Michael J. A. Girard
Medical Application of Geometric Deep Learning for the Diagnosis of Glaucoma
Apr 14, 2022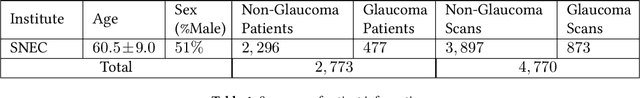
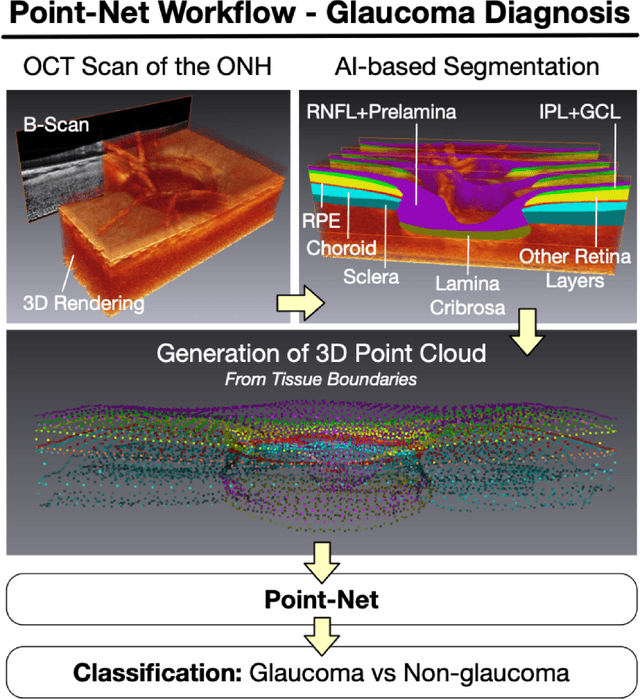
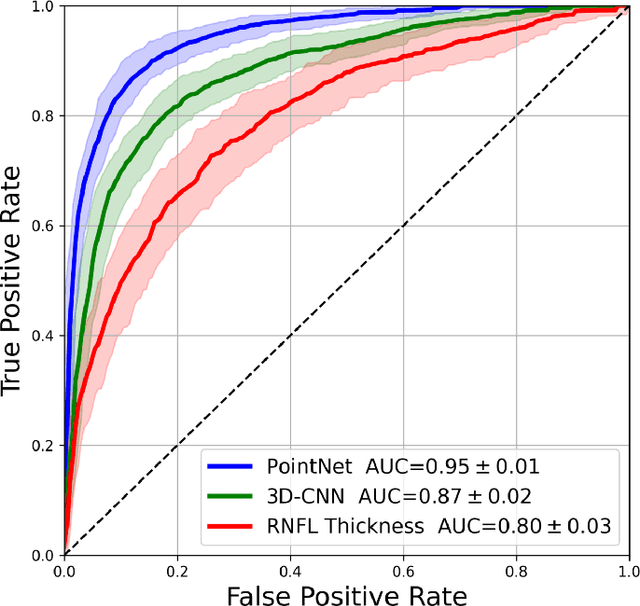
Abstract:Purpose: (1) To assess the performance of geometric deep learning (PointNet) in diagnosing glaucoma from a single optical coherence tomography (OCT) 3D scan of the optic nerve head (ONH); (2) To compare its performance to that obtained with a standard 3D convolutional neural network (CNN), and with a gold-standard glaucoma parameter, i.e. retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness. Methods: 3D raster scans of the ONH were acquired with Spectralis OCT for 477 glaucoma and 2,296 non-glaucoma subjects at the Singapore National Eye Centre. All volumes were automatically segmented using deep learning to identify 7 major neural and connective tissues including the RNFL, the prelamina, and the lamina cribrosa (LC). Each ONH was then represented as a 3D point cloud with 1,000 points chosen randomly from all tissue boundaries. To simplify the problem, all ONH point clouds were aligned with respect to the plane and center of Bruch's membrane opening. Geometric deep learning (PointNet) was then used to provide a glaucoma diagnosis from a single OCT point cloud. The performance of our approach was compared to that obtained with a 3D CNN, and with RNFL thickness. Results: PointNet was able to provide a robust glaucoma diagnosis solely from the ONH represented as a 3D point cloud (AUC=95%). The performance of PointNet was superior to that obtained with a standard 3D CNN (AUC=87%) and with that obtained from RNFL thickness alone (AUC=80%). Discussion: We provide a proof-of-principle for the application of geometric deep learning in the field of glaucoma. Our technique requires significantly less information as input to perform better than a 3D CNN, and with an AUC superior to that obtained from RNFL thickness alone. Geometric deep learning may have wide applicability in the field of Ophthalmology.
Explainable and Interpretable Diabetic Retinopathy Classification Based on Neural-Symbolic Learning
Apr 01, 2022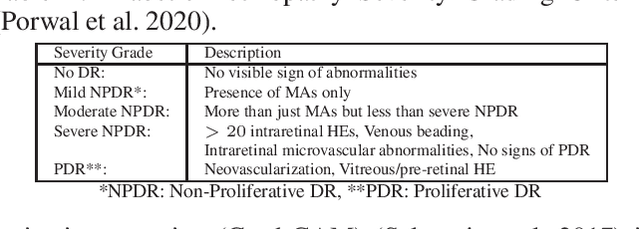
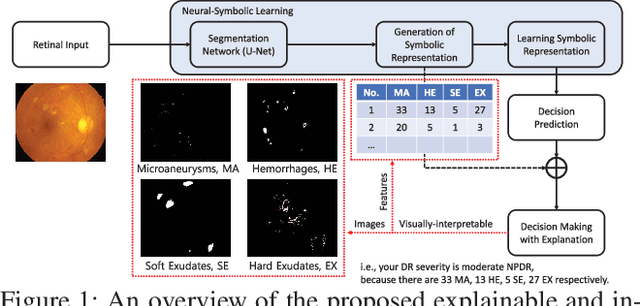
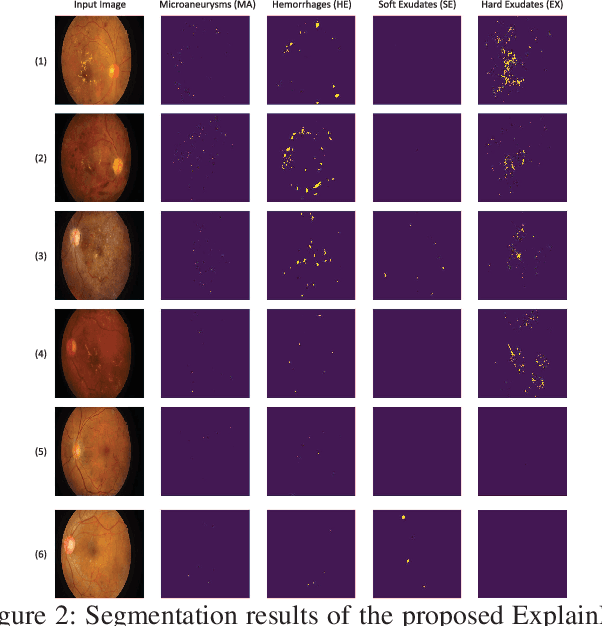

Abstract:In this paper, we propose an explainable and interpretable diabetic retinopathy (ExplainDR) classification model based on neural-symbolic learning. To gain explainability, a highlevel symbolic representation should be considered in decision making. Specifically, we introduce a human-readable symbolic representation, which follows a taxonomy style of diabetic retinopathy characteristics related to eye health conditions to achieve explainability. We then include humanreadable features obtained from the symbolic representation in the disease prediction. Experimental results on a diabetic retinopathy classification dataset show that our proposed ExplainDR method exhibits promising performance when compared to that from state-of-the-art methods applied to the IDRiD dataset, while also providing interpretability and explainability.
The Three-Dimensional Structural Configuration of the Central Retinal Vessel Trunk and Branches as a Glaucoma Biomarker
Nov 09, 2021
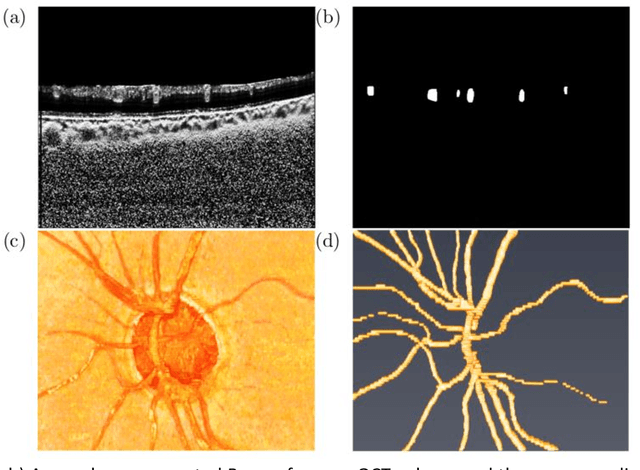
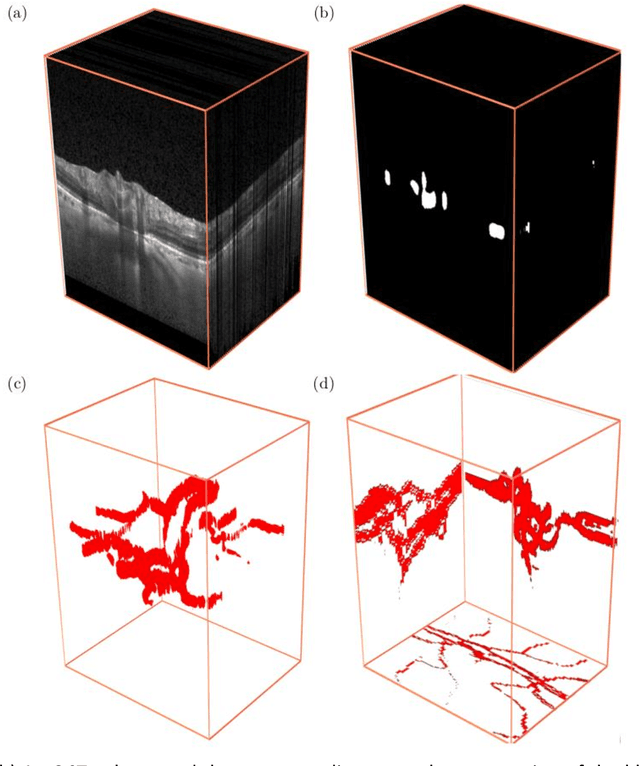

Abstract:Purpose: To assess whether the three-dimensional (3D) structural configuration of the central retinal vessel trunk and its branches (CRVT&B) could be used as a diagnostic marker for glaucoma. Method: We trained a deep learning network to automatically segment the CRVT&B from the B-scans of the optical coherence tomography (OCT) volume of the optic nerve head (ONH). Subsequently, two different approaches were used for glaucoma diagnosis using the structural configuration of the CRVT&B as extracted from the OCT volumes. In the first approach, we aimed to provide a diagnosis using only 3D CNN and the 3D structure of the CRVT&B. For the second approach, we projected the 3D structure of the CRVT&B orthographically onto three planes to obtain 2D images, and then a 2D CNN was used for diagnosis. The segmentation accuracy was evaluated using the Dice coefficient, whereas the diagnostic accuracy was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC). The diagnostic performance of the CRVT&B was also compared with that of retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness. Results: Our segmentation network was able to efficiently segment retinal blood vessels from OCT scans. On a test set, we achieved a Dice coefficient of 0.81\pm0.07. The 3D and 2D diagnostic networks were able to differentiate glaucoma from non-glaucoma subjects with accuracies of 82.7% and 83.3%, respectively. The corresponding AUCs for CRVT&B were 0.89 and 0.90, higher than those obtained with RNFL thickness alone. Conclusions: Our work demonstrated that the diagnostic power of the CRVT&B is superior to that of a gold-standard glaucoma parameter, i.e., RNFL thickness. Our work also suggested that the major retinal blood vessels form a skeleton -- the configuration of which may be representative of major ONH structural changes as typically observed with the development and progression of glaucoma.
DeshadowGAN: A Deep Learning Approach to Remove Shadows from Optical Coherence Tomography Images
Oct 07, 2019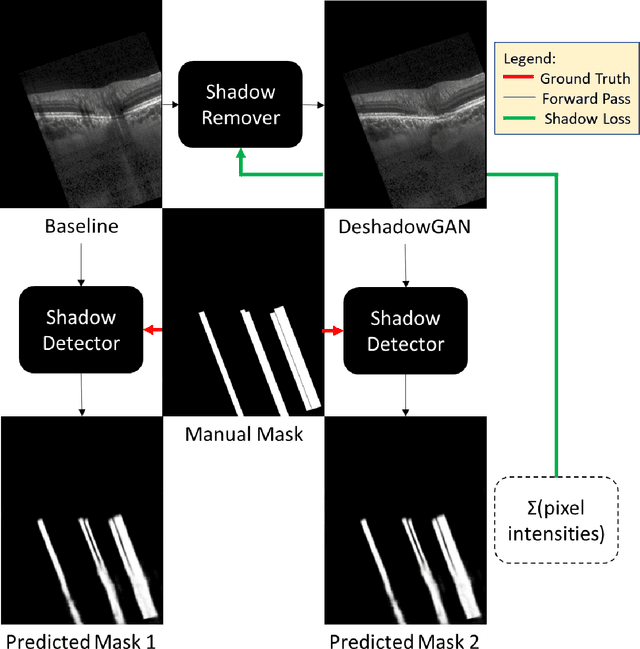
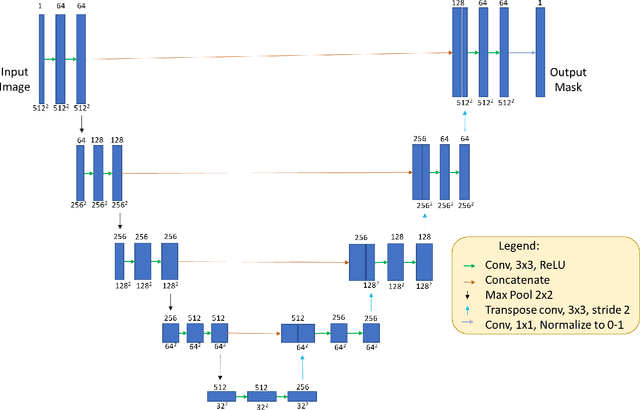
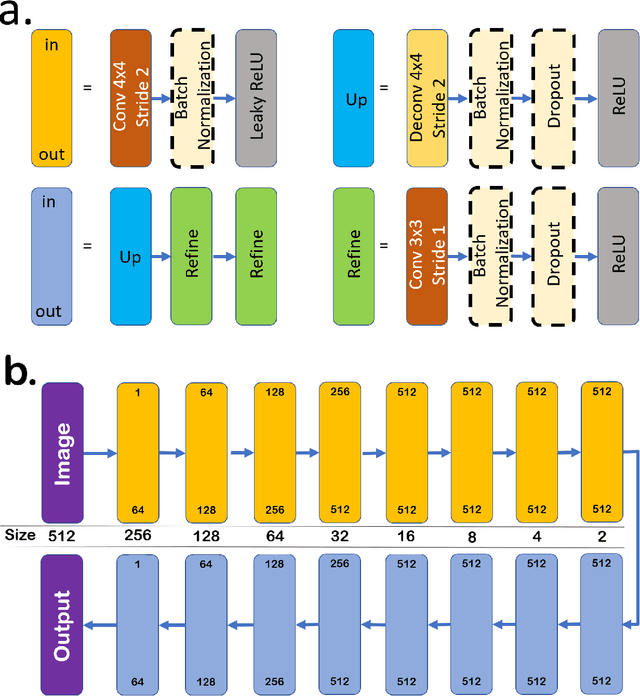
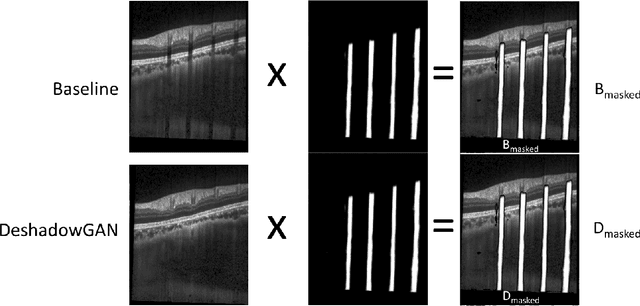
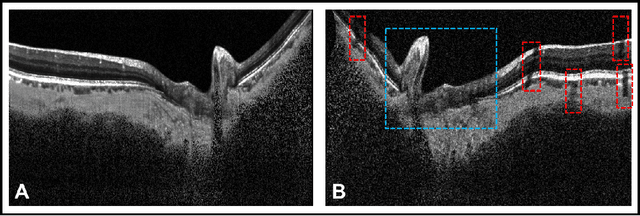
Abstract:Purpose: To remove retinal shadows from optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the optic nerve head(ONH). Methods:2328 OCT images acquired through the center of the ONH using a Spectralis OCT machine for both eyes of 13 subjects were used to train a generative adversarial network (GAN) using a custom loss function. Image quality was assessed qualitatively (for artifacts) and quantitatively using the intralayer contrast: a measure of shadow visibility ranging from 0 (shadow-free) to 1 (strong shadow) and compared to compensated images. This was computed in the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer (RNFL), the Inner Plexiform Layer (IPL), the Photoreceptor layer (PR) and the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) layers. Results: Output images had improved intralayer contrast in all ONH tissue layers. On average the intralayer contrast decreased by 33.7$\pm$6.81%, 28.8$\pm$10.4%, 35.9$\pm$13.0%, and43.0$\pm$19.5%for the RNFL, IPL, PR, and RPE layers respectively, indicating successful shadow removal across all depths. This compared to 70.3$\pm$22.7%, 33.9$\pm$11.5%, 47.0$\pm$11.2%, 26.7$\pm$19.0%for compensation. Output images were also free from artifacts commonly observed with compensation. Conclusions: DeshadowGAN significantly corrected blood vessel shadows in OCT images of the ONH. Our algorithm may be considered as a pre-processing step to improve the performance of a wide range of algorithms including those currently being used for OCT image segmentation, denoising, and classification. Translational Relevance: DeshadowGAN could be integrated to existing OCT devices to improve the diagnosis and prognosis of ocular pathologies.
Deep Learning Algorithms to Isolate and Quantify the Structures of the Anterior Segment in Optical Coherence Tomography Images
Sep 01, 2019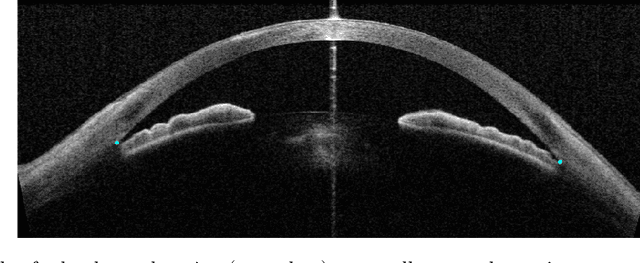
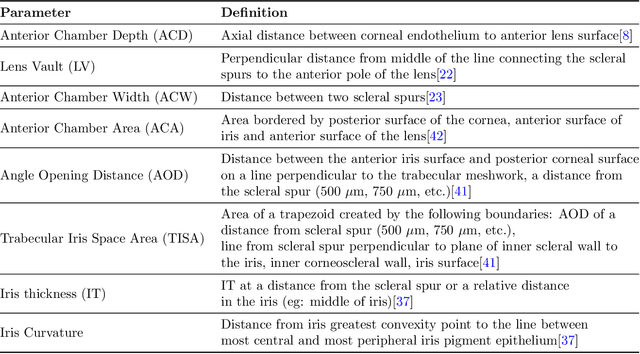
Abstract:Accurate isolation and quantification of intraocular dimensions in the anterior segment (AS) of the eye using optical coherence tomography (OCT) images is important in the diagnosis and treatment of many eye diseases, especially angle closure glaucoma. In this study, we developed a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) for the localization of the scleral spur, and the segmentation of anterior segment structures (iris, corneo-sclera shell, anterior chamber). With limited training data, the DCNN was able to detect the scleral spur on unseen ASOCT images as accurately as an experienced ophthalmologist; and simultaneously isolated the anterior segment structures with a Dice coefficient of 95.7%. We then automatically extracted eight clinically relevant ASOCT parameters and proposed an automated quality check process that asserts the reliability of these parameters. When combined with an OCT machine capable of imaging multiple radial sections, the algorithms can provide a more complete objective assessment. This is an essential step toward providing a robust automated framework for reliable quantification of ASOCT scans, for applications in the diagnosis and management of angle closure glaucoma.
A Deep Learning Approach to Denoise Optical Coherence Tomography Images of the Optic Nerve Head
Sep 27, 2018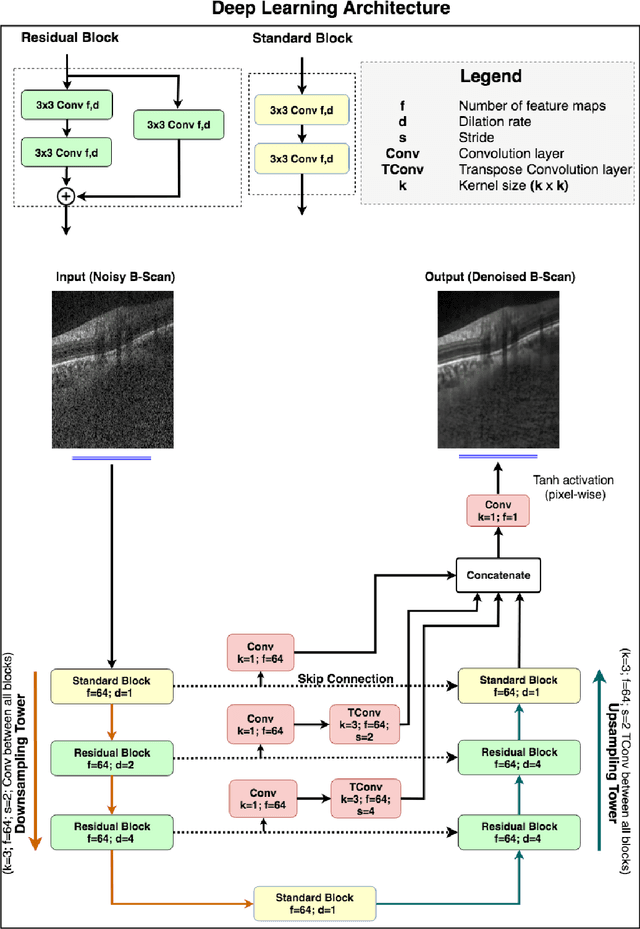
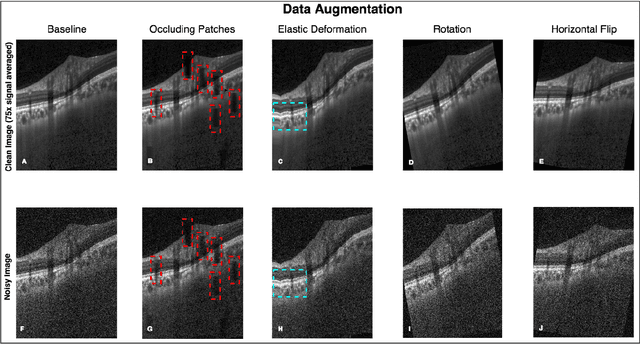
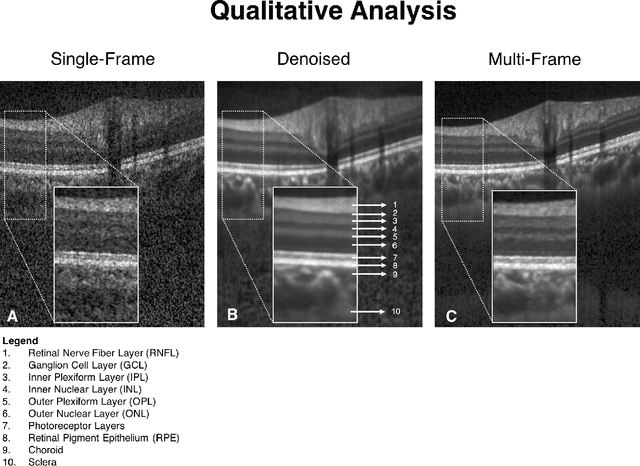
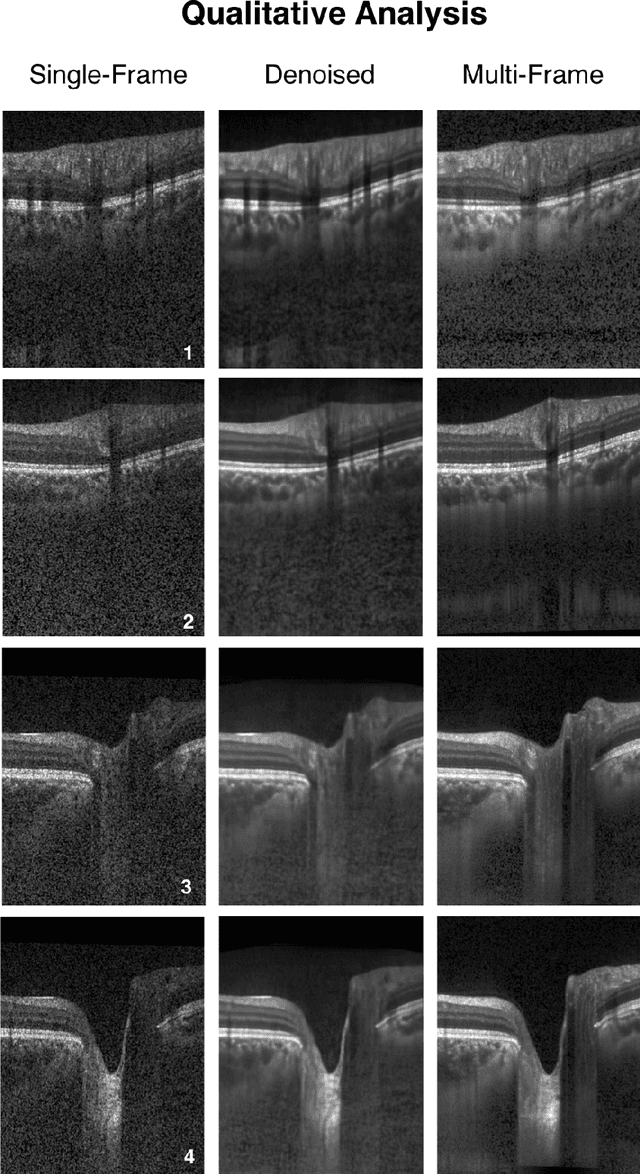
Abstract:Purpose: To develop a deep learning approach to de-noise optical coherence tomography (OCT) B-scans of the optic nerve head (ONH). Methods: Volume scans consisting of 97 horizontal B-scans were acquired through the center of the ONH using a commercial OCT device (Spectralis) for both eyes of 20 subjects. For each eye, single-frame (without signal averaging), and multi-frame (75x signal averaging) volume scans were obtained. A custom deep learning network was then designed and trained with 2,328 "clean B-scans" (multi-frame B-scans), and their corresponding "noisy B-scans" (clean B-scans + gaussian noise) to de-noise the single-frame B-scans. The performance of the de-noising algorithm was assessed qualitatively, and quantitatively on 1,552 B-scans using the signal to noise ratio (SNR), contrast to noise ratio (CNR), and mean structural similarity index metrics (MSSIM). Results: The proposed algorithm successfully denoised unseen single-frame OCT B-scans. The denoised B-scans were qualitatively similar to their corresponding multi-frame B-scans, with enhanced visibility of the ONH tissues. The mean SNR increased from $4.02 \pm 0.68$ dB (single-frame) to $8.14 \pm 1.03$ dB (denoised). For all the ONH tissues, the mean CNR increased from $3.50 \pm 0.56$ (single-frame) to $7.63 \pm 1.81$ (denoised). The MSSIM increased from $0.13 \pm 0.02$ (single frame) to $0.65 \pm 0.03$ (denoised) when compared with the corresponding multi-frame B-scans. Conclusions: Our deep learning algorithm can denoise a single-frame OCT B-scan of the ONH in under 20 ms, thus offering a framework to obtain superior quality OCT B-scans with reduced scanning times and minimal patient discomfort.
DRUNET: A Dilated-Residual U-Net Deep Learning Network to Digitally Stain Optic Nerve Head Tissues in Optical Coherence Tomography Images
Mar 01, 2018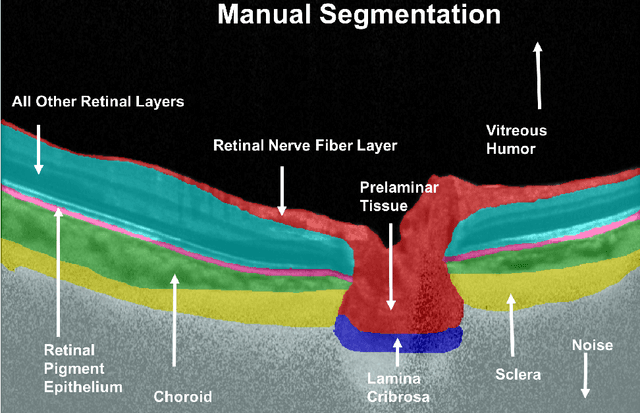
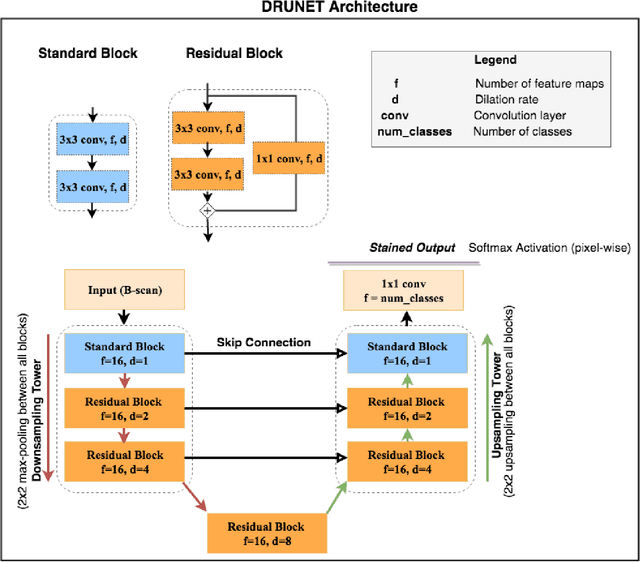
Abstract:Given that the neural and connective tissues of the optic nerve head (ONH) exhibit complex morphological changes with the development and progression of glaucoma, their simultaneous isolation from optical coherence tomography (OCT) images may be of great interest for the clinical diagnosis and management of this pathology. A deep learning algorithm was designed and trained to digitally stain (i.e. highlight) 6 ONH tissue layers by capturing both the local (tissue texture) and contextual information (spatial arrangement of tissues). The overall dice coefficient (mean of all tissues) was $0.91 \pm 0.05$ when assessed against manual segmentations performed by an expert observer. We offer here a robust segmentation framework that could be extended for the automated parametric study of the ONH tissues.
A Deep Learning Approach to Digitally Stain Optical Coherence Tomography Images of the Optic Nerve Head
Jul 24, 2017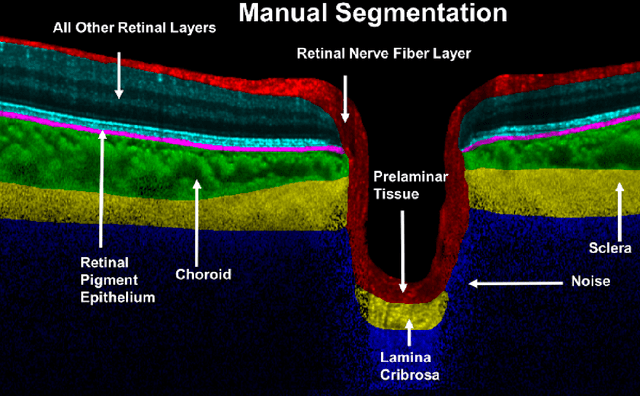
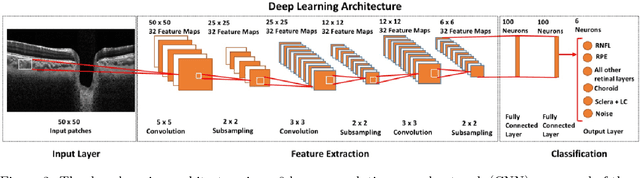
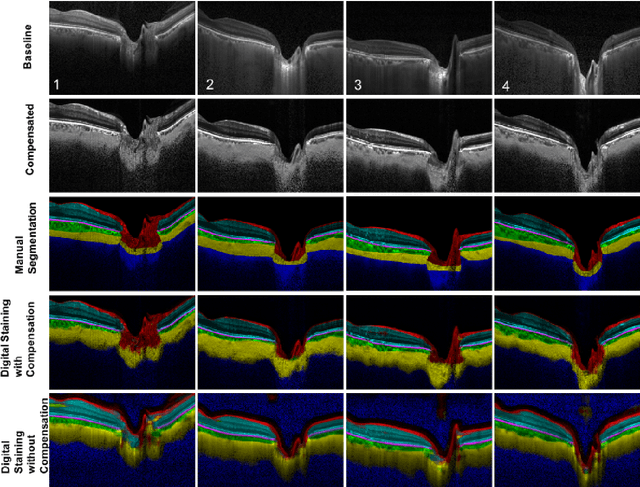
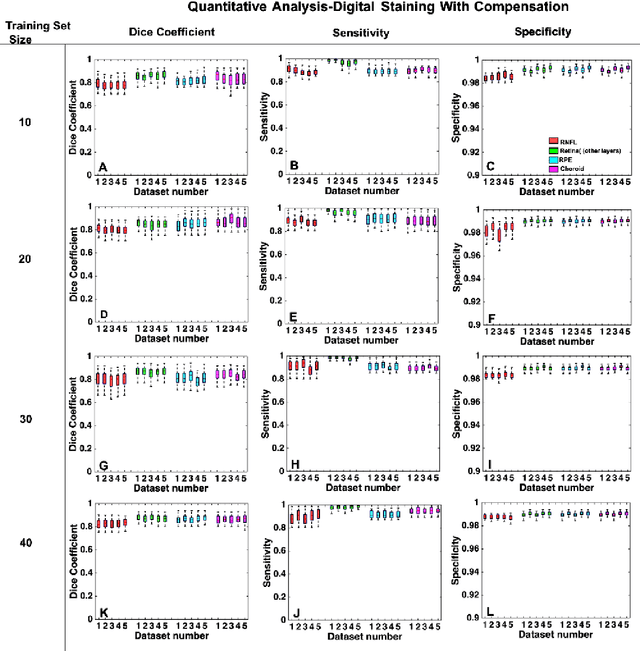
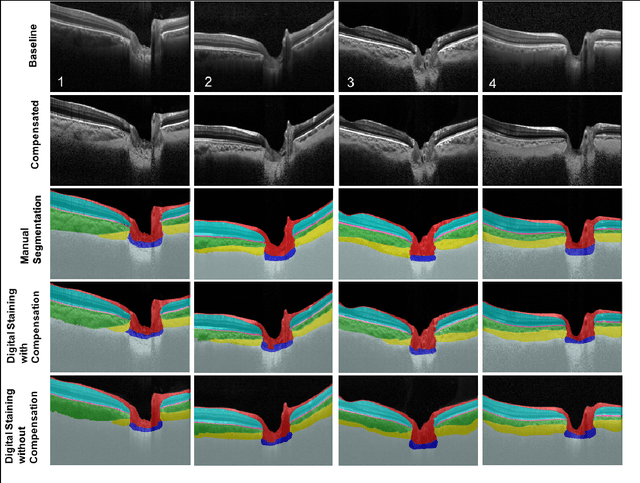
Abstract:Purpose: To develop a deep learning approach to digitally-stain optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the optic nerve head (ONH). Methods: A horizontal B-scan was acquired through the center of the ONH using OCT (Spectralis) for 1 eye of each of 100 subjects (40 normal & 60 glaucoma). All images were enhanced using adaptive compensation. A custom deep learning network was then designed and trained with the compensated images to digitally stain (i.e. highlight) 6 tissue layers of the ONH. The accuracy of our algorithm was assessed (against manual segmentations) using the Dice coefficient, sensitivity, and specificity. We further studied how compensation and the number of training images affected the performance of our algorithm. Results: For images it had not yet assessed, our algorithm was able to digitally stain the retinal nerve fiber layer + prelamina, the retinal pigment epithelium, all other retinal layers, the choroid, and the peripapillary sclera and lamina cribrosa. For all tissues, the mean dice coefficient was $0.84 \pm 0.03$, the mean sensitivity $0.92 \pm 0.03$, and the mean specificity $0.99 \pm 0.00$. Our algorithm performed significantly better when compensated images were used for training. Increasing the number of images (from 10 to 40) to train our algorithm did not significantly improve performance, except for the RPE. Conclusion. Our deep learning algorithm can simultaneously stain neural and connective tissues in ONH images. Our approach offers a framework to automatically measure multiple key structural parameters of the ONH that may be critical to improve glaucoma management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge