Syed Mobassir Hossen
OOD-Speech: A Large Bengali Speech Recognition Dataset for Out-of-Distribution Benchmarking
May 15, 2023Abstract:We present OOD-Speech, the first out-of-distribution (OOD) benchmarking dataset for Bengali automatic speech recognition (ASR). Being one of the most spoken languages globally, Bengali portrays large diversity in dialects and prosodic features, which demands ASR frameworks to be robust towards distribution shifts. For example, islamic religious sermons in Bengali are delivered with a tonality that is significantly different from regular speech. Our training dataset is collected via massively online crowdsourcing campaigns which resulted in 1177.94 hours collected and curated from $22,645$ native Bengali speakers from South Asia. Our test dataset comprises 23.03 hours of speech collected and manually annotated from 17 different sources, e.g., Bengali TV drama, Audiobook, Talk show, Online class, and Islamic sermons to name a few. OOD-Speech is jointly the largest publicly available speech dataset, as well as the first out-of-distribution ASR benchmarking dataset for Bengali.
BaDLAD: A Large Multi-Domain Bengali Document Layout Analysis Dataset
Mar 10, 2023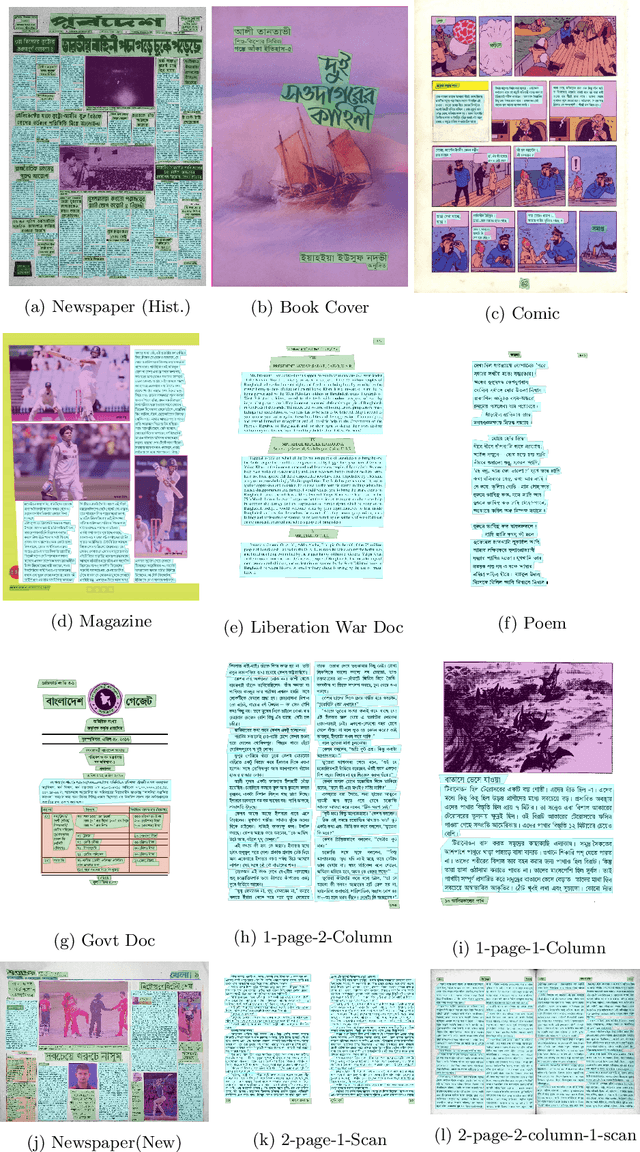
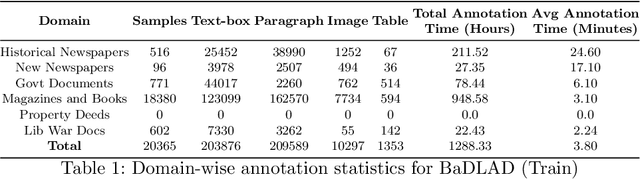
Abstract:While strides have been made in deep learning based Bengali Optical Character Recognition (OCR) in the past decade, the absence of large Document Layout Analysis (DLA) datasets has hindered the application of OCR in document transcription, e.g., transcribing historical documents and newspapers. Moreover, rule-based DLA systems that are currently being employed in practice are not robust to domain variations and out-of-distribution layouts. To this end, we present the first multidomain large Bengali Document Layout Analysis Dataset: BaDLAD. This dataset contains 33,695 human annotated document samples from six domains - i) books and magazines, ii) public domain govt. documents, iii) liberation war documents, iv) newspapers, v) historical newspapers, and vi) property deeds, with 710K polygon annotations for four unit types: text-box, paragraph, image, and table. Through preliminary experiments benchmarking the performance of existing state-of-the-art deep learning architectures for English DLA, we demonstrate the efficacy of our dataset in training deep learning based Bengali document digitization models.
Bengali Common Voice Speech Dataset for Automatic Speech Recognition
Jun 29, 2022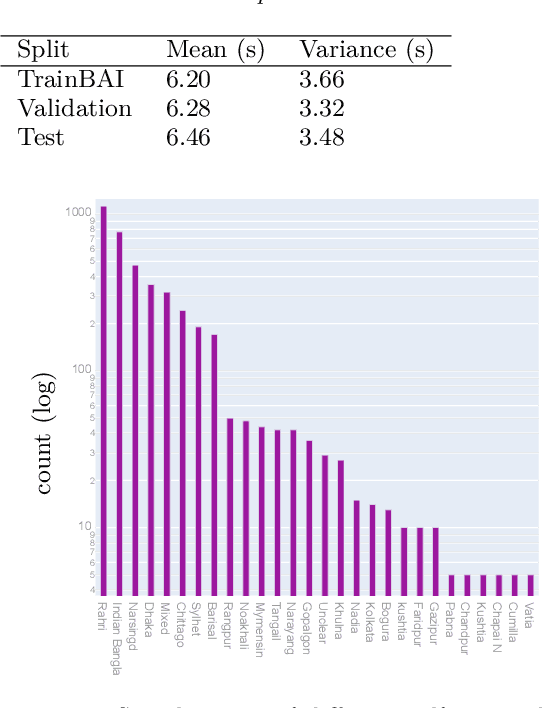
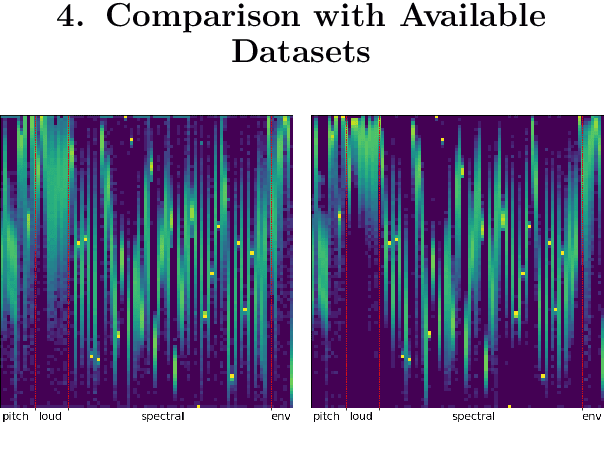

Abstract:Bengali is one of the most spoken languages in the world with over 300 million speakers globally. Despite its popularity, research into the development of Bengali speech recognition systems is hindered due to the lack of diverse open-source datasets. As a way forward, we have crowdsourced the Bengali Common Voice Speech Dataset, which is a sentence-level automatic speech recognition corpus. Collected on the Mozilla Common Voice platform, the dataset is part of an ongoing campaign that has led to the collection of over 400 hours of data in 2 months and is growing rapidly. Our analysis shows that this dataset has more speaker, phoneme, and environmental diversity compared to the OpenSLR Bengali ASR dataset, the largest existing open-source Bengali speech dataset. We present insights obtained from the dataset and discuss key linguistic challenges that need to be addressed in future versions. Additionally, we report the current performance of a few Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) algorithms and set a benchmark for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge