Gregory Eady
Self-Reflection Outcome is Sensitive to Prompt Construction
Jun 14, 2024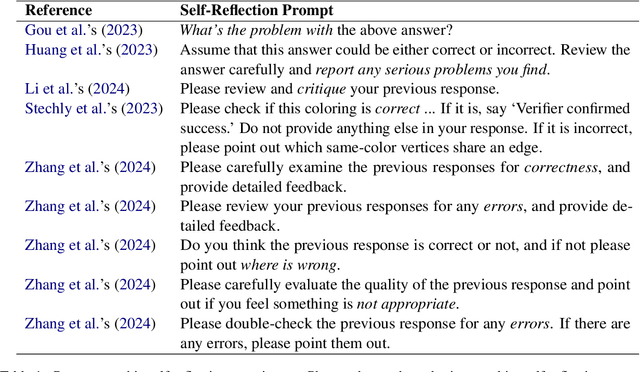
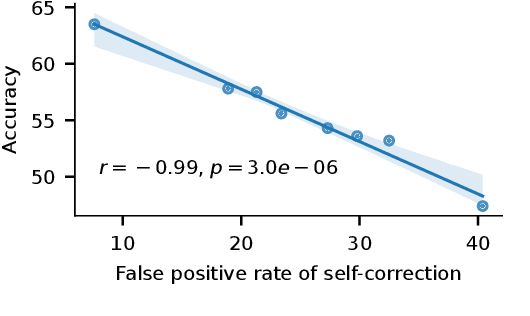
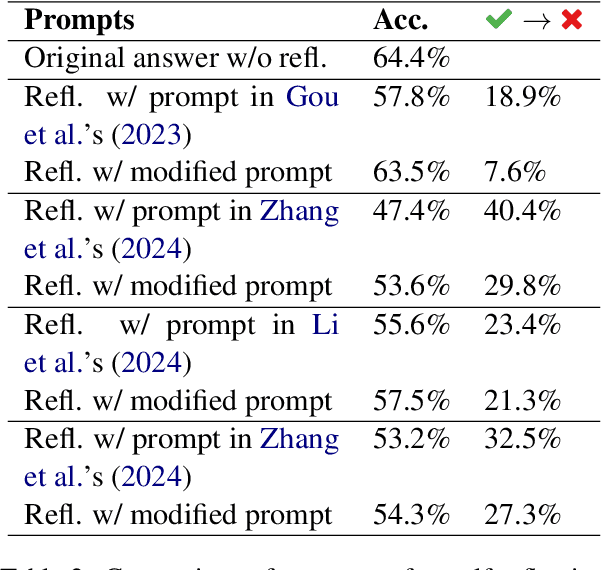
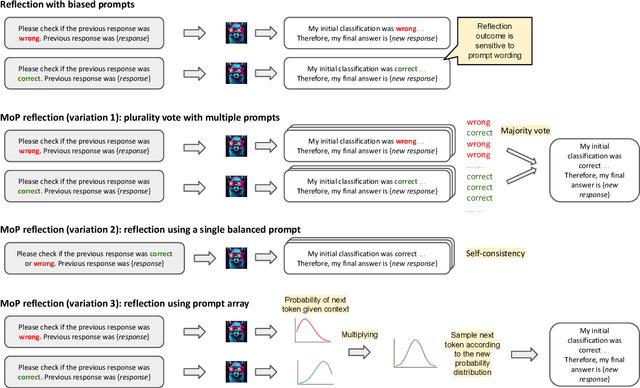
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive zero-shot and few-shot reasoning capabilities. Some propose that such capabilities can be improved through self-reflection, i.e., letting LLMs reflect on their own output to identify and correct mistakes in the initial responses. However, despite some evidence showing the benefits of self-reflection, recent studies offer mixed results. Here, we aim to reconcile these conflicting findings by first demonstrating that the outcome of self-reflection is sensitive to prompt wording; e.g., LLMs are more likely to conclude that it has made a mistake when explicitly prompted to find mistakes. Consequently, idiosyncrasies in reflection prompts may lead LLMs to change correct responses unnecessarily. We show that most prompts used in the self-reflection literature are prone to this bias. We then propose different ways of constructing prompts that are conservative in identifying mistakes and show that self-reflection using such prompts results in higher accuracy. Our findings highlight the importance of prompt engineering in self-reflection tasks. We release our code at https://github.com/Michael98Liu/mixture-of-prompts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge