Susmit Agrawal
Walking the Web of Concept-Class Relationships in Incrementally Trained Interpretable Models
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Concept-based methods have emerged as a promising direction to develop interpretable neural networks in standard supervised settings. However, most works that study them in incremental settings assume either a static concept set across all experiences or assume that each experience relies on a distinct set of concepts. In this work, we study concept-based models in a more realistic, dynamic setting where new classes may rely on older concepts in addition to introducing new concepts themselves. We show that concepts and classes form a complex web of relationships, which is susceptible to degradation and needs to be preserved and augmented across experiences. We introduce new metrics to show that existing concept-based models cannot preserve these relationships even when trained using methods to prevent catastrophic forgetting, since they cannot handle forgetting at concept, class, and concept-class relationship levels simultaneously. To address these issues, we propose a novel method - MuCIL - that uses multimodal concepts to perform classification without increasing the number of trainable parameters across experiences. The multimodal concepts are aligned to concepts provided in natural language, making them interpretable by design. Through extensive experimentation, we show that our approach obtains state-of-the-art classification performance compared to other concept-based models, achieving over 2$\times$ the classification performance in some cases. We also study the ability of our model to perform interventions on concepts, and show that it can localize visual concepts in input images, providing post-hoc interpretations.
Analyzing Memorization in Large Language Models through the Lens of Model Attribution
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are prevalent in modern applications but often memorize training data, leading to privacy breaches and copyright issues. Existing research has mainly focused on posthoc analyses, such as extracting memorized content or developing memorization metrics, without exploring the underlying architectural factors that contribute to memorization. In this work, we investigate memorization from an architectural lens by analyzing how attention modules at different layers impact its memorization and generalization performance. Using attribution techniques, we systematically intervene in the LLM architecture by bypassing attention modules at specific blocks while keeping other components like layer normalization and MLP transformations intact. We provide theorems analyzing our intervention mechanism from a mathematical view, bounding the difference in layer outputs with and without our attributions. Our theoretical and empirical analyses reveal that attention modules in deeper transformer blocks are primarily responsible for memorization, whereas earlier blocks are crucial for the models generalization and reasoning capabilities. We validate our findings through comprehensive experiments on different LLM families (Pythia and GPTNeo) and five benchmark datasets. Our insights offer a practical approach to mitigate memorization in LLMs while preserving their performance, contributing to safer and more ethical deployment in real world applications.
ISLTranslate: Dataset for Translating Indian Sign Language
Jul 11, 2023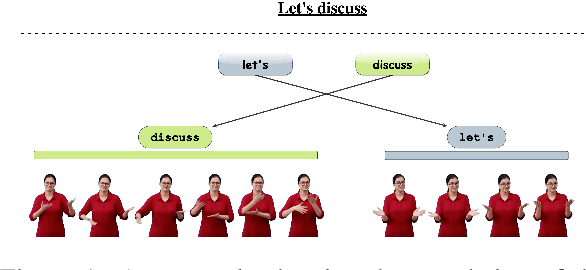
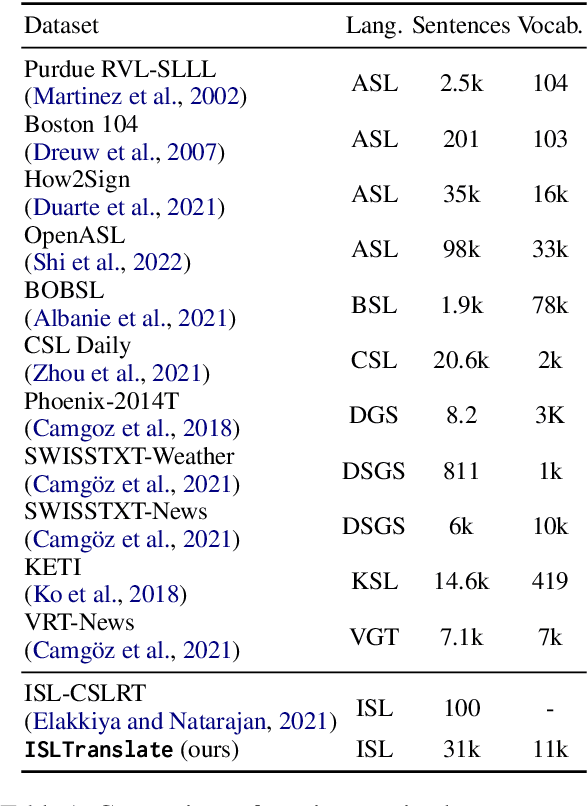
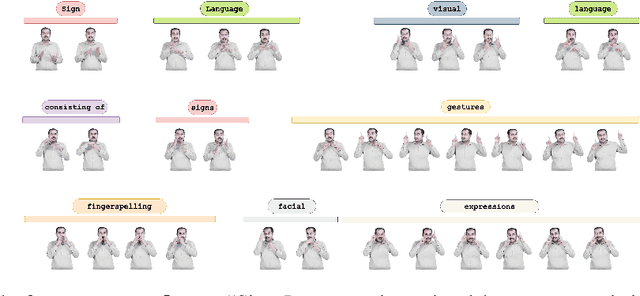

Abstract:Sign languages are the primary means of communication for many hard-of-hearing people worldwide. Recently, to bridge the communication gap between the hard-of-hearing community and the rest of the population, several sign language translation datasets have been proposed to enable the development of statistical sign language translation systems. However, there is a dearth of sign language resources for the Indian sign language. This resource paper introduces ISLTranslate, a translation dataset for continuous Indian Sign Language (ISL) consisting of 31k ISL-English sentence/phrase pairs. To the best of our knowledge, it is the largest translation dataset for continuous Indian Sign Language. We provide a detailed analysis of the dataset. To validate the performance of existing end-to-end Sign language to spoken language translation systems, we benchmark the created dataset with a transformer-based model for ISL translation.
Hierarchical Semantic Regularization of Latent Spaces in StyleGANs
Aug 07, 2022
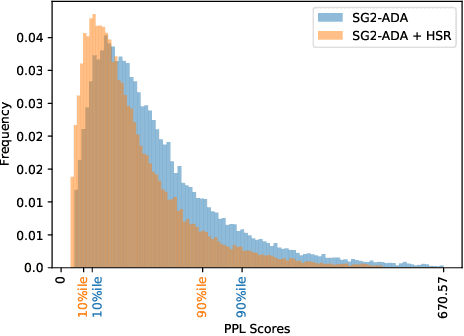
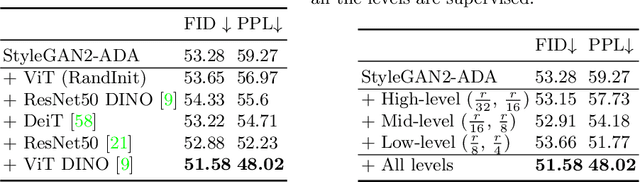
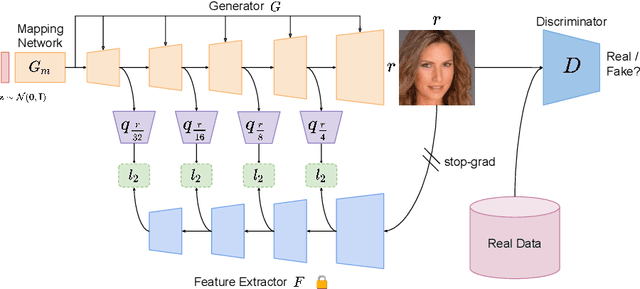
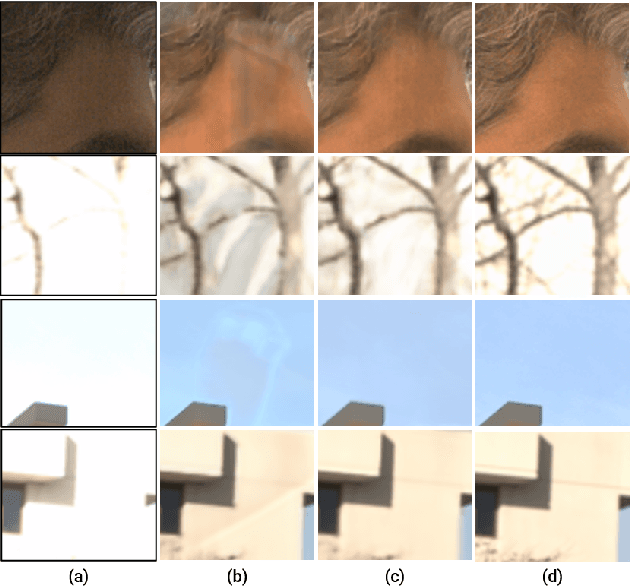
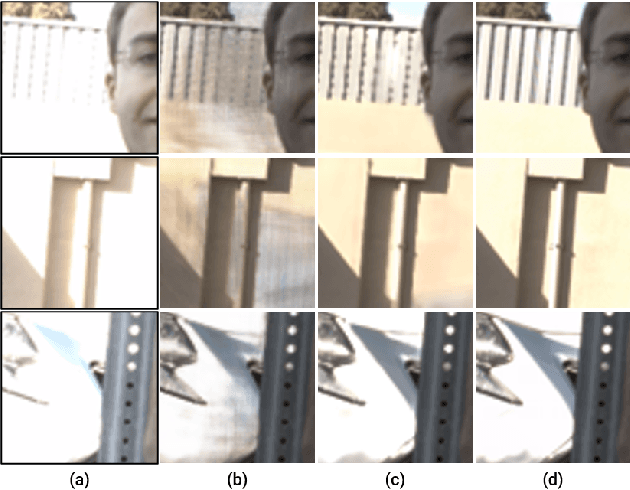
Abstract:Progress in GANs has enabled the generation of high-resolution photorealistic images of astonishing quality. StyleGANs allow for compelling attribute modification on such images via mathematical operations on the latent style vectors in the W/W+ space that effectively modulate the rich hierarchical representations of the generator. Such operations have recently been generalized beyond mere attribute swapping in the original StyleGAN paper to include interpolations. In spite of many significant improvements in StyleGANs, they are still seen to generate unnatural images. The quality of the generated images is predicated on two assumptions; (a) The richness of the hierarchical representations learnt by the generator, and, (b) The linearity and smoothness of the style spaces. In this work, we propose a Hierarchical Semantic Regularizer (HSR) which aligns the hierarchical representations learnt by the generator to corresponding powerful features learnt by pretrained networks on large amounts of data. HSR is shown to not only improve generator representations but also the linearity and smoothness of the latent style spaces, leading to the generation of more natural-looking style-edited images. To demonstrate improved linearity, we propose a novel metric - Attribute Linearity Score (ALS). A significant reduction in the generation of unnatural images is corroborated by improvement in the Perceptual Path Length (PPL) metric by 16.19% averaged across different standard datasets while simultaneously improving the linearity of attribute-change in the attribute editing tasks.
Segmentation Guided Deep HDR Deghosting
Jul 04, 2022
Abstract:We present a motion segmentation guided convolutional neural network (CNN) approach for high dynamic range (HDR) image deghosting. First, we segment the moving regions in the input sequence using a CNN. Then, we merge static and moving regions separately with different fusion networks and combine fused features to generate the final ghost-free HDR image. Our motion segmentation guided HDR fusion approach offers significant advantages over existing HDR deghosting methods. First, by segmenting the input sequence into static and moving regions, our proposed approach learns effective fusion rules for various challenging saturation and motion types. Second, we introduce a novel memory network that accumulates the necessary features required to generate plausible details in the saturated regions. The proposed method outperforms nine existing state-of-the-art methods on two publicly available datasets and generates visually pleasing ghost-free HDR results. We also present a large-scale motion segmentation dataset of 3683 varying exposure images to benefit the research community.
LEAD: Self-Supervised Landmark Estimation by Aligning Distributions of Feature Similarity
Apr 06, 2022
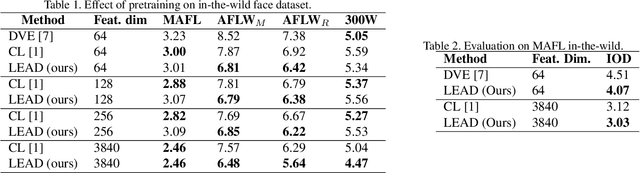


Abstract:In this work, we introduce LEAD, an approach to discover landmarks from an unannotated collection of category-specific images. Existing works in self-supervised landmark detection are based on learning dense (pixel-level) feature representations from an image, which are further used to learn landmarks in a semi-supervised manner. While there have been advances in self-supervised learning of image features for instance-level tasks like classification, these methods do not ensure dense equivariant representations. The property of equivariance is of interest for dense prediction tasks like landmark estimation. In this work, we introduce an approach to enhance the learning of dense equivariant representations in a self-supervised fashion. We follow a two-stage training approach: first, we train a network using the BYOL objective which operates at an instance level. The correspondences obtained through this network are further used to train a dense and compact representation of the image using a lightweight network. We show that having such a prior in the feature extractor helps in landmark detection, even under drastically limited number of annotations while also improving generalization across scale variations.
SISL:Self-Supervised Image Signature Learning for Splicing Detection and Localization
Mar 15, 2022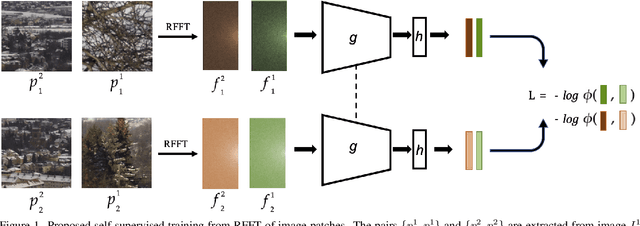
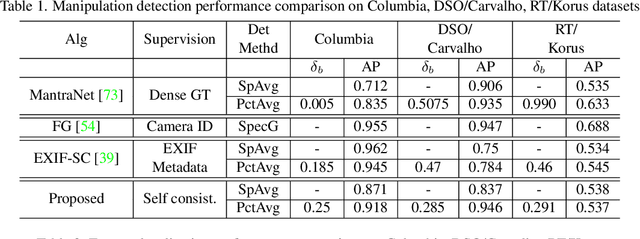
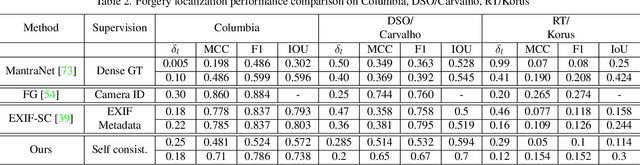
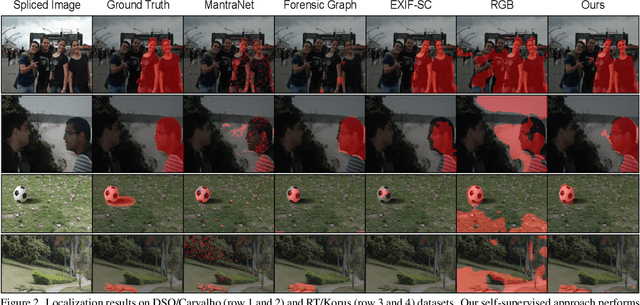
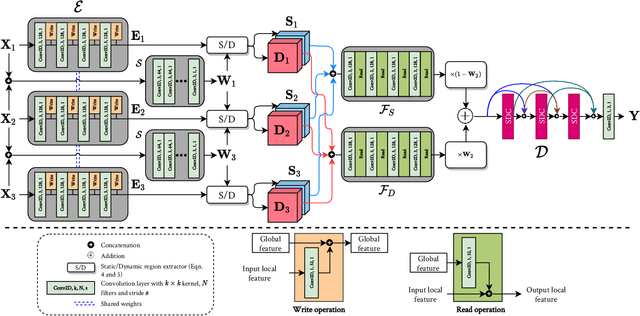
Abstract:Recent algorithms for image manipulation detection almost exclusively use deep network models. These approaches require either dense pixelwise groundtruth masks, camera ids, or image metadata to train the networks. On one hand, constructing a training set to represent the countless tampering possibilities is impractical. On the other hand, social media platforms or commercial applications are often constrained to remove camera ids as well as metadata from images. A self-supervised algorithm for training manipulation detection models without dense groundtruth or camera/image metadata would be extremely useful for many forensics applications. In this paper, we propose self-supervised approach for training splicing detection/localization models from frequency transforms of images. To identify the spliced regions, our deep network learns a representation to capture an image specific signature by enforcing (image) self consistency . We experimentally demonstrate that our proposed model can yield similar or better performances of multiple existing methods on standard datasets without relying on labels or metadata.
Self-Gated Memory Recurrent Network for Efficient Scalable HDR Deghosting
Dec 24, 2021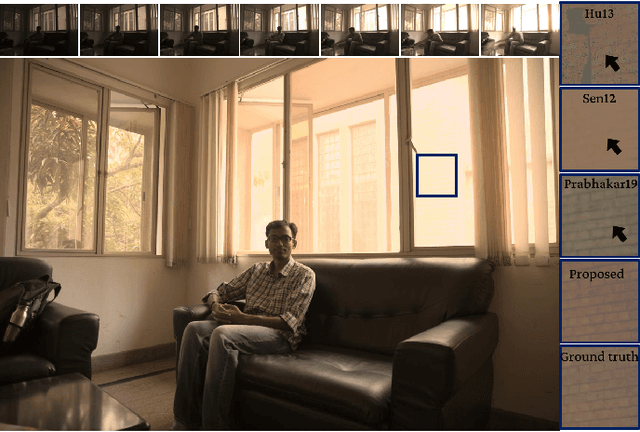

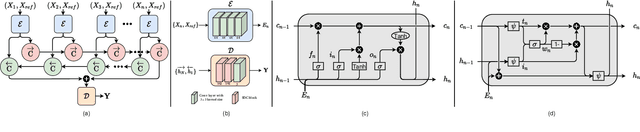

Abstract:We propose a novel recurrent network-based HDR deghosting method for fusing arbitrary length dynamic sequences. The proposed method uses convolutional and recurrent architectures to generate visually pleasing, ghosting-free HDR images. We introduce a new recurrent cell architecture, namely Self-Gated Memory (SGM) cell, that outperforms the standard LSTM cell while containing fewer parameters and having faster running times. In the SGM cell, the information flow through a gate is controlled by multiplying the gate's output by a function of itself. Additionally, we use two SGM cells in a bidirectional setting to improve output quality. The proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing HDR deghosting methods quantitatively across three publicly available datasets while simultaneously achieving scalability to fuse variable-length input sequence without necessitating re-training. Through extensive ablations, we demonstrate the importance of individual components in our proposed approach. The code is available at https://val.cds.iisc.ac.in/HDR/HDRRNN/index.html.
* 12 pages
Multilingual Medical Question Answering and Information Retrieval for Rural Health Intelligence Access
Jun 02, 2021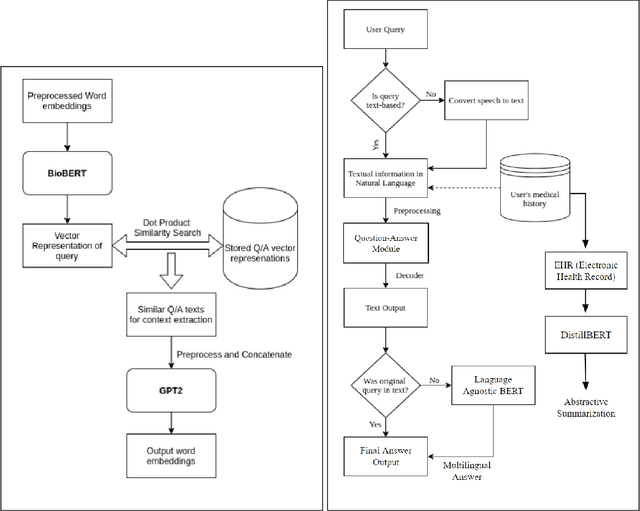
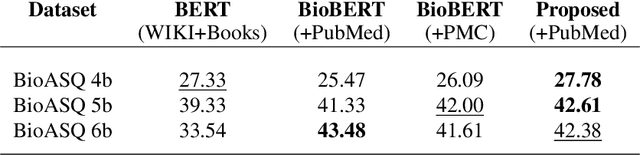
Abstract:In rural regions of several developing countries, access to quality healthcare, medical infrastructure, and professional diagnosis is largely unavailable. Many of these regions are gradually gaining access to internet infrastructure, although not with a strong enough connection to allow for sustained communication with a medical practitioner. Several deaths resulting from this lack of medical access, absence of patient's previous health records, and the unavailability of information in indigenous languages can be easily prevented. In this paper, we describe an approach leveraging the phenomenal progress in Machine Learning and NLP (Natural Language Processing) techniques to design a model that is low-resource, multilingual, and a preliminary first-point-of-contact medical assistant. Our contribution includes defining the NLP pipeline required for named-entity-recognition, language-agnostic sentence embedding, natural language translation, information retrieval, question answering, and generative pre-training for final query processing. We obtain promising results for this pipeline and preliminary results for EHR (Electronic Health Record) analysis with text summarization for medical practitioners to peruse for their diagnosis. Through this NLP pipeline, we aim to provide preliminary medical information to the user and do not claim to supplant diagnosis from qualified medical practitioners. Using the input from subject matter experts, we have compiled a large corpus to pre-train and fine-tune our BioBERT based NLP model for the specific tasks. We expect recent advances in NLP architectures, several of which are efficient and privacy-preserving models, to further the impact of our solution and improve on individual task performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge