AI-based Clinical Assessment of Optic Nerve Head Robustness Superseding Biomechanical Testing
Paper and Code
Jun 09, 2022
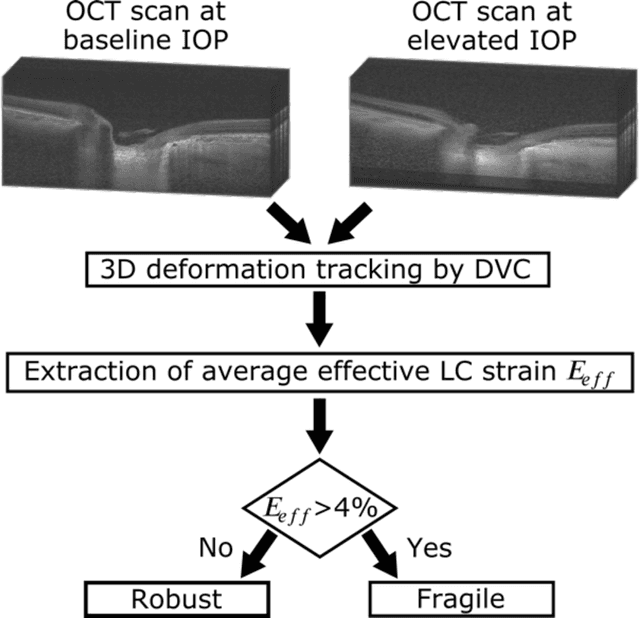
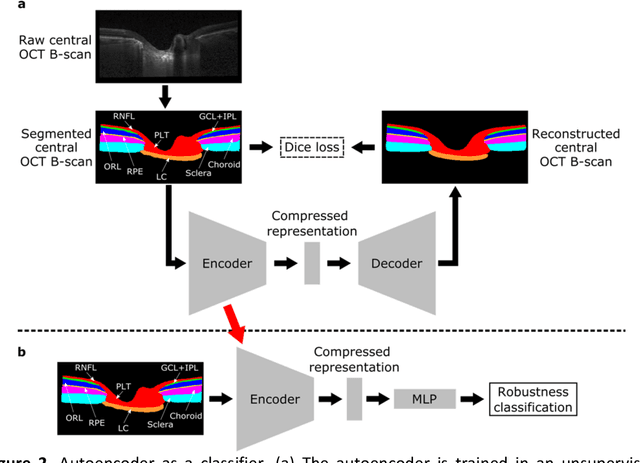
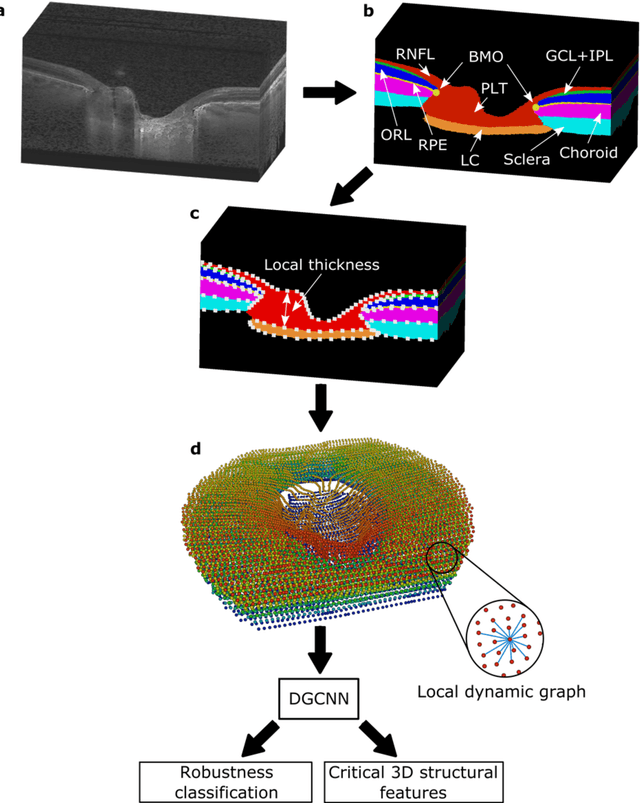
$\mathbf{Purpose}$: To use artificial intelligence (AI) to: (1) exploit biomechanical knowledge of the optic nerve head (ONH) from a relatively large population; (2) assess ONH robustness from a single optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan of the ONH; (3) identify what critical three-dimensional (3D) structural features make a given ONH robust. $\mathbf{Design}$: Retrospective cross-sectional study. $\mathbf{Methods}$: 316 subjects had their ONHs imaged with OCT before and after acute intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation through ophthalmo-dynamometry. IOP-induced lamina-cribrosa deformations were then mapped in 3D and used to classify ONHs. Those with LC deformations superior to 4% were considered fragile, while those with deformations inferior to 4% robust. Learning from these data, we compared three AI algorithms to predict ONH robustness strictly from a baseline (undeformed) OCT volume: (1) a random forest classifier; (2) an autoencoder; and (3) a dynamic graph CNN (DGCNN). The latter algorithm also allowed us to identify what critical 3D structural features make a given ONH robust. $\mathbf{Results}$: All 3 methods were able to predict ONH robustness from 3D structural information alone and without the need to perform biomechanical testing. The DGCNN (area under the receiver operating curve [AUC]: 0.76 $\pm$ 0.08) outperformed the autoencoder (AUC: 0.70 $\pm$ 0.07) and the random forest classifier (AUC: 0.69 $\pm$ 0.05). Interestingly, to assess ONH robustness, the DGCNN mainly used information from the scleral canal and the LC insertion sites. $\mathbf{Conclusions}$: We propose an AI-driven approach that can assess the robustness of a given ONH solely from a single OCT scan of the ONH, and without the need to perform biomechanical testing. Longitudinal studies should establish whether ONH robustness could help us identify fast visual field loss progressors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge