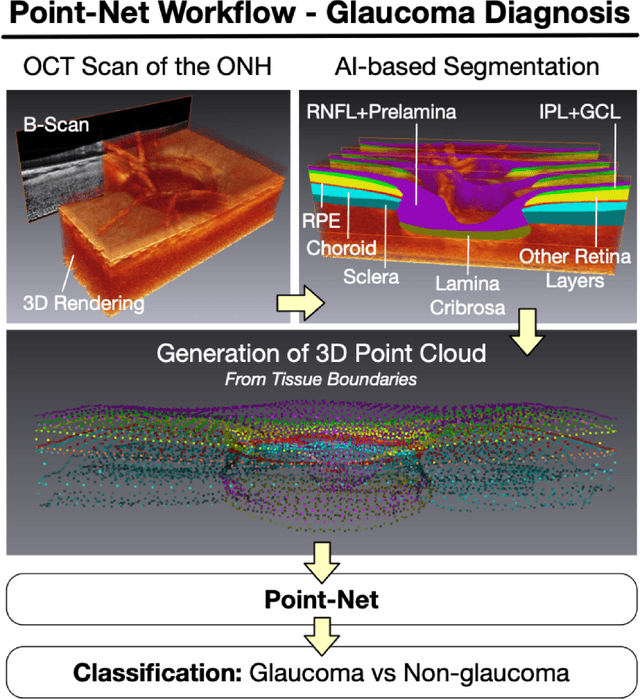
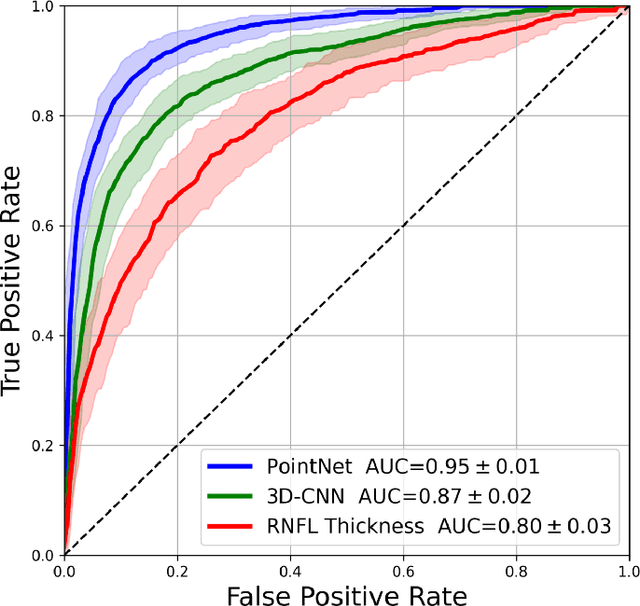
Abstract:Purpose: (1) To assess the performance of geometric deep learning (PointNet) in diagnosing glaucoma from a single optical coherence tomography (OCT) 3D scan of the optic nerve head (ONH); (2) To compare its performance to that obtained with a standard 3D convolutional neural network (CNN), and with a gold-standard glaucoma parameter, i.e. retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness. Methods: 3D raster scans of the ONH were acquired with Spectralis OCT for 477 glaucoma and 2,296 non-glaucoma subjects at the Singapore National Eye Centre. All volumes were automatically segmented using deep learning to identify 7 major neural and connective tissues including the RNFL, the prelamina, and the lamina cribrosa (LC). Each ONH was then represented as a 3D point cloud with 1,000 points chosen randomly from all tissue boundaries. To simplify the problem, all ONH point clouds were aligned with respect to the plane and center of Bruch's membrane opening. Geometric deep learning (PointNet) was then used to provide a glaucoma diagnosis from a single OCT point cloud. The performance of our approach was compared to that obtained with a 3D CNN, and with RNFL thickness. Results: PointNet was able to provide a robust glaucoma diagnosis solely from the ONH represented as a 3D point cloud (AUC=95%). The performance of PointNet was superior to that obtained with a standard 3D CNN (AUC=87%) and with that obtained from RNFL thickness alone (AUC=80%). Discussion: We provide a proof-of-principle for the application of geometric deep learning in the field of glaucoma. Our technique requires significantly less information as input to perform better than a 3D CNN, and with an AUC superior to that obtained from RNFL thickness alone. Geometric deep learning may have wide applicability in the field of Ophthalmology.
The Three-Dimensional Structural Configuration of the Central Retinal Vessel Trunk and Branches as a Glaucoma Biomarker
Nov 09, 2021
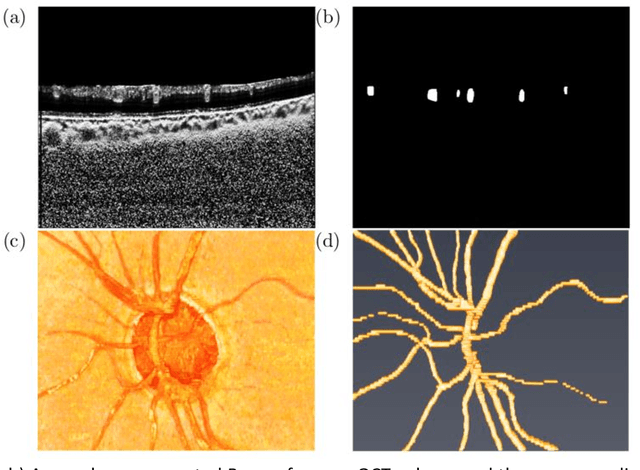
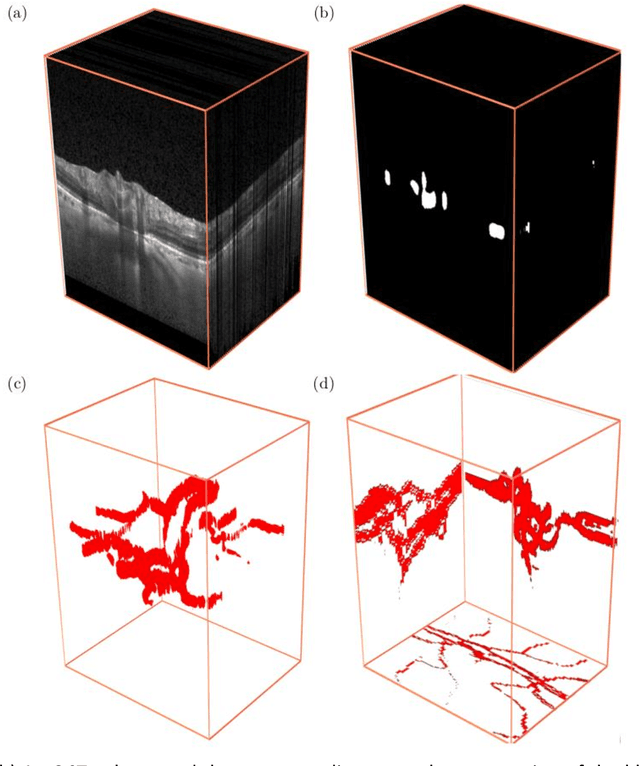

Abstract:Purpose: To assess whether the three-dimensional (3D) structural configuration of the central retinal vessel trunk and its branches (CRVT&B) could be used as a diagnostic marker for glaucoma. Method: We trained a deep learning network to automatically segment the CRVT&B from the B-scans of the optical coherence tomography (OCT) volume of the optic nerve head (ONH). Subsequently, two different approaches were used for glaucoma diagnosis using the structural configuration of the CRVT&B as extracted from the OCT volumes. In the first approach, we aimed to provide a diagnosis using only 3D CNN and the 3D structure of the CRVT&B. For the second approach, we projected the 3D structure of the CRVT&B orthographically onto three planes to obtain 2D images, and then a 2D CNN was used for diagnosis. The segmentation accuracy was evaluated using the Dice coefficient, whereas the diagnostic accuracy was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC). The diagnostic performance of the CRVT&B was also compared with that of retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness. Results: Our segmentation network was able to efficiently segment retinal blood vessels from OCT scans. On a test set, we achieved a Dice coefficient of 0.81\pm0.07. The 3D and 2D diagnostic networks were able to differentiate glaucoma from non-glaucoma subjects with accuracies of 82.7% and 83.3%, respectively. The corresponding AUCs for CRVT&B were 0.89 and 0.90, higher than those obtained with RNFL thickness alone. Conclusions: Our work demonstrated that the diagnostic power of the CRVT&B is superior to that of a gold-standard glaucoma parameter, i.e., RNFL thickness. Our work also suggested that the major retinal blood vessels form a skeleton -- the configuration of which may be representative of major ONH structural changes as typically observed with the development and progression of glaucoma.
Describing the Structural Phenotype of the Glaucomatous Optic Nerve Head Using Artificial Intelligence
Dec 17, 2020
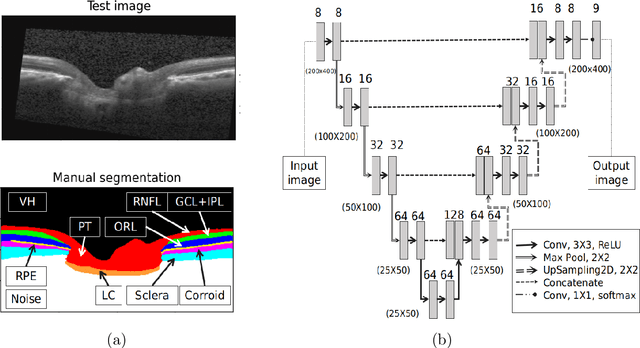
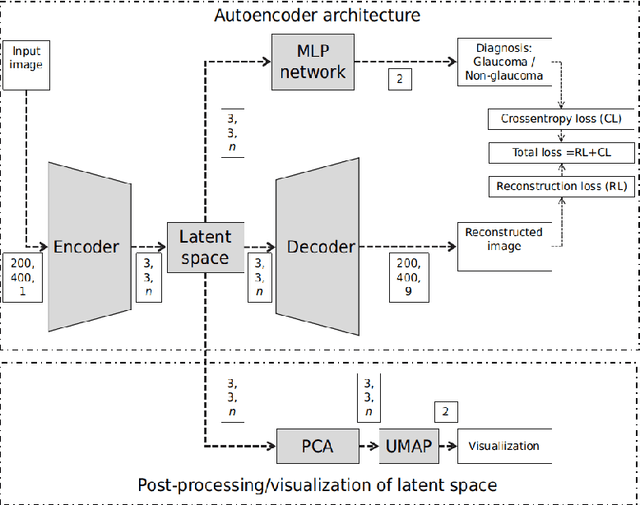

Abstract:The optic nerve head (ONH) typically experiences complex neural- and connective-tissue structural changes with the development and progression of glaucoma, and monitoring these changes could be critical for improved diagnosis and prognosis in the glaucoma clinic. The gold-standard technique to assess structural changes of the ONH clinically is optical coherence tomography (OCT). However, OCT is limited to the measurement of a few hand-engineered parameters, such as the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL), and has not yet been qualified as a stand-alone device for glaucoma diagnosis and prognosis applications. We argue this is because the vast amount of information available in a 3D OCT scan of the ONH has not been fully exploited. In this study we propose a deep learning approach that can: \textbf{(1)} fully exploit information from an OCT scan of the ONH; \textbf{(2)} describe the structural phenotype of the glaucomatous ONH; and that can \textbf{(3)} be used as a robust glaucoma diagnosis tool. Specifically, the structural features identified by our algorithm were found to be related to clinical observations of glaucoma. The diagnostic accuracy from these structural features was $92.0 \pm 2.3 \%$ with a sensitivity of $90.0 \pm 2.4 \% $ (at $95 \%$ specificity). By changing their magnitudes in steps, we were able to reveal how the morphology of the ONH changes as one transitions from a `non-glaucoma' to a `glaucoma' condition. We believe our work may have strong clinical implication for our understanding of glaucoma pathogenesis, and could be improved in the future to also predict future loss of vision.
OCT-GAN: Single Step Shadow and Noise Removal from Optical Coherence Tomography Images of the Human Optic Nerve Head
Oct 06, 2020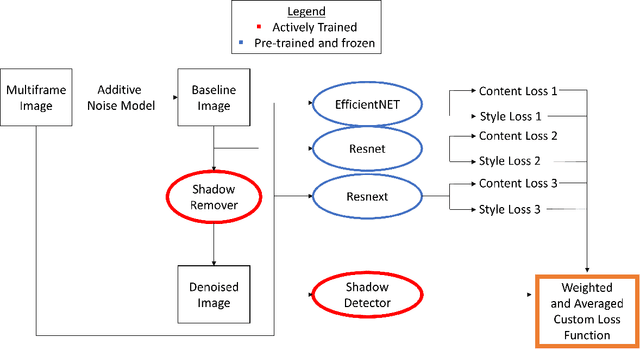
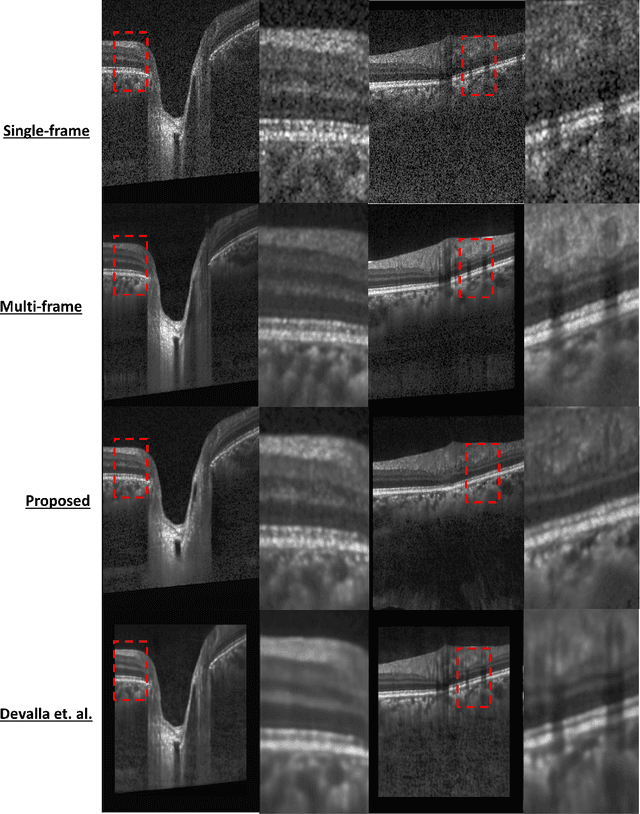
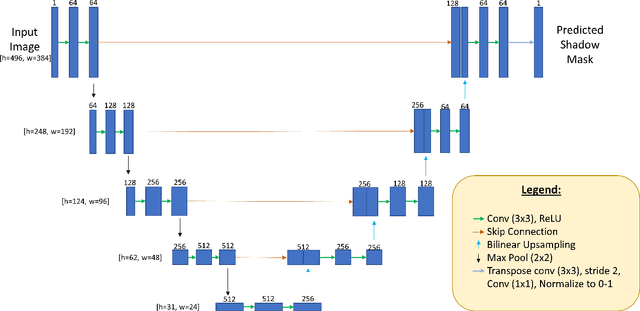
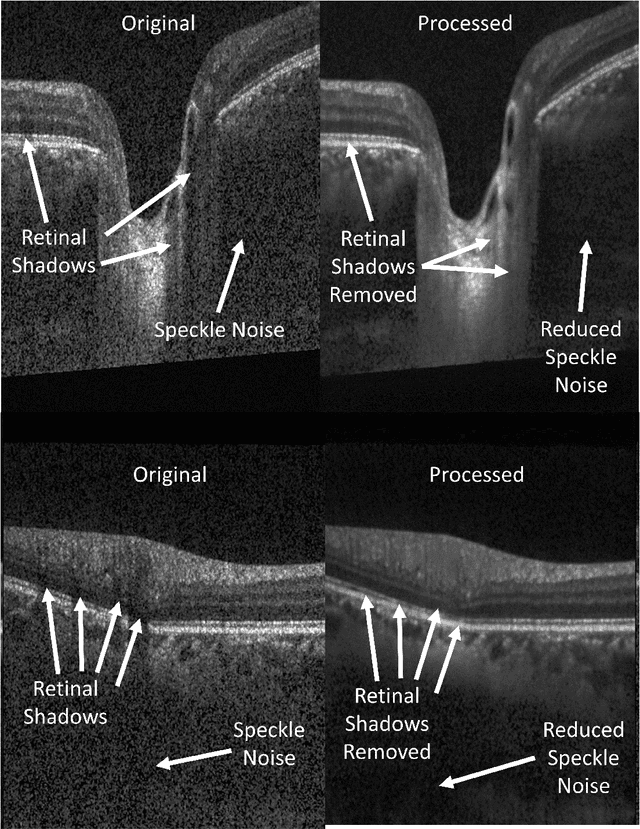

Abstract:Speckle noise and retinal shadows within OCT B-scans occlude important edges, fine textures and deep tissues, preventing accurate and robust diagnosis by algorithms and clinicians. We developed a single process that successfully removed both noise and retinal shadows from unseen single-frame B-scans within 10.4ms. Mean average gradient magnitude (AGM) for the proposed algorithm was 57.2% higher than current state-of-the-art, while mean peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), contrast to noise ratio (CNR), and structural similarity index metric (SSIM) increased by 11.1%, 154% and 187% respectively compared to single-frame B-scans. Mean intralayer contrast (ILC) improvement for the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL), photoreceptor layer (PR) and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) layers decreased from 0.362 \pm 0.133 to 0.142 \pm 0.102, 0.449 \pm 0.116 to 0.0904 \pm 0.0769, 0.381 \pm 0.100 to 0.0590 \pm 0.0451 respectively. The proposed algorithm reduces the necessity for long image acquisition times, minimizes expensive hardware requirements and reduces motion artifacts in OCT images.
Towards Label-Free 3D Segmentation of Optical Coherence Tomography Images of the Optic Nerve Head Using Deep Learning
Feb 22, 2020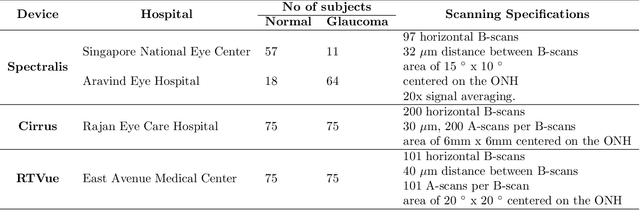
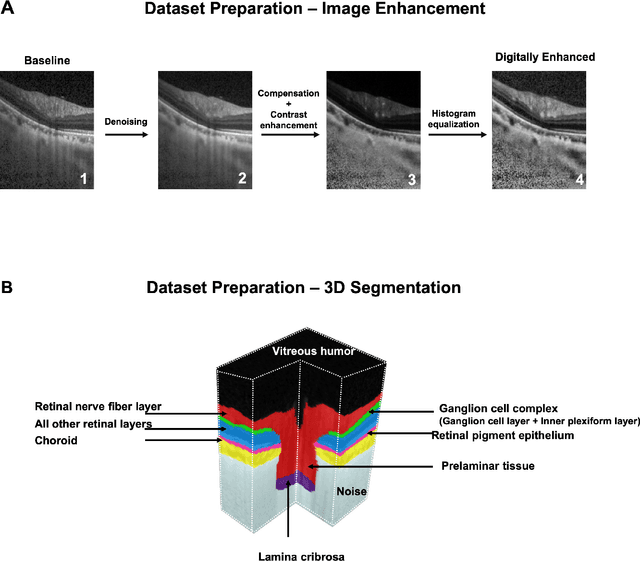
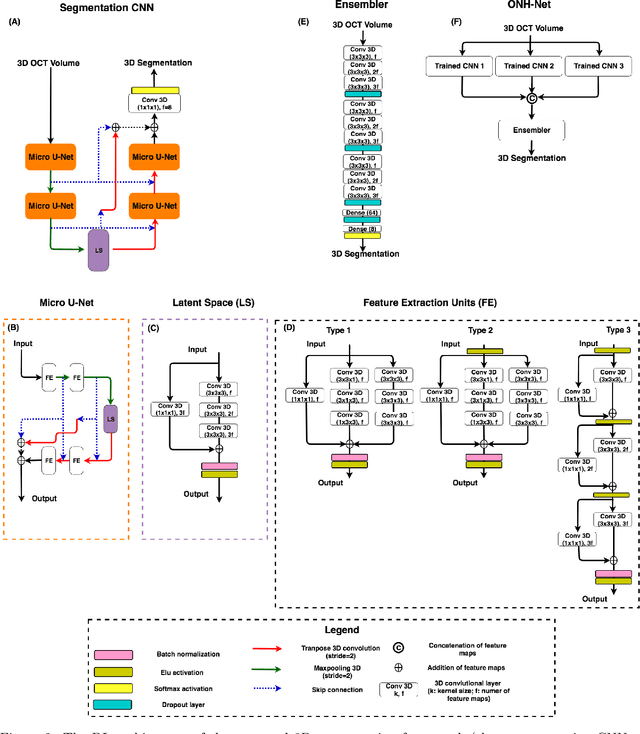
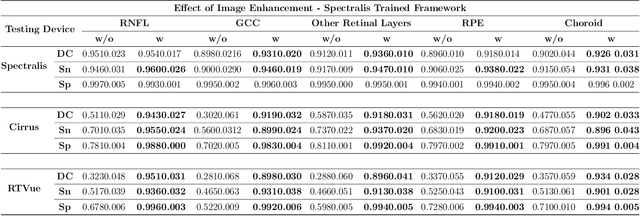
Abstract:Since the introduction of optical coherence tomography (OCT), it has been possible to study the complex 3D morphological changes of the optic nerve head (ONH) tissues that occur along with the progression of glaucoma. Although several deep learning (DL) techniques have been recently proposed for the automated extraction (segmentation) and quantification of these morphological changes, the device specific nature and the difficulty in preparing manual segmentations (training data) limit their clinical adoption. With several new manufacturers and next-generation OCT devices entering the market, the complexity in deploying DL algorithms clinically is only increasing. To address this, we propose a DL based 3D segmentation framework that is easily translatable across OCT devices in a label-free manner (i.e. without the need to manually re-segment data for each device). Specifically, we developed 2 sets of DL networks. The first (referred to as the enhancer) was able to enhance OCT image quality from 3 OCT devices, and harmonized image-characteristics across these devices. The second performed 3D segmentation of 6 important ONH tissue layers. We found that the use of the enhancer was critical for our segmentation network to achieve device independency. In other words, our 3D segmentation network trained on any of 3 devices successfully segmented ONH tissue layers from the other two devices with high performance (Dice coefficients > 0.92). With such an approach, we could automatically segment images from new OCT devices without ever needing manual segmentation data from such devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge