Tianli Liu
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Night Photography Rendering
Jun 18, 2024


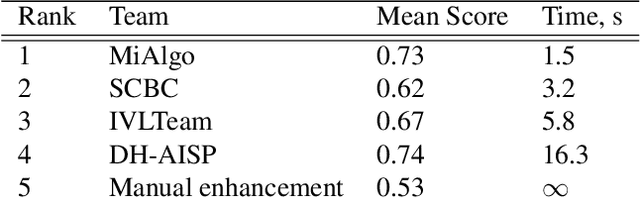
Abstract:This paper presents a review of the NTIRE 2024 challenge on night photography rendering. The goal of the challenge was to find solutions that process raw camera images taken in nighttime conditions, and thereby produce a photo-quality output images in the standard RGB (sRGB) space. Unlike the previous year's competition, the challenge images were collected with a mobile phone and the speed of algorithms was also measured alongside the quality of their output. To evaluate the results, a sufficient number of viewers were asked to assess the visual quality of the proposed solutions, considering the subjective nature of the task. There were 2 nominations: quality and efficiency. Top 5 solutions in terms of output quality were sorted by evaluation time (see Fig. 1). The top ranking participants' solutions effectively represent the state-of-the-art in nighttime photography rendering. More results can be found at https://nightimaging.org.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Low Light Image Enhancement: Methods and Results
Apr 22, 2024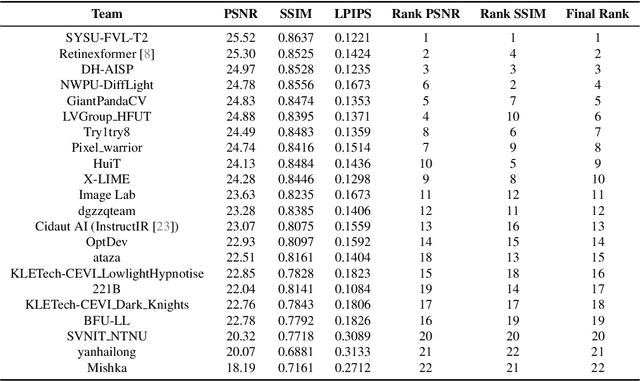

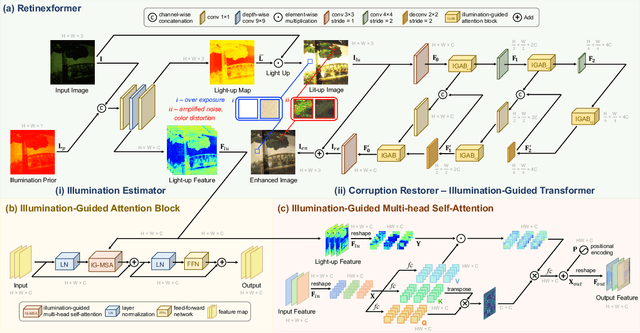

Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 low light image enhancement challenge, highlighting the proposed solutions and results. The aim of this challenge is to discover an effective network design or solution capable of generating brighter, clearer, and visually appealing results when dealing with a variety of conditions, including ultra-high resolution (4K and beyond), non-uniform illumination, backlighting, extreme darkness, and night scenes. A notable total of 428 participants registered for the challenge, with 22 teams ultimately making valid submissions. This paper meticulously evaluates the state-of-the-art advancements in enhancing low-light images, reflecting the significant progress and creativity in this field.
Using Linguistic Features to Estimate Suicide Probability of Chinese Microblog Users
Nov 04, 2014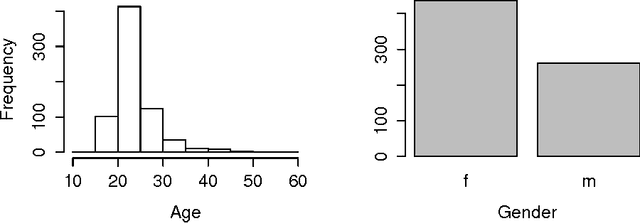

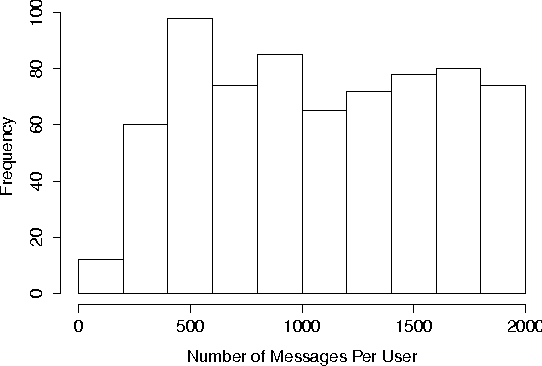
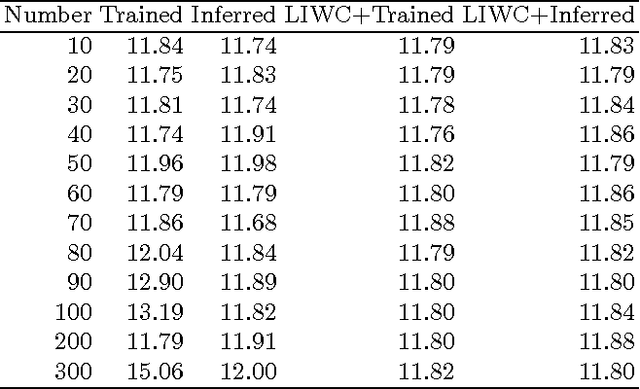
Abstract:If people with high risk of suicide can be identified through social media like microblog, it is possible to implement an active intervention system to save their lives. Based on this motivation, the current study administered the Suicide Probability Scale(SPS) to 1041 weibo users at Sina Weibo, which is a leading microblog service provider in China. Two NLP (Natural Language Processing) methods, the Chinese edition of Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC) lexicon and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), are used to extract linguistic features from the Sina Weibo data. We trained predicting models by machine learning algorithm based on these two types of features, to estimate suicide probability based on linguistic features. The experiment results indicate that LDA can find topics that relate to suicide probability, and improve the performance of prediction. Our study adds value in prediction of suicidal probability of social network users with their behaviors.
Detecting Suicidal Ideation in Chinese Microblogs with Psychological Lexicons
Nov 04, 2014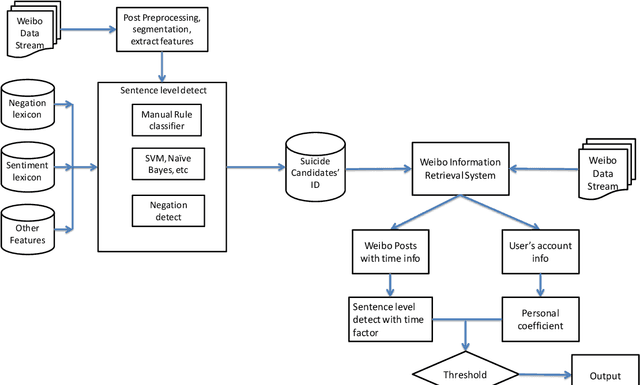
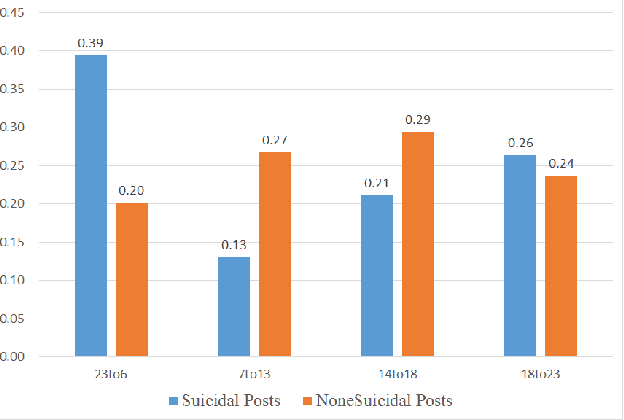
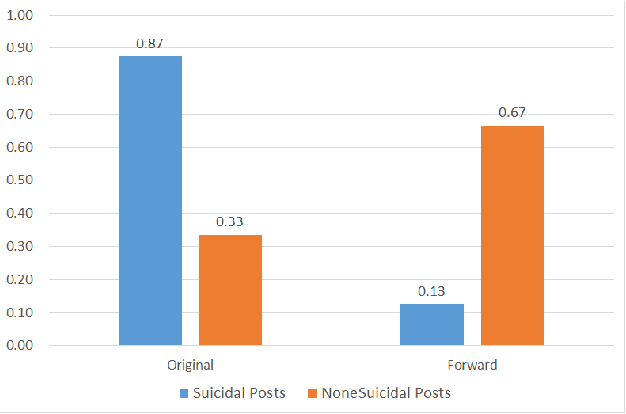
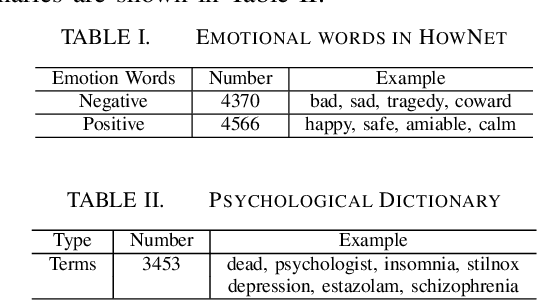
Abstract:Suicide is among the leading causes of death in China. However, technical approaches toward preventing suicide are challenging and remaining under development. Recently, several actual suicidal cases were preceded by users who posted microblogs with suicidal ideation to Sina Weibo, a Chinese social media network akin to Twitter. It would therefore be desirable to detect suicidal ideations from microblogs in real-time, and immediately alert appropriate support groups, which may lead to successful prevention. In this paper, we propose a real-time suicidal ideation detection system deployed over Weibo, using machine learning and known psychological techniques. Currently, we have identified 53 known suicidal cases who posted suicide notes on Weibo prior to their deaths.We explore linguistic features of these known cases using a psychological lexicon dictionary, and train an effective suicidal Weibo post detection model. 6714 tagged posts and several classifiers are used to verify the model. By combining both machine learning and psychological knowledge, SVM classifier has the best performance of different classifiers, yielding an F-measure of 68:3%, a Precision of 78:9%, and a Recall of 60:3%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge