Dmitrii Iarchuk
HapticVLM: VLM-Driven Texture Recognition Aimed at Intelligent Haptic Interaction
May 05, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces HapticVLM, a novel multimodal system that integrates vision-language reasoning with deep convolutional networks to enable real-time haptic feedback. HapticVLM leverages a ConvNeXt-based material recognition module to generate robust visual embeddings for accurate identification of object materials, while a state-of-the-art Vision-Language Model (Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct) infers ambient temperature from environmental cues. The system synthesizes tactile sensations by delivering vibrotactile feedback through speakers and thermal cues via a Peltier module, thereby bridging the gap between visual perception and tactile experience. Experimental evaluations demonstrate an average recognition accuracy of 84.67% across five distinct auditory-tactile patterns and a temperature estimation accuracy of 86.7% based on a tolerance-based evaluation method with an 8{\deg}C margin of error across 15 scenarios. Although promising, the current study is limited by the use of a small set of prominent patterns and a modest participant pool. Future work will focus on expanding the range of tactile patterns and increasing user studies to further refine and validate the system's performance. Overall, HapticVLM presents a significant step toward context-aware, multimodal haptic interaction with potential applications in virtual reality, and assistive technologies.
Shake-VLA: Vision-Language-Action Model-Based System for Bimanual Robotic Manipulations and Liquid Mixing
Jan 12, 2025


Abstract:This paper introduces Shake-VLA, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model-based system designed to enable bimanual robotic manipulation for automated cocktail preparation. The system integrates a vision module for detecting ingredient bottles and reading labels, a speech-to-text module for interpreting user commands, and a language model to generate task-specific robotic instructions. Force Torque (FT) sensors are employed to precisely measure the quantity of liquid poured, ensuring accuracy in ingredient proportions during the mixing process. The system architecture includes a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) module for accessing and adapting recipes, an anomaly detection mechanism to address ingredient availability issues, and bimanual robotic arms for dexterous manipulation. Experimental evaluations demonstrated a high success rate across system components, with the speech-to-text module achieving a 93% success rate in noisy environments, the vision module attaining a 91% success rate in object and label detection in cluttered environment, the anomaly module successfully identified 95% of discrepancies between detected ingredients and recipe requirements, and the system achieved an overall success rate of 100% in preparing cocktails, from recipe formulation to action generation.
Expert-aware uncertainty estimation for quality control of neural-based blood typing
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:In medical diagnostics, accurate uncertainty estimation for neural-based models is essential for complementing second-opinion systems. Despite neural network ensembles' proficiency in this problem, a gap persists between actual uncertainties and predicted estimates. A major difficulty here is the lack of labels on the hardness of examples: a typical dataset includes only ground truth target labels, making the uncertainty estimation problem almost unsupervised. Our novel approach narrows this gap by integrating expert assessments of case complexity into the neural network's learning process, utilizing both definitive target labels and supplementary complexity ratings. We validate our methodology for blood typing, leveraging a new dataset "BloodyWell" unique in augmenting labeled reaction images with complexity scores from six medical specialists. Experiments demonstrate enhancement of our approach in uncertainty prediction, achieving a 2.5-fold improvement with expert labels and a 35% increase in performance with estimates of neural-based expert consensus.
NTIRE 2024 Challenge on Night Photography Rendering
Jun 18, 2024


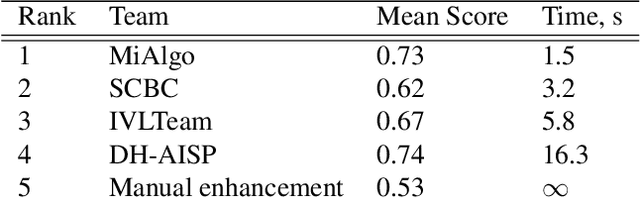
Abstract:This paper presents a review of the NTIRE 2024 challenge on night photography rendering. The goal of the challenge was to find solutions that process raw camera images taken in nighttime conditions, and thereby produce a photo-quality output images in the standard RGB (sRGB) space. Unlike the previous year's competition, the challenge images were collected with a mobile phone and the speed of algorithms was also measured alongside the quality of their output. To evaluate the results, a sufficient number of viewers were asked to assess the visual quality of the proposed solutions, considering the subjective nature of the task. There were 2 nominations: quality and efficiency. Top 5 solutions in terms of output quality were sorted by evaluation time (see Fig. 1). The top ranking participants' solutions effectively represent the state-of-the-art in nighttime photography rendering. More results can be found at https://nightimaging.org.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge