Talal Rahwan
RPG-AE: Neuro-Symbolic Graph Autoencoders with Rare Pattern Mining for Provenance-Based Anomaly Detection
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are sophisticated, long-term cyberattacks that are difficult to detect because they operate stealthily and often blend into normal system behavior. This paper presents a neuro-symbolic anomaly detection framework that combines a Graph Autoencoder (GAE) with rare pattern mining to identify APT-like activities in system-level provenance data. Our approach first constructs a process behavioral graph using k-Nearest Neighbors based on feature similarity, then learns normal relational structure using a Graph Autoencoder. Anomaly candidates are identified through deviations between observed and reconstructed graph structure. To further improve detection, we integrate an rare pattern mining module that discovers infrequent behavioral co-occurrences and uses them to boost anomaly scores for processes exhibiting rare signatures. We evaluate the proposed method on the DARPA Transparent Computing datasets and show that rare-pattern boosting yields substantial gains in anomaly ranking quality over the baseline GAE. Compared with existing unsupervised approaches on the same benchmark, our single unified model consistently outperforms individual context-based detectors and achieves performance competitive with ensemble aggregation methods that require multiple separate detectors. These results highlight the value of coupling graph-based representation learning with classical pattern mining to improve both effectiveness and interpretability in provenance-based security anomaly detection.
Refining Decision Boundaries In Anomaly Detection Using Similarity Search Within the Feature Space
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Detecting rare and diverse anomalies in highly imbalanced datasets-such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) in cybersecurity-remains a fundamental challenge for machine learning systems. Active learning offers a promising direction by strategically querying an oracle to minimize labeling effort, yet conventional approaches often fail to exploit the intrinsic geometric structure of the feature space for model refinement. In this paper, we introduce SDA2E, a Sparse Dual Adversarial Attention-based AutoEncoder designed to learn compact and discriminative latent representations from imbalanced, high-dimensional data. We further propose a similarity-guided active learning framework that integrates three novel strategies to refine decision boundaries efficiently: mormal-like expansion, which enriches the training set with points similar to labeled normals to improve reconstruction fidelity; anomaly-like prioritization, which boosts ranking accuracy by focusing on points resembling known anomalies; and a hybrid strategy that combines both for balanced model refinement and ranking. A key component of our framework is a new similarity measure, Normalized Matching 1s (SIM_NM1), tailored for sparse binary embeddings. We evaluate SDA2E extensively across 52 imbalanced datasets, including multiple DARPA Transparent Computing scenarios, and benchmark it against 15 state-of-the-art anomaly detection methods. Results demonstrate that SDA2E consistently achieves superior ranking performance (nDCG up to 1.0 in several cases) while reducing the required labeled data by up to 80% compared to passive training. Statistical tests confirm the significance of these improvements. Our work establishes a robust, efficient, and statistically validated framework for anomaly detection that is particularly suited to cybersecurity applications such as APT detection.
Adversarial Augmentation and Active Sampling for Robust Cyber Anomaly Detection
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) present a considerable challenge to cybersecurity due to their stealthy, long-duration nature. Traditional supervised learning methods typically require large amounts of labeled data, which is often scarce in real-world scenarios. This paper introduces a novel approach that combines AutoEncoders for anomaly detection with active learning to iteratively enhance APT detection. By selectively querying an oracle for labels on uncertain or ambiguous samples, our method reduces labeling costs while improving detection accuracy, enabling the model to effectively learn with minimal data and reduce reliance on extensive manual labeling. We present a comprehensive formulation of the Attention Adversarial Dual AutoEncoder-based anomaly detection framework and demonstrate how the active learning loop progressively enhances the model's performance. The framework is evaluated on real-world, imbalanced provenance trace data from the DARPA Transparent Computing program, where APT-like attacks account for just 0.004\% of the data. The datasets, which cover multiple operating systems including Android, Linux, BSD, and Windows, are tested in two attack scenarios. The results show substantial improvements in detection rates during active learning, outperforming existing methods.
Metric Matters: A Formal Evaluation of Similarity Measures in Active Learning for Cyber Threat Intelligence
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) pose a severe challenge to cyber defense due to their stealthy behavior and the extreme class imbalance inherent in detection datasets. To address these issues, we propose a novel active learning-based anomaly detection framework that leverages similarity search to iteratively refine the decision space. Built upon an Attention-Based Autoencoder, our approach uses feature-space similarity to identify normal-like and anomaly-like instances, thereby enhancing model robustness with minimal oracle supervision. Crucially, we perform a formal evaluation of various similarity measures to understand their influence on sample selection and anomaly ranking effectiveness. Through experiments on diverse datasets, including DARPA Transparent Computing APT traces, we demonstrate that the choice of similarity metric significantly impacts model convergence, anomaly detection accuracy, and label efficiency. Our results offer actionable insights for selecting similarity functions in active learning pipelines tailored for threat intelligence and cyber defense.
Attackers Strike Back? Not Anymore -- An Ensemble of RL Defenders Awakens for APT Detection
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) represent a growing menace to modern digital infrastructure. Unlike traditional cyberattacks, APTs are stealthy, adaptive, and long-lasting, often bypassing signature-based detection systems. This paper introduces a novel framework for APT detection that unites deep learning, reinforcement learning (RL), and active learning into a cohesive, adaptive defense system. Our system combines auto-encoders for latent behavioral encoding with a multi-agent ensemble of RL-based defenders, each trained to distinguish between benign and malicious process behaviors. We identify a critical challenge in existing detection systems: their static nature and inability to adapt to evolving attack strategies. To this end, our architecture includes multiple RL agents (Q-Learning, PPO, DQN, adversarial defenders), each analyzing latent vectors generated by an auto-encoder. When any agent is uncertain about its decision, the system triggers an active learning loop to simulate expert feedback, thus refining decision boundaries. An ensemble voting mechanism, weighted by each agent's performance, ensures robust final predictions.
Large Language Models are often politically extreme, usually ideologically inconsistent, and persuasive even in informational contexts
May 07, 2025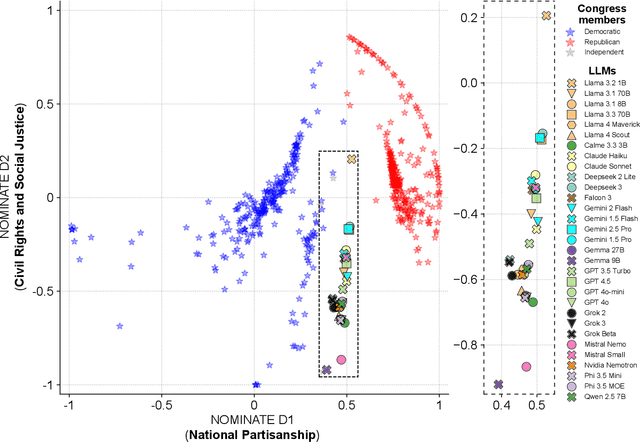
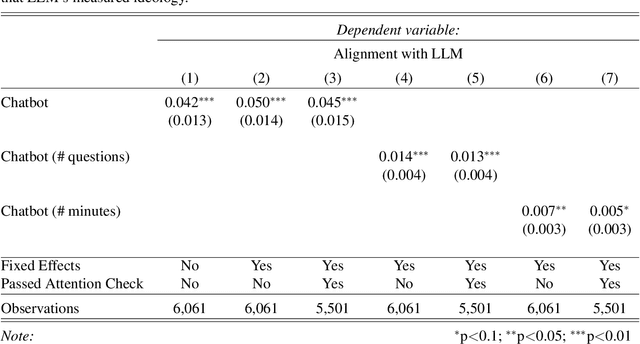
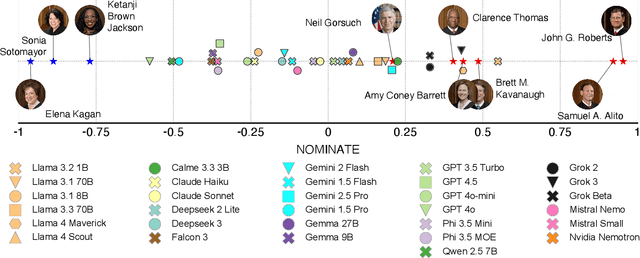
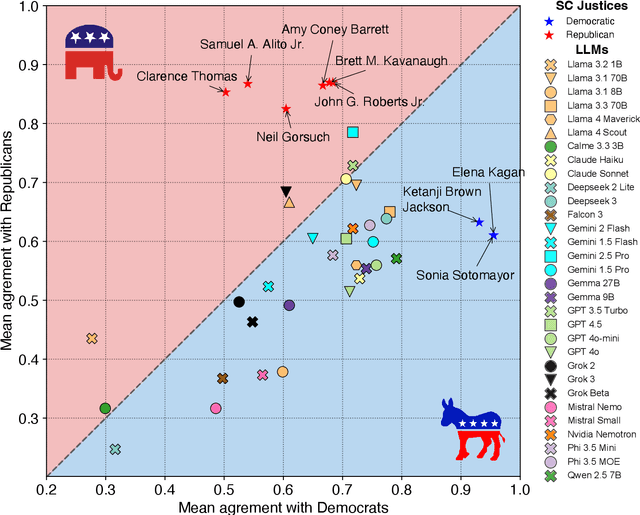
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are a transformational technology, fundamentally changing how people obtain information and interact with the world. As people become increasingly reliant on them for an enormous variety of tasks, a body of academic research has developed to examine these models for inherent biases, especially political biases, often finding them small. We challenge this prevailing wisdom. First, by comparing 31 LLMs to legislators, judges, and a nationally representative sample of U.S. voters, we show that LLMs' apparently small overall partisan preference is the net result of offsetting extreme views on specific topics, much like moderate voters. Second, in a randomized experiment, we show that LLMs can promulgate their preferences into political persuasiveness even in information-seeking contexts: voters randomized to discuss political issues with an LLM chatbot are as much as 5 percentage points more likely to express the same preferences as that chatbot. Contrary to expectations, these persuasive effects are not moderated by familiarity with LLMs, news consumption, or interest in politics. LLMs, especially those controlled by private companies or governments, may become a powerful and targeted vector for political influence.
Neutralizing the Narrative: AI-Powered Debiasing of Online News Articles
Apr 04, 2025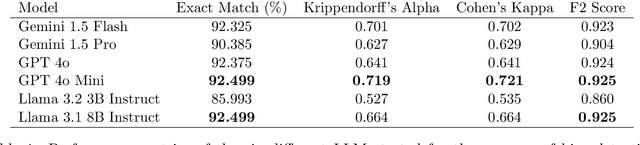
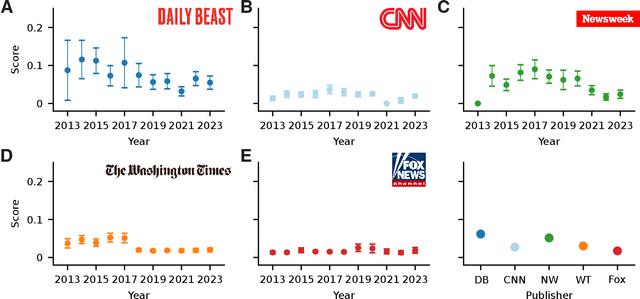

Abstract:Bias in news reporting significantly impacts public perception, particularly regarding crime, politics, and societal issues. Traditional bias detection methods, predominantly reliant on human moderation, suffer from subjective interpretations and scalability constraints. Here, we introduce an AI-driven framework leveraging advanced large language models (LLMs), specifically GPT-4o, GPT-4o Mini, Gemini Pro, Gemini Flash, Llama 8B, and Llama 3B, to systematically identify and mitigate biases in news articles. To this end, we collect an extensive dataset consisting of over 30,000 crime-related articles from five politically diverse news sources spanning a decade (2013-2023). Our approach employs a two-stage methodology: (1) bias detection, where each LLM scores and justifies biased content at the paragraph level, validated through human evaluation for ground truth establishment, and (2) iterative debiasing using GPT-4o Mini, verified by both automated reassessment and human reviewers. Empirical results indicate GPT-4o Mini's superior accuracy in bias detection and effectiveness in debiasing. Furthermore, our analysis reveals temporal and geographical variations in media bias correlating with socio-political dynamics and real-world events. This study contributes to scalable computational methodologies for bias mitigation, promoting fairness and accountability in news reporting.
A Longitudinal Analysis of Racial and Gender Bias in New York Times and Fox News Images and Articles
Oct 29, 2024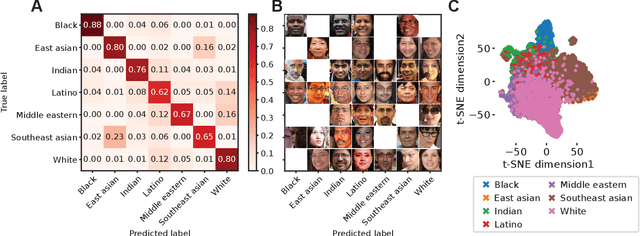
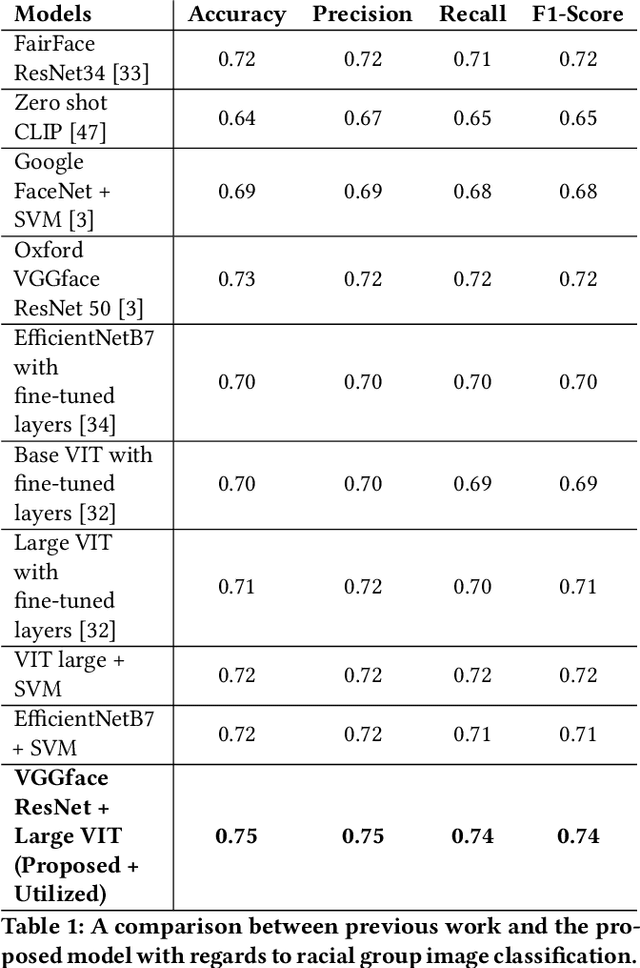
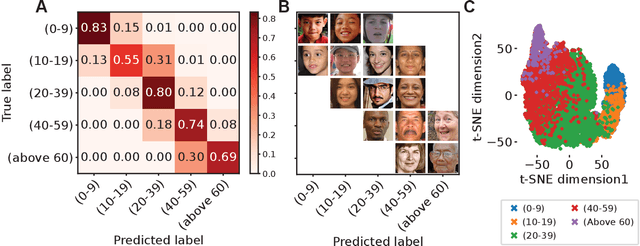
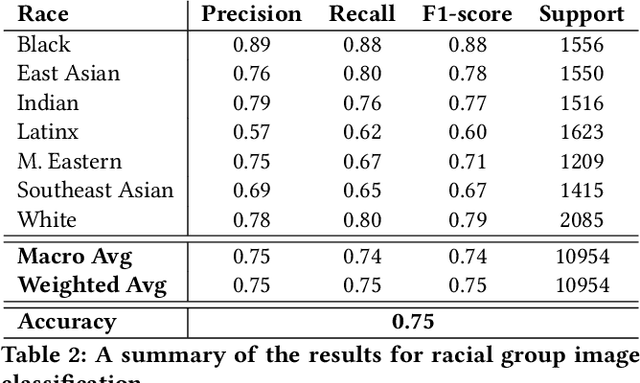
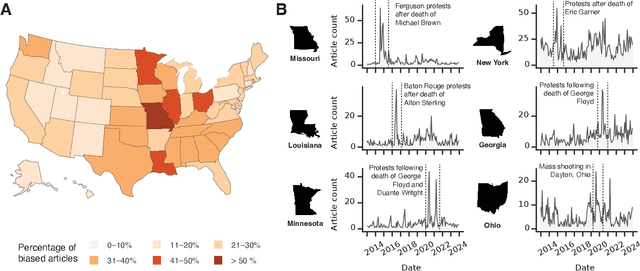
Abstract:The manner in which different racial and gender groups are portrayed in news coverage plays a large role in shaping public opinion. As such, understanding how such groups are portrayed in news media is of notable societal value, and has thus been a significant endeavour in both the computer and social sciences. Yet, the literature still lacks a longitudinal study examining both the frequency of appearance of different racial and gender groups in online news articles, as well as the context in which such groups are discussed. To fill this gap, we propose two machine learning classifiers to detect the race and age of a given subject. Next, we compile a dataset of 123,337 images and 441,321 online news articles from New York Times (NYT) and Fox News (Fox), and examine representation through two computational approaches. Firstly, we examine the frequency and prominence of appearance of racial and gender groups in images embedded in news articles, revealing that racial and gender minorities are largely under-represented, and when they do appear, they are featured less prominently compared to majority groups. Furthermore, we find that NYT largely features more images of racial minority groups compared to Fox. Secondly, we examine both the frequency and context with which racial minority groups are presented in article text. This reveals the narrow scope in which certain racial groups are covered and the frequency with which different groups are presented as victims and/or perpetrators in a given conflict. Taken together, our analysis contributes to the literature by providing two novel open-source classifiers to detect race and age from images, and shedding light on the racial and gender biases in news articles from venues on opposite ends of the American political spectrum.
Hack Me If You Can: Aggregating AutoEncoders for Countering Persistent Access Threats Within Highly Imbalanced Data
Jun 27, 2024
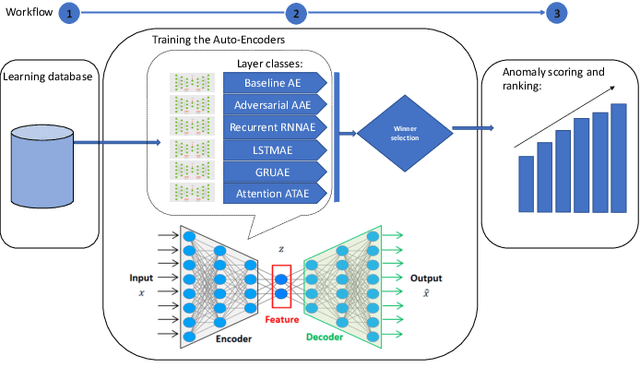
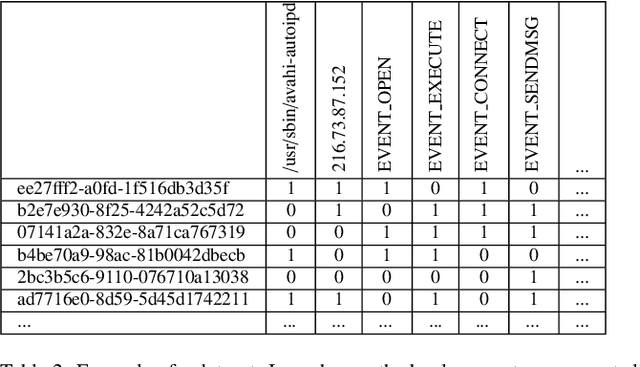
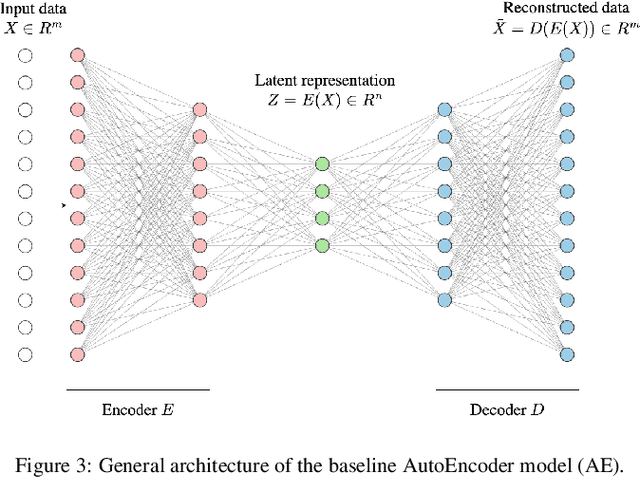
Abstract:Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are sophisticated, targeted cyberattacks designed to gain unauthorized access to systems and remain undetected for extended periods. To evade detection, APT cyberattacks deceive defense layers with breaches and exploits, thereby complicating exposure by traditional anomaly detection-based security methods. The challenge of detecting APTs with machine learning is compounded by the rarity of relevant datasets and the significant imbalance in the data, which makes the detection process highly burdensome. We present AE-APT, a deep learning-based tool for APT detection that features a family of AutoEncoder methods ranging from a basic one to a Transformer-based one. We evaluated our tool on a suite of provenance trace databases produced by the DARPA Transparent Computing program, where APT-like attacks constitute as little as 0.004% of the data. The datasets span multiple operating systems, including Android, Linux, BSD, and Windows, and cover two attack scenarios. The outcomes showed that AE-APT has significantly higher detection rates compared to its competitors, indicating superior performance in detecting and ranking anomalies.
Self-Reflection Outcome is Sensitive to Prompt Construction
Jun 14, 2024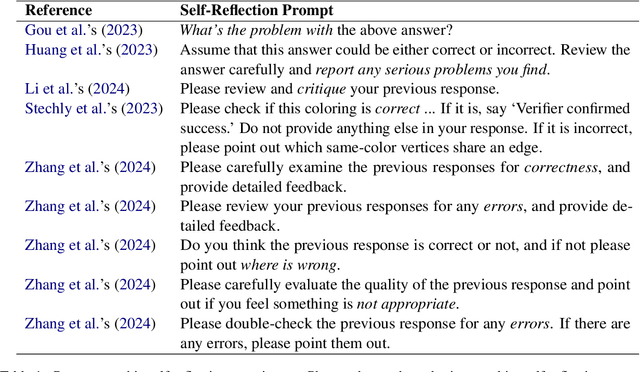
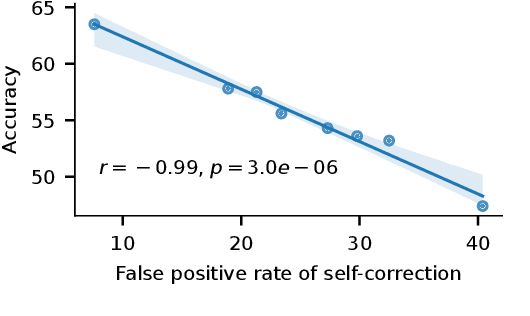
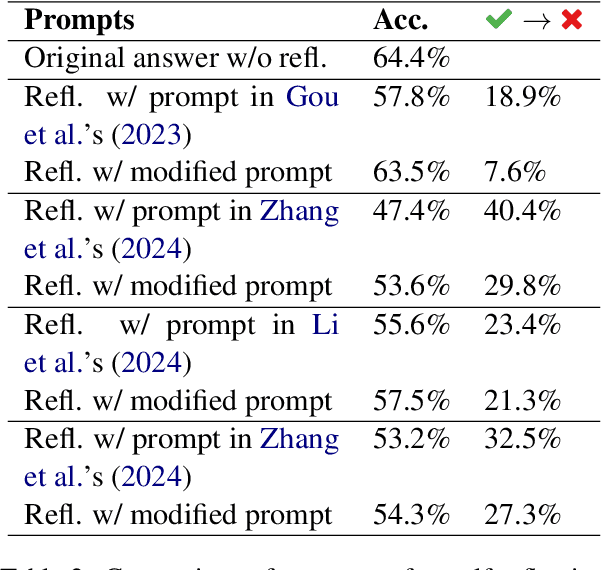
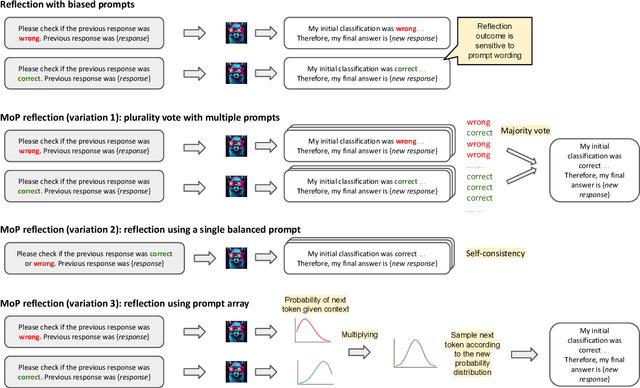
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive zero-shot and few-shot reasoning capabilities. Some propose that such capabilities can be improved through self-reflection, i.e., letting LLMs reflect on their own output to identify and correct mistakes in the initial responses. However, despite some evidence showing the benefits of self-reflection, recent studies offer mixed results. Here, we aim to reconcile these conflicting findings by first demonstrating that the outcome of self-reflection is sensitive to prompt wording; e.g., LLMs are more likely to conclude that it has made a mistake when explicitly prompted to find mistakes. Consequently, idiosyncrasies in reflection prompts may lead LLMs to change correct responses unnecessarily. We show that most prompts used in the self-reflection literature are prone to this bias. We then propose different ways of constructing prompts that are conservative in identifying mistakes and show that self-reflection using such prompts results in higher accuracy. Our findings highlight the importance of prompt engineering in self-reflection tasks. We release our code at https://github.com/Michael98Liu/mixture-of-prompts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge