Hazem Ibrahim
Large Language Models are often politically extreme, usually ideologically inconsistent, and persuasive even in informational contexts
May 07, 2025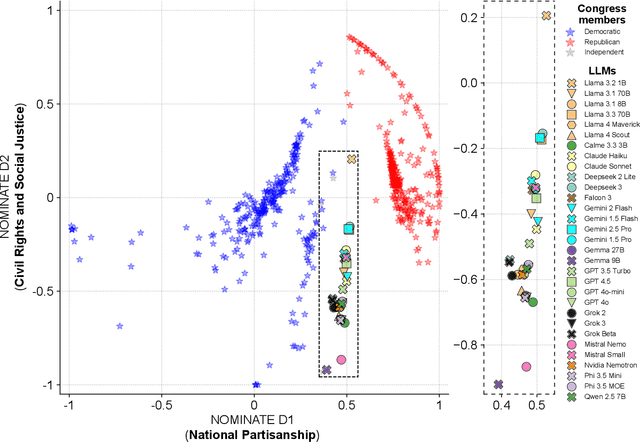
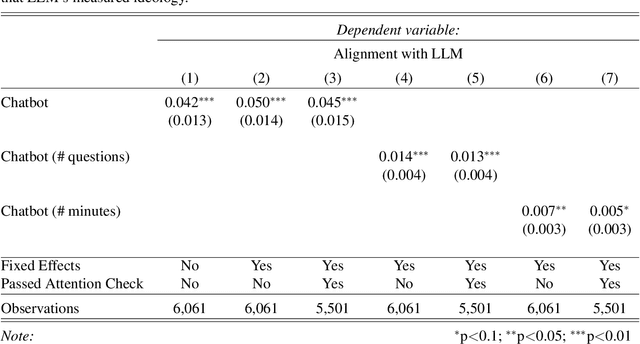
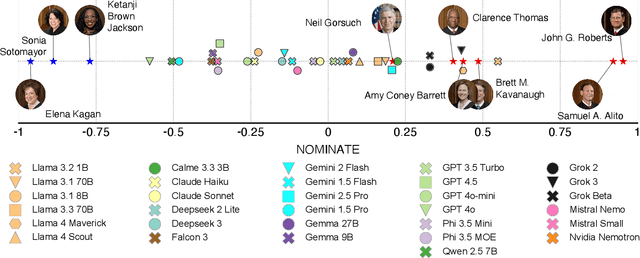
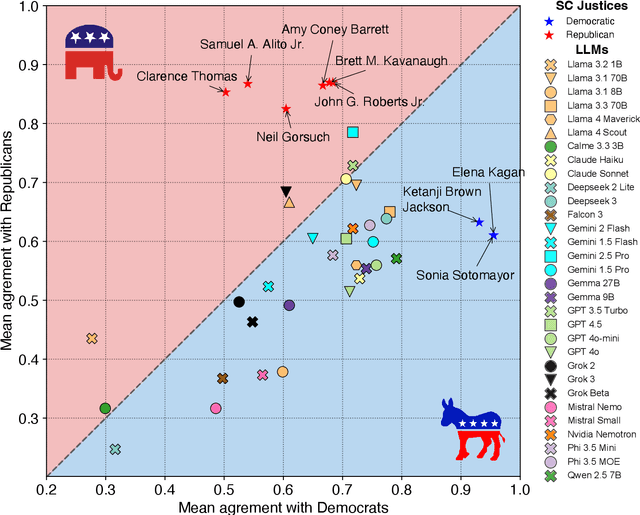
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are a transformational technology, fundamentally changing how people obtain information and interact with the world. As people become increasingly reliant on them for an enormous variety of tasks, a body of academic research has developed to examine these models for inherent biases, especially political biases, often finding them small. We challenge this prevailing wisdom. First, by comparing 31 LLMs to legislators, judges, and a nationally representative sample of U.S. voters, we show that LLMs' apparently small overall partisan preference is the net result of offsetting extreme views on specific topics, much like moderate voters. Second, in a randomized experiment, we show that LLMs can promulgate their preferences into political persuasiveness even in information-seeking contexts: voters randomized to discuss political issues with an LLM chatbot are as much as 5 percentage points more likely to express the same preferences as that chatbot. Contrary to expectations, these persuasive effects are not moderated by familiarity with LLMs, news consumption, or interest in politics. LLMs, especially those controlled by private companies or governments, may become a powerful and targeted vector for political influence.
Neutralizing the Narrative: AI-Powered Debiasing of Online News Articles
Apr 04, 2025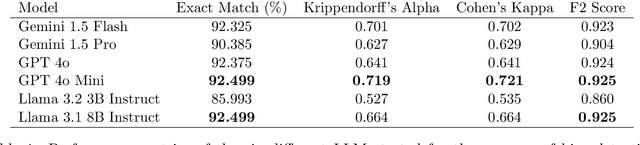
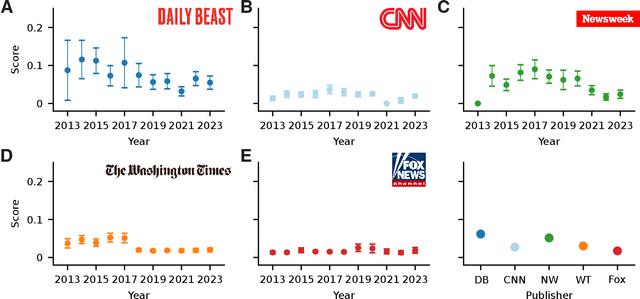
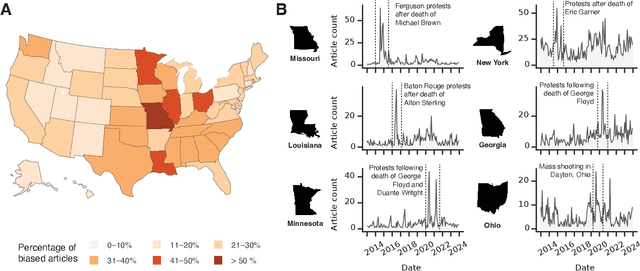

Abstract:Bias in news reporting significantly impacts public perception, particularly regarding crime, politics, and societal issues. Traditional bias detection methods, predominantly reliant on human moderation, suffer from subjective interpretations and scalability constraints. Here, we introduce an AI-driven framework leveraging advanced large language models (LLMs), specifically GPT-4o, GPT-4o Mini, Gemini Pro, Gemini Flash, Llama 8B, and Llama 3B, to systematically identify and mitigate biases in news articles. To this end, we collect an extensive dataset consisting of over 30,000 crime-related articles from five politically diverse news sources spanning a decade (2013-2023). Our approach employs a two-stage methodology: (1) bias detection, where each LLM scores and justifies biased content at the paragraph level, validated through human evaluation for ground truth establishment, and (2) iterative debiasing using GPT-4o Mini, verified by both automated reassessment and human reviewers. Empirical results indicate GPT-4o Mini's superior accuracy in bias detection and effectiveness in debiasing. Furthermore, our analysis reveals temporal and geographical variations in media bias correlating with socio-political dynamics and real-world events. This study contributes to scalable computational methodologies for bias mitigation, promoting fairness and accountability in news reporting.
A Longitudinal Analysis of Racial and Gender Bias in New York Times and Fox News Images and Articles
Oct 29, 2024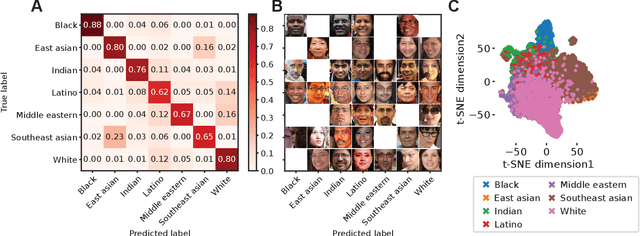
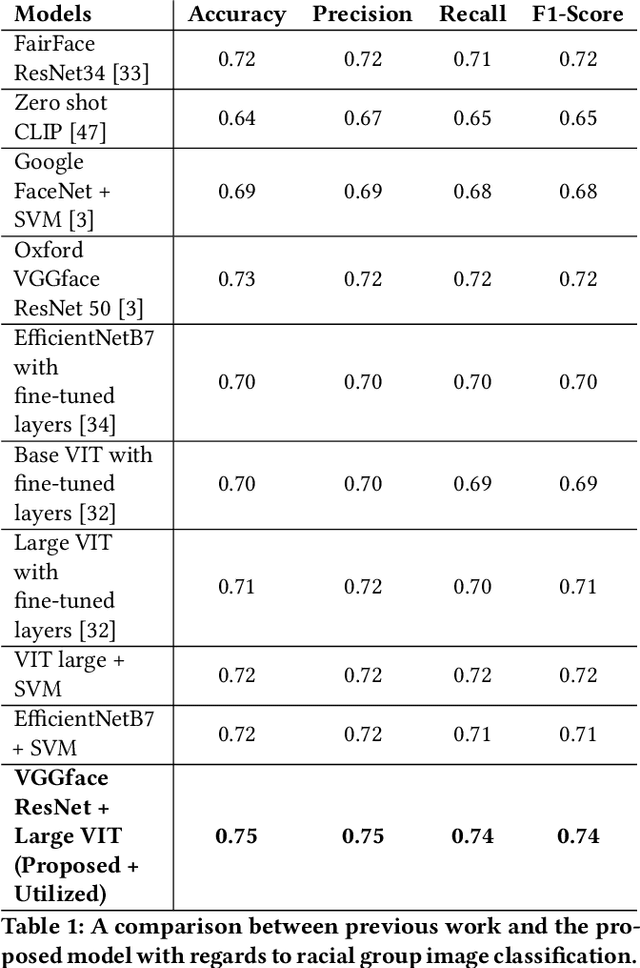
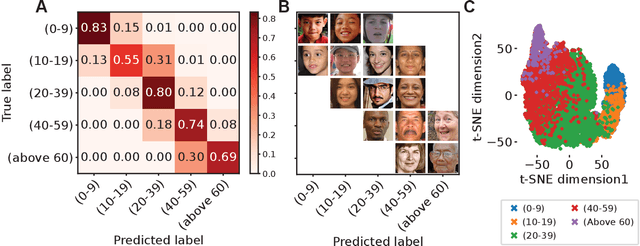
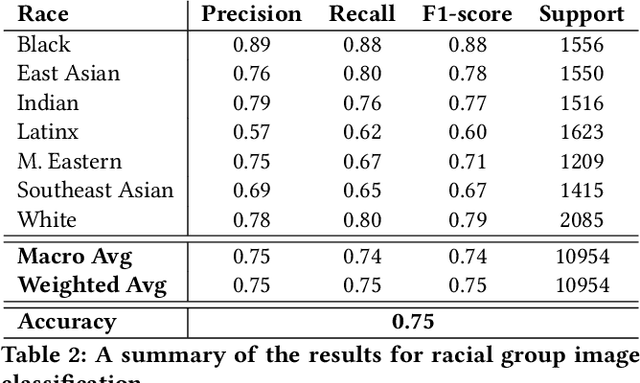
Abstract:The manner in which different racial and gender groups are portrayed in news coverage plays a large role in shaping public opinion. As such, understanding how such groups are portrayed in news media is of notable societal value, and has thus been a significant endeavour in both the computer and social sciences. Yet, the literature still lacks a longitudinal study examining both the frequency of appearance of different racial and gender groups in online news articles, as well as the context in which such groups are discussed. To fill this gap, we propose two machine learning classifiers to detect the race and age of a given subject. Next, we compile a dataset of 123,337 images and 441,321 online news articles from New York Times (NYT) and Fox News (Fox), and examine representation through two computational approaches. Firstly, we examine the frequency and prominence of appearance of racial and gender groups in images embedded in news articles, revealing that racial and gender minorities are largely under-represented, and when they do appear, they are featured less prominently compared to majority groups. Furthermore, we find that NYT largely features more images of racial minority groups compared to Fox. Secondly, we examine both the frequency and context with which racial minority groups are presented in article text. This reveals the narrow scope in which certain racial groups are covered and the frequency with which different groups are presented as victims and/or perpetrators in a given conflict. Taken together, our analysis contributes to the literature by providing two novel open-source classifiers to detect race and age from images, and shedding light on the racial and gender biases in news articles from venues on opposite ends of the American political spectrum.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge