Tahsin Reasat
MSTT-199: MRI Dataset for Musculoskeletal Soft Tissue Tumor Segmentation
Sep 04, 2024



Abstract:Accurate musculoskeletal soft tissue tumor segmentation is vital for assessing tumor size, location, diagnosis, and response to treatment, thereby influencing patient outcomes. However, segmentation of these tumors requires clinical expertise, and an automated segmentation model would save valuable time for both clinician and patient. Training an automatic model requires a large dataset of annotated images. In this work, we describe the collection of an MR imaging dataset of 199 musculoskeletal soft tissue tumors from 199 patients. We trained segmentation models on this dataset and then benchmarked them on a publicly available dataset. Our model achieved the state-of-the-art dice score of 0.79 out of the box without any fine tuning, which shows the diversity and utility of our curated dataset. We analyzed the model predictions and found that its performance suffered on fibrous and vascular tumors due to their diverse anatomical location, size, and intensity heterogeneity. The code and models are available in the following github repository, https://github.com/Reasat/mstt
OOD-Speech: A Large Bengali Speech Recognition Dataset for Out-of-Distribution Benchmarking
May 15, 2023Abstract:We present OOD-Speech, the first out-of-distribution (OOD) benchmarking dataset for Bengali automatic speech recognition (ASR). Being one of the most spoken languages globally, Bengali portrays large diversity in dialects and prosodic features, which demands ASR frameworks to be robust towards distribution shifts. For example, islamic religious sermons in Bengali are delivered with a tonality that is significantly different from regular speech. Our training dataset is collected via massively online crowdsourcing campaigns which resulted in 1177.94 hours collected and curated from $22,645$ native Bengali speakers from South Asia. Our test dataset comprises 23.03 hours of speech collected and manually annotated from 17 different sources, e.g., Bengali TV drama, Audiobook, Talk show, Online class, and Islamic sermons to name a few. OOD-Speech is jointly the largest publicly available speech dataset, as well as the first out-of-distribution ASR benchmarking dataset for Bengali.
Data Efficient Contrastive Learning in Histopathology using Active Sampling
Apr 03, 2023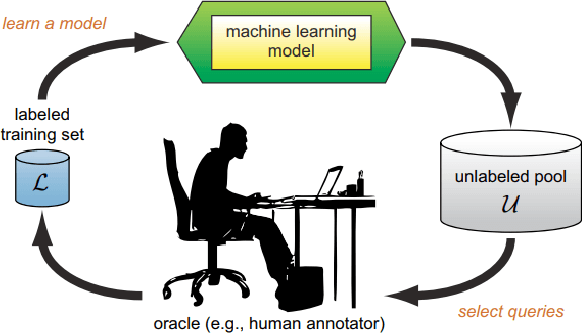
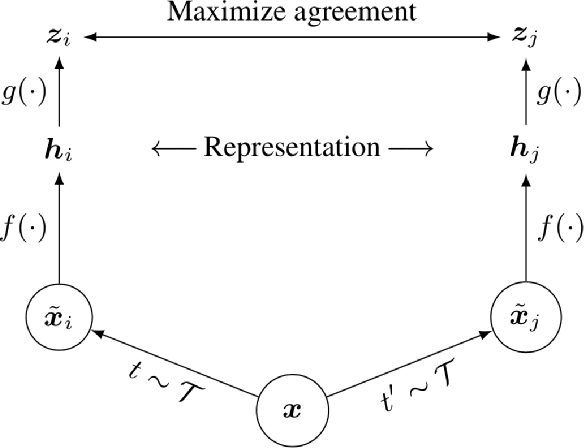
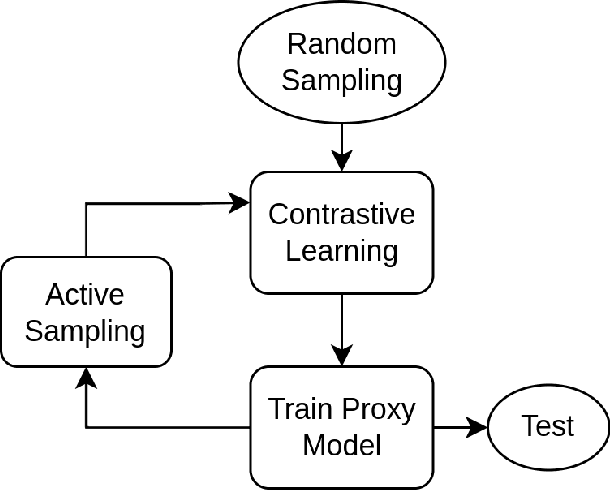
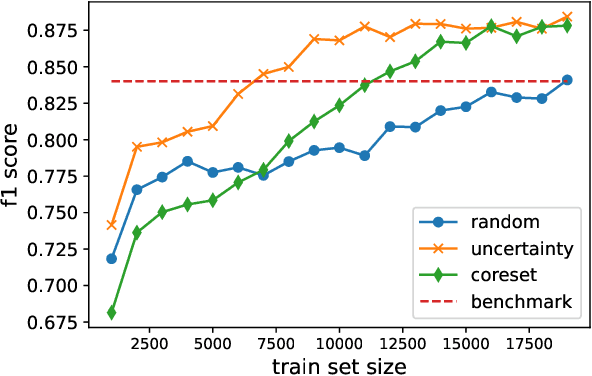
Abstract:Deep Learning based diagnostics systems can provide accurate and robust quantitative analysis in digital pathology. These algorithms require large amounts of annotated training data which is impractical in pathology due to the high resolution of histopathological images. Hence, self-supervised methods have been proposed to learn features using ad-hoc pretext tasks. The self-supervised training process is time consuming and often leads to subpar feature representation due to a lack of constrain on the learnt feature space, particularly prominent under data imbalance. In this work, we propose to actively sample the training set using a handful of labels and a small proxy network, decreasing sample requirement by 93% and training time by 99%.
BaDLAD: A Large Multi-Domain Bengali Document Layout Analysis Dataset
Mar 10, 2023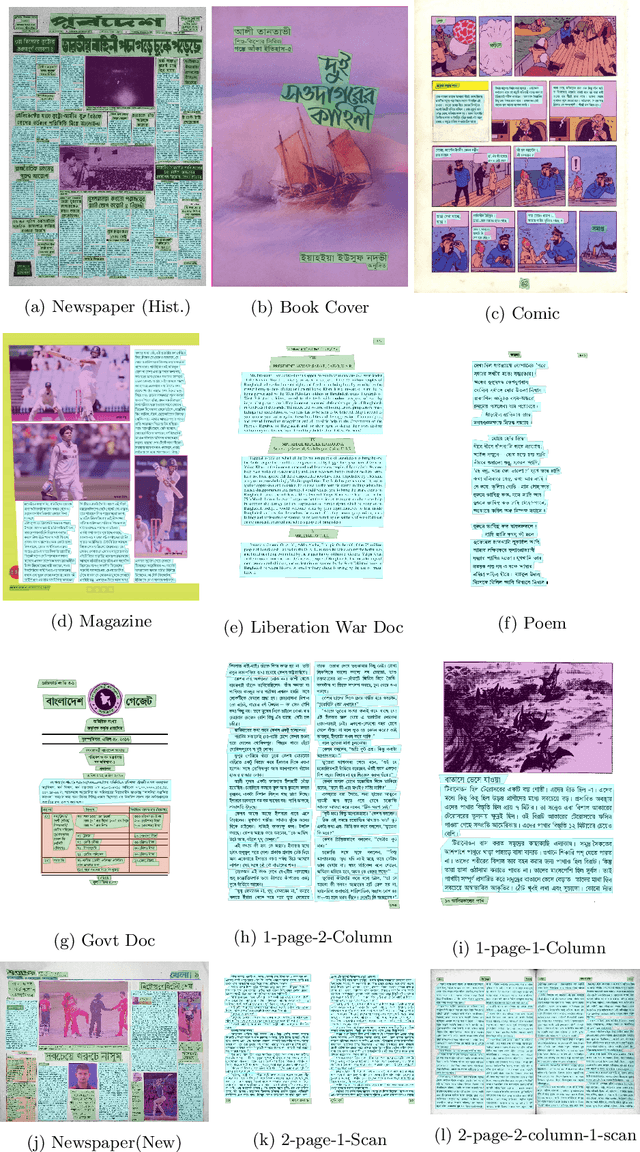
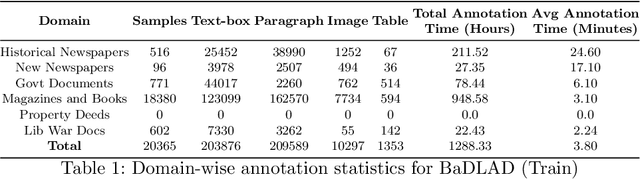
Abstract:While strides have been made in deep learning based Bengali Optical Character Recognition (OCR) in the past decade, the absence of large Document Layout Analysis (DLA) datasets has hindered the application of OCR in document transcription, e.g., transcribing historical documents and newspapers. Moreover, rule-based DLA systems that are currently being employed in practice are not robust to domain variations and out-of-distribution layouts. To this end, we present the first multidomain large Bengali Document Layout Analysis Dataset: BaDLAD. This dataset contains 33,695 human annotated document samples from six domains - i) books and magazines, ii) public domain govt. documents, iii) liberation war documents, iv) newspapers, v) historical newspapers, and vi) property deeds, with 710K polygon annotations for four unit types: text-box, paragraph, image, and table. Through preliminary experiments benchmarking the performance of existing state-of-the-art deep learning architectures for English DLA, we demonstrate the efficacy of our dataset in training deep learning based Bengali document digitization models.
Bengali Common Voice Speech Dataset for Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 29, 2022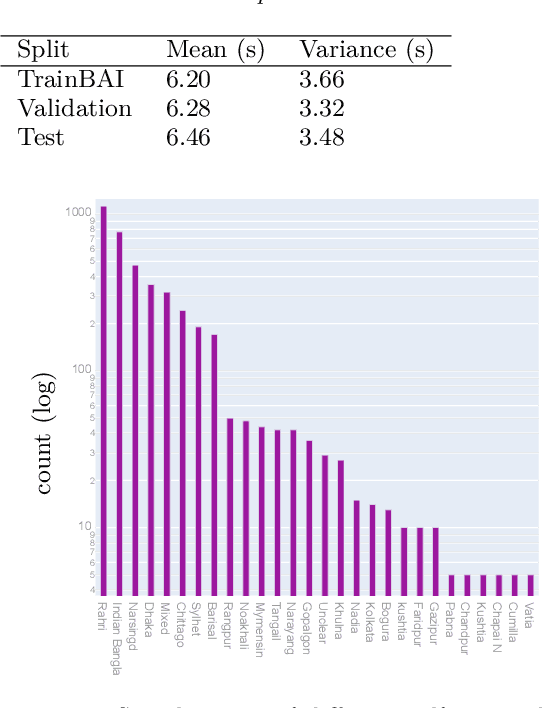
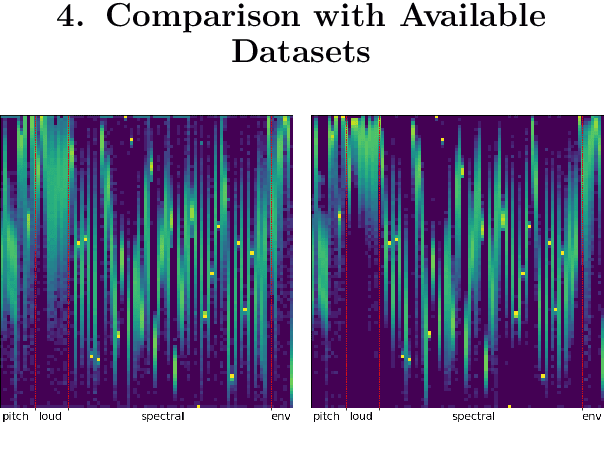

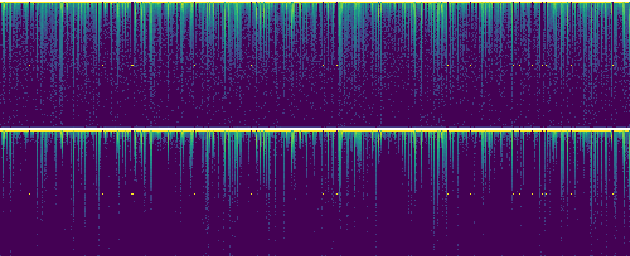
Abstract:Bengali is one of the most spoken languages in the world with over 300 million speakers globally. Despite its popularity, research into the development of Bengali speech recognition systems is hindered due to the lack of diverse open-source datasets. As a way forward, we have crowdsourced the Bengali Common Voice Speech Dataset, which is a sentence-level automatic speech recognition corpus. Collected on the Mozilla Common Voice platform, the dataset is part of an ongoing campaign that has led to the collection of over 400 hours of data in 2 months and is growing rapidly. Our analysis shows that this dataset has more speaker, phoneme, and environmental diversity compared to the OpenSLR Bengali ASR dataset, the largest existing open-source Bengali speech dataset. We present insights obtained from the dataset and discuss key linguistic challenges that need to be addressed in future versions. Additionally, we report the current performance of a few Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) algorithms and set a benchmark for future research.
Multi-label Classification of Common Bengali Handwritten Graphemes: Dataset and Challenge
Oct 29, 2020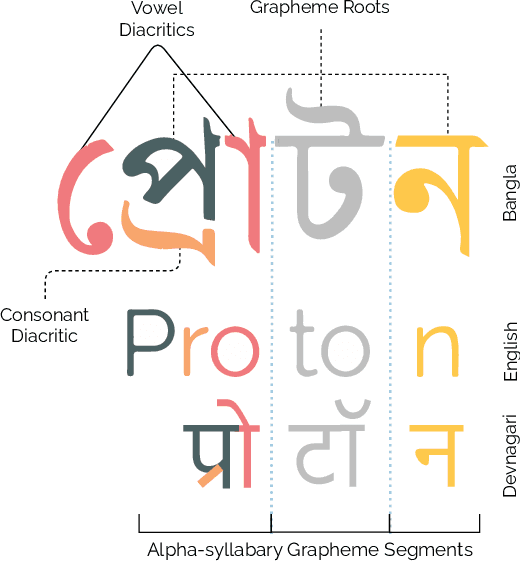
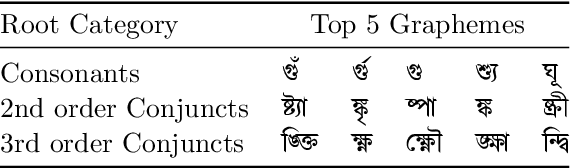


Abstract:Latin has historically led the state-of-the-art in handwritten optical character recognition (OCR) research. Adapting existing systems from Latin to alpha-syllabary languages is particularly challenging due to a sharp contrast between their orthographies. The segmentation of graphical constituents corresponding to characters becomes significantly hard due to a cursive writing system and frequent use of diacritics in the alpha-syllabary family of languages. We propose a labeling scheme based on graphemes (linguistic segments of word formation) that makes segmentation inside alpha-syllabary words linear and present the first dataset of Bengali handwritten graphemes that are commonly used in an everyday context. The dataset is open-sourced as a part of the BengaliAI Handwritten Grapheme Classification Challenge on Kaggle to benchmark vision algorithms for multi-label grapheme classification. From competition proceedings, we see that deep learning methods can generalize to a large span of uncommon graphemes even when they are absent during training. Dataset and starter codes at www.kaggle.com/c/bengaliai-cv19.
AI Learns to Recognize Bengali Handwritten Digits: Bengali.AI Computer Vision Challenge 2018
Oct 10, 2018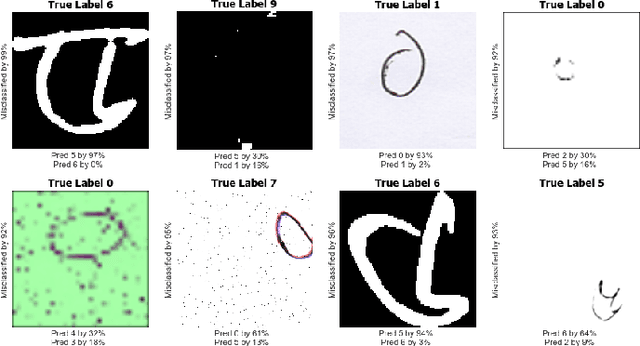
Abstract:Solving problems with Artificial intelligence in a competitive manner has long been absent in Bangladesh and Bengali-speaking community. On the other hand, there has not been a well structured database for Bengali Handwritten digits for mass public use. To bring out the best minds working in machine learning and use their expertise to create a model which can easily recognize Bengali Handwritten digits, we organized Bengali.AI Computer Vision Challenge.The challenge saw both local and international teams participating with unprecedented efforts.
Detection of Inferior Myocardial Infarction using Shallow Convolutional Neural Networks
Aug 18, 2018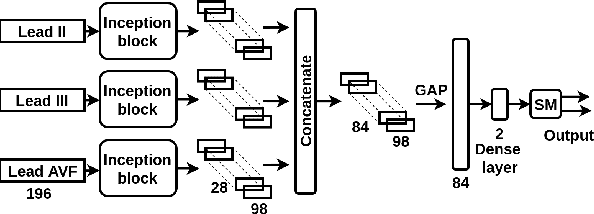
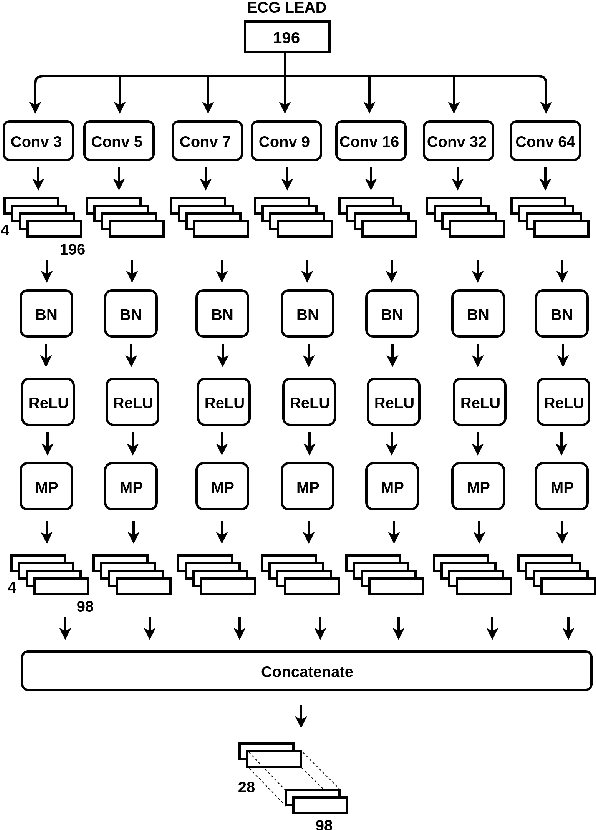
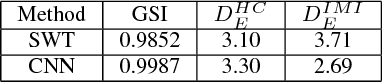
Abstract:Myocardial Infarction is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. This paper presents a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture which takes raw Electrocardiography (ECG) signal from lead II, III and AVF and differentiates between inferior myocardial infarction (IMI) and healthy signals. The performance of the model is evaluated on IMI and healthy signals obtained from Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) database. A subject-oriented approach is taken to comprehend the generalization capability of the model and compared with the current state of the art. In a subject-oriented approach, the network is tested on one patient and trained on rest of the patients. Our model achieved a superior metrics scores (accuracy= 84.54%, sensitivity= 85.33% and specificity= 84.09%) when compared to the benchmark. We also analyzed the discriminating strength of the features extracted by the convolutional layers by means of geometric separability index and euclidean distance and compared it with the benchmark model.
NumtaDB - Assembled Bengali Handwritten Digits
Jun 06, 2018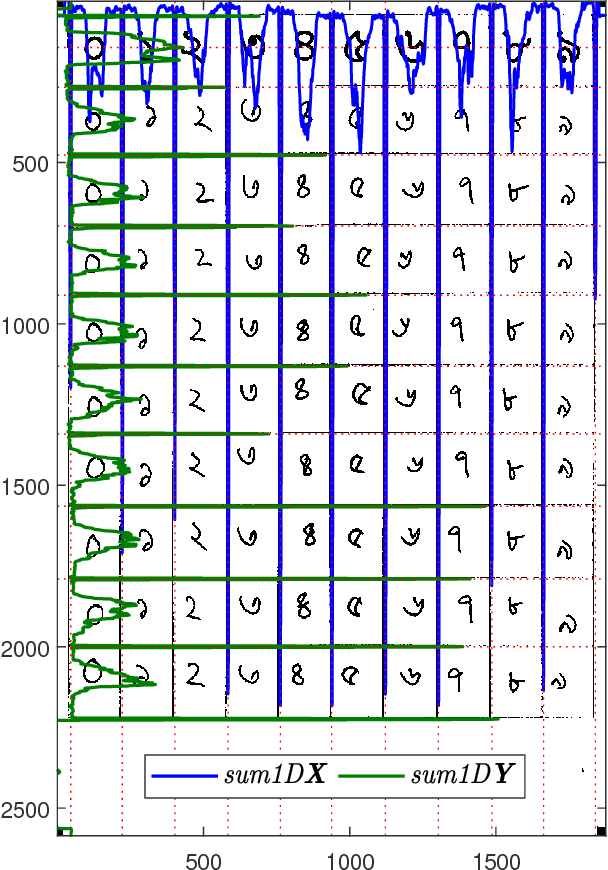
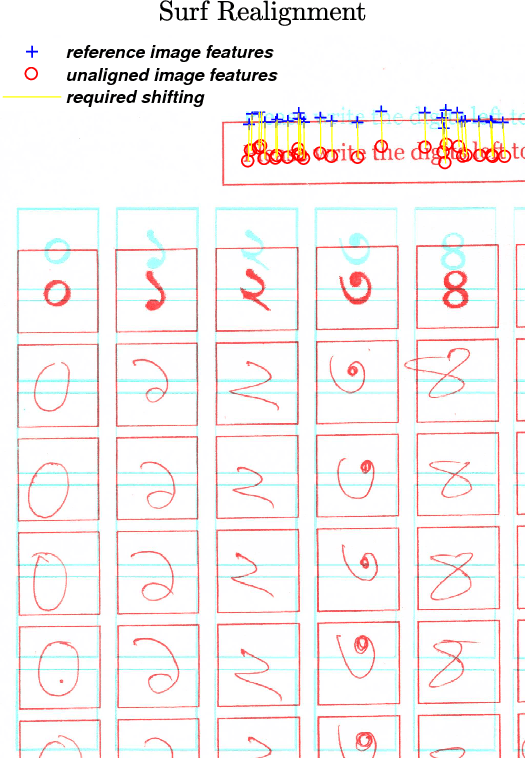
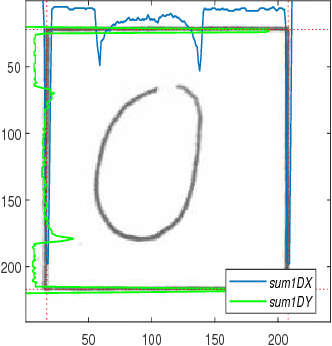
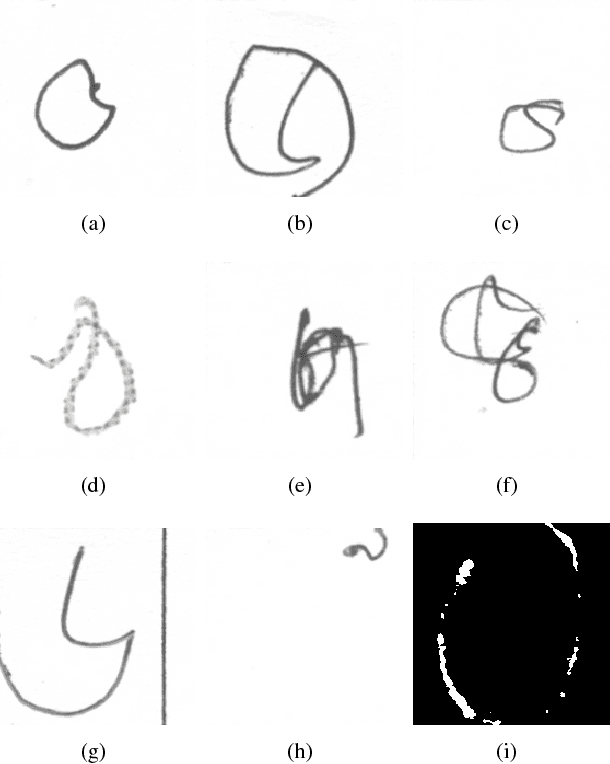
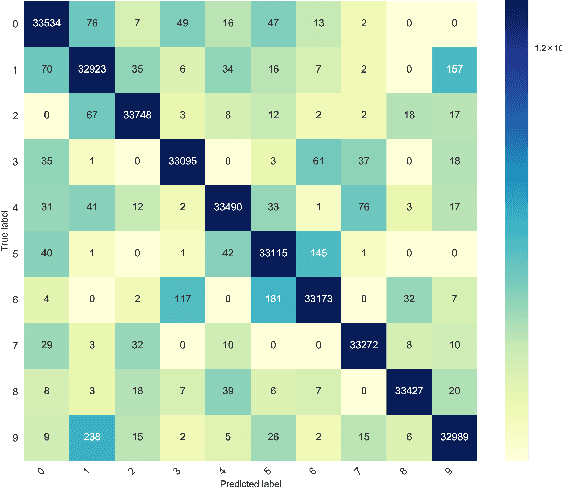
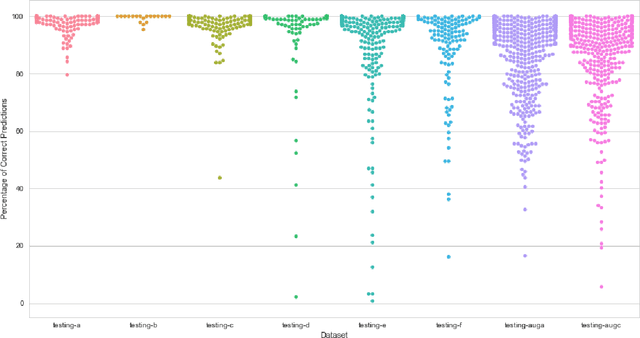
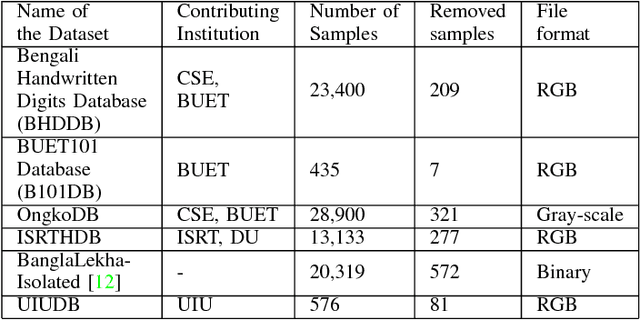
Abstract:To benchmark Bengali digit recognition algorithms, a large publicly available dataset is required which is free from biases originating from geographical location, gender, and age. With this aim in mind, NumtaDB, a dataset consisting of more than 85,000 images of hand-written Bengali digits, has been assembled. This paper documents the collection and curation process of numerals along with the salient statistics of the dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge