Shahan Ali Memon
From job titles to jawlines: Using context voids to study generative AI systems
Apr 16, 2025

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a speculative design methodology for studying the behavior of generative AI systems, framing design as a mode of inquiry. We propose bridging seemingly unrelated domains to generate intentional context voids, using these tasks as probes to elicit AI model behavior. We demonstrate this through a case study: probing the ChatGPT system (GPT-4 and DALL-E) to generate headshots from professional Curricula Vitae (CVs). In contrast to traditional ways, our approach assesses system behavior under conditions of radical uncertainty -- when forced to invent entire swaths of missing context -- revealing subtle stereotypes and value-laden assumptions. We qualitatively analyze how the system interprets identity and competence markers from CVs, translating them into visual portraits despite the missing context (i.e. physical descriptors). We show that within this context void, the AI system generates biased representations, potentially relying on stereotypical associations or blatant hallucinations.
Search Engines Post-ChatGPT: How Generative Artificial Intelligence Could Make Search Less Reliable
Feb 18, 2024Abstract:In this commentary, we discuss the evolving nature of search engines, as they begin to generate, index, and distribute content created by generative artificial intelligence (GenAI). Our discussion highlights challenges in the early stages of GenAI integration, particularly around factual inconsistencies and biases. We discuss how output from GenAI carries an unwarranted sense of credibility, while decreasing transparency and sourcing ability. Furthermore, search engines are already answering queries with error-laden, generated content, further blurring the provenance of information and impacting the integrity of the information ecosystem. We argue how all these factors could reduce the reliability of search engines. Finally, we summarize some of the active research directions and open questions.
China and the U.S. produce more impactful AI research when collaborating together
Apr 21, 2023Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a disruptive technology, promising to grant a significant economic and strategic advantage to the nations that harness its power. China, with its recent push towards AI adoption, is challenging the U.S.'s position as the global leader in this field. Given AI's massive potential, as well as the fierce geopolitical tensions between the two nations, a number of policies have been put in place that discourage AI scientists from migrating to, or collaborating with, the other country. However, the extents of such brain drain and cross-border collaboration are not fully understood. Here, we analyze a dataset of over 350,000 AI scientists and 5,000,000 AI papers. We find that, since the year 2000, China and the U.S. have been leading the field in terms of impact, novelty, productivity, and workforce. Most AI scientists who migrate to China come from the U.S., and most who migrate to the U.S. come from China, highlighting a notable brain drain in both directions. Upon migrating from one country to the other, scientists continue to collaborate frequently with the origin country. Although the number of collaborations between the two countries has been increasing since the dawn of the millennium, such collaborations continue to be relatively rare. A matching experiment reveals that the two countries have always been more impactful when collaborating than when each of them works without the other. These findings suggest that instead of suppressing cross-border migration and collaboration between the two nations, the field could benefit from promoting such activities.
Characterizing COVID-19 Misinformation Communities Using a Novel Twitter Dataset
Aug 31, 2020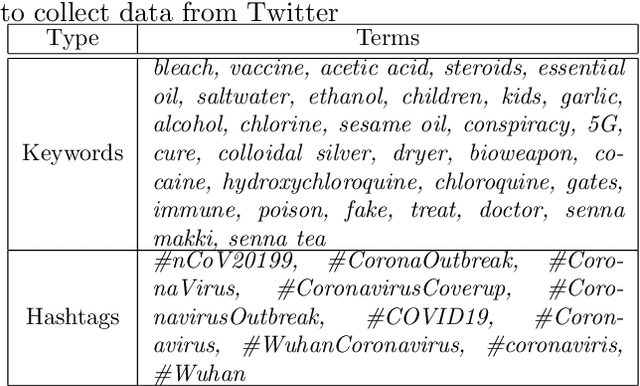
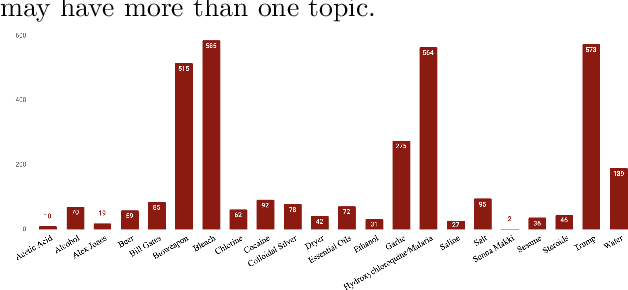
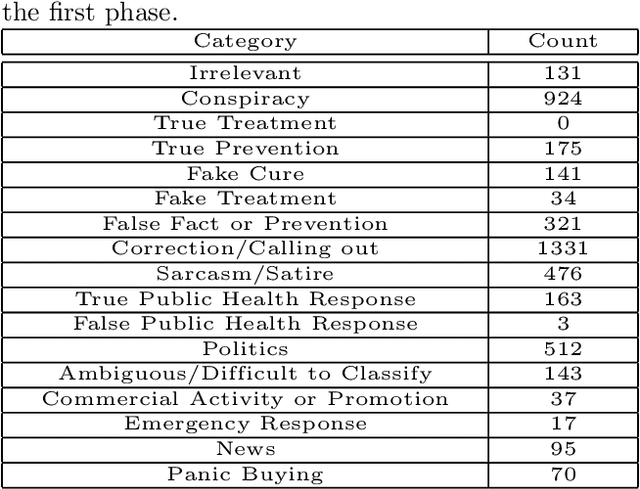
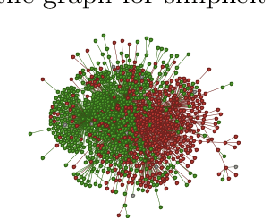
Abstract:From conspiracy theories to fake cures and fake treatments, COVID-19 has become a hot-bed for the spread of misinformation online. It is more important than ever to identify methods to debunk and correct false information online. In this paper, we present a methodology and analyses to characterize the two competing COVID-19 misinformation communities online: (i) misinformed users or users who are actively posting misinformation, and (ii) informed users or users who are actively spreading true information, or calling out misinformation. The goals of this study are two-fold: (i) collecting a diverse set of annotated COVID-19 Twitter dataset that can be used by the research community to conduct meaningful analysis; and (ii) characterizing the two target communities in terms of their network structure, linguistic patterns, and their membership in other communities. Our analyses show that COVID-19 misinformed communities are denser, and more organized than informed communities, with a possibility of a high volume of the misinformation being part of disinformation campaigns. Our analyses also suggest that a large majority of misinformed users may be anti-vaxxers. Finally, our sociolinguistic analyses suggest that COVID-19 informed users tend to use more narratives than misinformed users.
Characterizing Sociolinguistic Variation in the Competing Vaccination Communities
Jul 01, 2020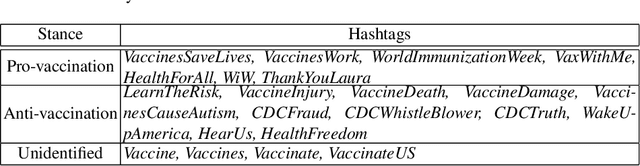

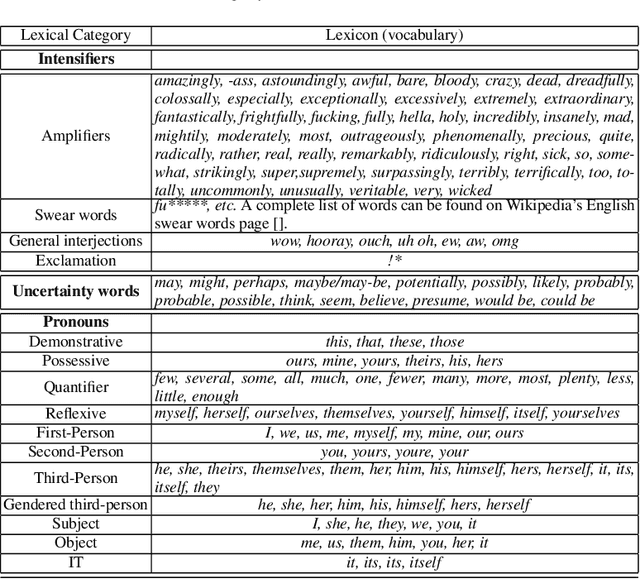
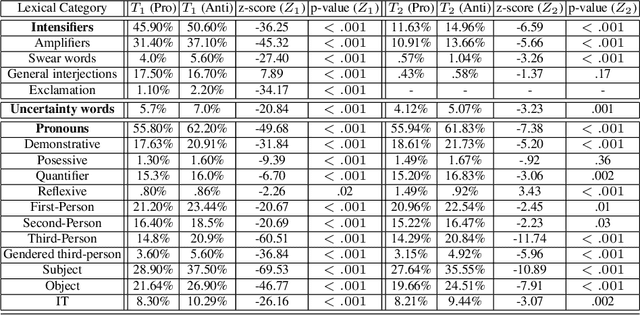
Abstract:Public health practitioners and policy makers grapple with the challenge of devising effective message-based interventions for debunking public health misinformation in cyber communities. "Framing" and "personalization" of the message is one of the key features for devising a persuasive messaging strategy. For an effective health communication, it is imperative to focus on "preference-based framing" where the preferences of the target sub-community are taken into consideration. To achieve that, it is important to understand and hence characterize the target sub-communities in terms of their social interactions. In the context of health-related misinformation, vaccination remains to be the most prevalent topic of discord. Hence, in this paper, we conduct a sociolinguistic analysis of the two competing vaccination communities on Twitter: "pro-vaxxers" or individuals who believe in the effectiveness of vaccinations, and "anti-vaxxers" or individuals who are opposed to vaccinations. Our data analysis show significant linguistic variation between the two communities in terms of their usage of linguistic intensifiers, pronouns, and uncertainty words. Our network-level analysis show significant differences between the two communities in terms of their network density, echo-chamberness, and the EI index. We hypothesize that these sociolinguistic differences can be used as proxies to characterize and understand these communities to devise better message interventions.
Detecting gender differences in perception of emotion in crowdsourced data
Nov 04, 2019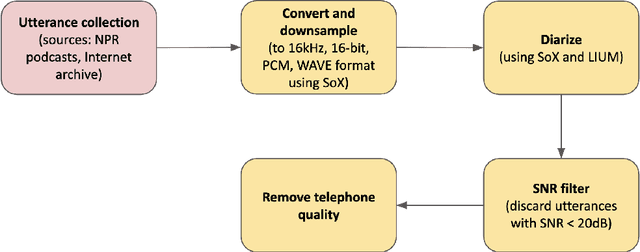
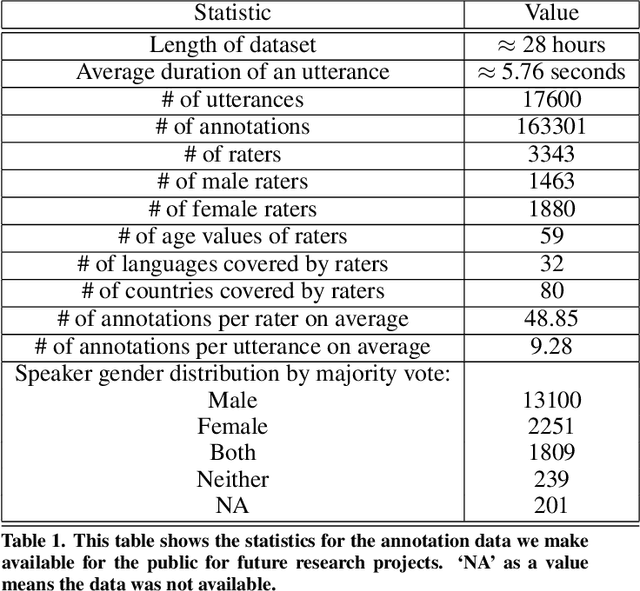
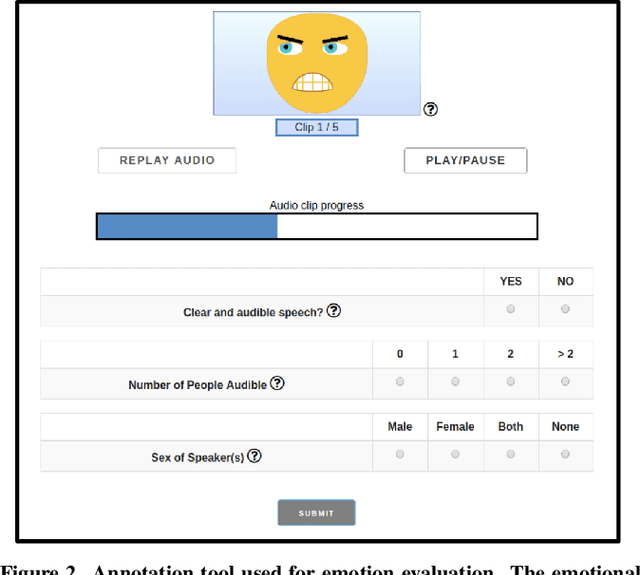
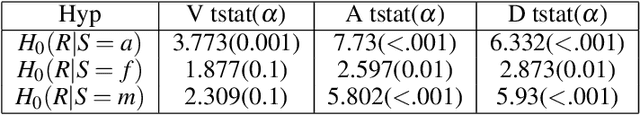
Abstract:Do men and women perceive emotions differently? Popular convictions place women as more emotionally perceptive than men. Empirical findings, however, remain inconclusive. Most prior studies focus on visual modalities. In addition, almost all of the studies are limited to experiments within controlled environments. Generalizability and scalability of these studies has not been sufficiently established. In this paper, we study the differences in perception of emotion between genders from speech data in the wild, annotated through crowdsourcing. While we limit ourselves to a single modality (i.e. speech), our framework is applicable to studies of emotion perception from all such loosely annotated data in general. Our paper addresses multiple serious challenges related to making statistically viable conclusions from crowdsourced data. Overall, the contributions of this paper are two fold: a reliable novel framework for perceptual studies from crowdsourced data; and the demonstration of statistically significant differences in speech-based emotion perception between genders.
Hierarchical Routing Mixture of Experts
Mar 18, 2019



Abstract:In regression tasks the distribution of the data is often too complex to be fitted by a single model. In contrast, partition-based models are developed where data is divided and fitted by local models. These models partition the input space and do not leverage the input-output dependency of multimodal-distributed data, and strong local models are needed to make good predictions. Addressing these problems, we propose a binary tree-structured hierarchical routing mixture of experts (HRME) model that has classifiers as non-leaf node experts and simple regression models as leaf node experts. The classifier nodes jointly soft-partition the input-output space based on the natural separateness of multimodal data. This enables simple leaf experts to be effective for prediction. Further, we develop a probabilistic framework for the HRME model, and propose a recursive Expectation-Maximization (EM) based algorithm to learn both the tree structure and the expert models. Experiments on a collection of regression tasks validate the effectiveness of our method compared to a variety of other regression models.
Neural Regression Trees
Oct 01, 2018



Abstract:Regression-via-Classification (RvC) is the process of converting a regression problem to a classification one. Current approaches for RvC use ad-hoc discretization strategies and are suboptimal. We propose a neural regression tree model for RvC. In this model, we employ a joint optimization framework where we learn optimal discretization thresholds while simultaneously optimizing the features for each node in the tree. We empirically show the validity of our model by testing it on two challenging regression tasks where we establish the state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge