Srikar Yellapragada
TICON: A Slide-Level Tile Contextualizer for Histopathology Representation Learning
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:The interpretation of small tiles in large whole slide images (WSI) often needs a larger image context. We introduce TICON, a transformer-based tile representation contextualizer that produces rich, contextualized embeddings for ''any'' application in computational pathology. Standard tile encoder-based pipelines, which extract embeddings of tiles stripped from their context, fail to model the rich slide-level information essential for both local and global tasks. Furthermore, different tile-encoders excel at different downstream tasks. Therefore, a unified model is needed to contextualize embeddings derived from ''any'' tile-level foundation model. TICON addresses this need with a single, shared encoder, pretrained using a masked modeling objective to simultaneously unify and contextualize representations from diverse tile-level pathology foundation models. Our experiments demonstrate that TICON-contextualized embeddings significantly improve performance across many different tasks, establishing new state-of-the-art results on tile-level benchmarks (i.e., HEST-Bench, THUNDER, CATCH) and slide-level benchmarks (i.e., Patho-Bench). Finally, we pretrain an aggregator on TICON to form a slide-level foundation model, using only 11K WSIs, outperforming SoTA slide-level foundation models pretrained with up to 350K WSIs.
PixCell: A generative foundation model for digital histopathology images
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:The digitization of histology slides has revolutionized pathology, providing massive datasets for cancer diagnosis and research. Contrastive self-supervised and vision-language models have been shown to effectively mine large pathology datasets to learn discriminative representations. On the other hand, generative models, capable of synthesizing realistic and diverse images, present a compelling solution to address unique problems in pathology that involve synthesizing images; overcoming annotated data scarcity, enabling privacy-preserving data sharing, and performing inherently generative tasks, such as virtual staining. We introduce PixCell, the first diffusion-based generative foundation model for histopathology. We train PixCell on PanCan-30M, a vast, diverse dataset derived from 69,184 H\&E-stained whole slide images covering various cancer types. We employ a progressive training strategy and a self-supervision-based conditioning that allows us to scale up training without any annotated data. PixCell generates diverse and high-quality images across multiple cancer types, which we find can be used in place of real data to train a self-supervised discriminative model. Synthetic images shared between institutions are subject to fewer regulatory barriers than would be the case with real clinical images. Furthermore, we showcase the ability to precisely control image generation using a small set of annotated images, which can be used for both data augmentation and educational purposes. Testing on a cell segmentation task, a mask-guided PixCell enables targeted data augmentation, improving downstream performance. Finally, we demonstrate PixCell's ability to use H\&E structural staining to infer results from molecular marker studies; we use this capability to infer IHC staining from H\&E images. Our trained models are publicly released to accelerate research in computational pathology.
PathSegDiff: Pathology Segmentation using Diffusion model representations
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Image segmentation is crucial in many computational pathology pipelines, including accurate disease diagnosis, subtyping, outcome, and survivability prediction. The common approach for training a segmentation model relies on a pre-trained feature extractor and a dataset of paired image and mask annotations. These are used to train a lightweight prediction model that translates features into per-pixel classes. The choice of the feature extractor is central to the performance of the final segmentation model, and recent literature has focused on finding tasks to pre-train the feature extractor. In this paper, we propose PathSegDiff, a novel approach for histopathology image segmentation that leverages Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) as pre-trained featured extractors. Our method utilizes a pathology-specific LDM, guided by a self-supervised encoder, to extract rich semantic information from H\&E stained histopathology images. We employ a simple, fully convolutional network to process the features extracted from the LDM and generate segmentation masks. Our experiments demonstrate significant improvements over traditional methods on the BCSS and GlaS datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of domain-specific diffusion pre-training in capturing intricate tissue structures and enhancing segmentation accuracy in histopathology images.
GECKO: Gigapixel Vision-Concept Contrastive Pretraining in Histopathology
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Pretraining a Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) aggregator enables the derivation of Whole Slide Image (WSI)-level embeddings from patch-level representations without supervision. While recent multimodal MIL pretraining approaches leveraging auxiliary modalities have demonstrated performance gains over unimodal WSI pretraining, the acquisition of these additional modalities necessitates extensive clinical profiling. This requirement increases costs and limits scalability in existing WSI datasets lacking such paired modalities. To address this, we propose Gigapixel Vision-Concept Knowledge Contrastive pretraining (GECKO), which aligns WSIs with a Concept Prior derived from the available WSIs. First, we derive an inherently interpretable concept prior by computing the similarity between each WSI patch and textual descriptions of predefined pathology concepts. GECKO then employs a dual-branch MIL network: one branch aggregates patch embeddings into a WSI-level deep embedding, while the other aggregates the concept prior into a corresponding WSI-level concept embedding. Both aggregated embeddings are aligned using a contrastive objective, thereby pretraining the entire dual-branch MIL model. Moreover, when auxiliary modalities such as transcriptomics data are available, GECKO seamlessly integrates them. Across five diverse tasks, GECKO consistently outperforms prior unimodal and multimodal pretraining approaches while also delivering clinically meaningful interpretability that bridges the gap between computational models and pathology expertise. Code is made available at https://github.com/bmi-imaginelab/GECKO
Pathology Image Compression with Pre-trained Autoencoders
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:The growing volume of high-resolution Whole Slide Images in digital histopathology poses significant storage, transmission, and computational efficiency challenges. Standard compression methods, such as JPEG, reduce file sizes but often fail to preserve fine-grained phenotypic details critical for downstream tasks. In this work, we repurpose autoencoders (AEs) designed for Latent Diffusion Models as an efficient learned compression framework for pathology images. We systematically benchmark three AE models with varying compression levels and evaluate their reconstruction ability using pathology foundation models. We introduce a fine-tuning strategy to further enhance reconstruction fidelity that optimizes a pathology-specific learned perceptual metric. We validate our approach on downstream tasks, including segmentation, patch classification, and multiple instance learning, showing that replacing images with AE-compressed reconstructions leads to minimal performance degradation. Additionally, we propose a K-means clustering-based quantization method for AE latents, improving storage efficiency while maintaining reconstruction quality. We provide the weights of the fine-tuned autoencoders at https://huggingface.co/collections/StonyBrook-CVLab/pathology-fine-tuned-aes-67d45f223a659ff2e3402dd0.
Leveraging Registers in Vision Transformers for Robust Adaptation
Jan 08, 2025


Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown success across a variety of tasks due to their ability to capture global image representations. Recent studies have identified the existence of high-norm tokens in ViTs, which can interfere with unsupervised object discovery. To address this, the use of "registers" which are additional tokens that isolate high norm patch tokens while capturing global image-level information has been proposed. While registers have been studied extensively for object discovery, their generalization properties particularly in out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios, remains underexplored. In this paper, we examine the utility of register token embeddings in providing additional features for improving generalization and anomaly rejection. To that end, we propose a simple method that combines the special CLS token embedding commonly employed in ViTs with the average-pooled register embeddings to create feature representations which are subsequently used for training a downstream classifier. We find that this enhances OOD generalization and anomaly rejection, while maintaining in-distribution (ID) performance. Extensive experiments across multiple ViT backbones trained with and without registers reveal consistent improvements of 2-4\% in top-1 OOD accuracy and a 2-3\% reduction in false positive rates for anomaly detection. Importantly, these gains are achieved without additional computational overhead.
Gen-SIS: Generative Self-augmentation Improves Self-supervised Learning
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) methods have emerged as strong visual representation learners by training an image encoder to maximize similarity between features of different views of the same image. To perform this view-invariance task, current SSL algorithms rely on hand-crafted augmentations such as random cropping and color jittering to create multiple views of an image. Recently, generative diffusion models have been shown to improve SSL by providing a wider range of data augmentations. However, these diffusion models require pre-training on large-scale image-text datasets, which might not be available for many specialized domains like histopathology. In this work, we introduce Gen-SIS, a diffusion-based augmentation technique trained exclusively on unlabeled image data, eliminating any reliance on external sources of supervision such as text captions. We first train an initial SSL encoder on a dataset using only hand-crafted augmentations. We then train a diffusion model conditioned on embeddings from that SSL encoder. Following training, given an embedding of the source image, this diffusion model can synthesize its diverse views. We show that these `self-augmentations', i.e. generative augmentations based on the vanilla SSL encoder embeddings, facilitate the training of a stronger SSL encoder. Furthermore, based on the ability to interpolate between images in the encoder latent space, we introduce the novel pretext task of disentangling the two source images of an interpolated synthetic image. We validate Gen-SIS's effectiveness by demonstrating performance improvements across various downstream tasks in both natural images, which are generally object-centric, as well as digital histopathology images, which are typically context-based.
ZoomLDM: Latent Diffusion Model for multi-scale image generation
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models have revolutionized image generation, yet several challenges restrict their application to large-image domains, such as digital pathology and satellite imagery. Given that it is infeasible to directly train a model on 'whole' images from domains with potential gigapixel sizes, diffusion-based generative methods have focused on synthesizing small, fixed-size patches extracted from these images. However, generating small patches has limited applicability since patch-based models fail to capture the global structures and wider context of large images, which can be crucial for synthesizing (semantically) accurate samples. In this paper, to overcome this limitation, we present ZoomLDM, a diffusion model tailored for generating images across multiple scales. Central to our approach is a novel magnification-aware conditioning mechanism that utilizes self-supervised learning (SSL) embeddings and allows the diffusion model to synthesize images at different 'zoom' levels, i.e., fixed-size patches extracted from large images at varying scales. ZoomLDM achieves state-of-the-art image generation quality across all scales, excelling particularly in the data-scarce setting of generating thumbnails of entire large images. The multi-scale nature of ZoomLDM unlocks additional capabilities in large image generation, enabling computationally tractable and globally coherent image synthesis up to $4096 \times 4096$ pixels and $4\times$ super-resolution. Additionally, multi-scale features extracted from ZoomLDM are highly effective in multiple instance learning experiments. We provide high-resolution examples of the generated images on our website https://histodiffusion.github.io/docs/publications/zoomldm/.
$\infty$-Brush: Controllable Large Image Synthesis with Diffusion Models in Infinite Dimensions
Jul 20, 2024



Abstract:Synthesizing high-resolution images from intricate, domain-specific information remains a significant challenge in generative modeling, particularly for applications in large-image domains such as digital histopathology and remote sensing. Existing methods face critical limitations: conditional diffusion models in pixel or latent space cannot exceed the resolution on which they were trained without losing fidelity, and computational demands increase significantly for larger image sizes. Patch-based methods offer computational efficiency but fail to capture long-range spatial relationships due to their overreliance on local information. In this paper, we introduce a novel conditional diffusion model in infinite dimensions, $\infty$-Brush for controllable large image synthesis. We propose a cross-attention neural operator to enable conditioning in function space. Our model overcomes the constraints of traditional finite-dimensional diffusion models and patch-based methods, offering scalability and superior capability in preserving global image structures while maintaining fine details. To our best knowledge, $\infty$-Brush is the first conditional diffusion model in function space, that can controllably synthesize images at arbitrary resolutions of up to $4096\times4096$ pixels. The code is available at https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/infinity-brush.
Learned representation-guided diffusion models for large-image generation
Dec 12, 2023
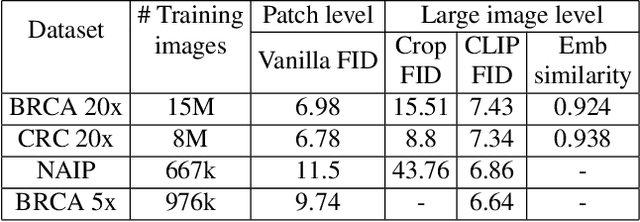

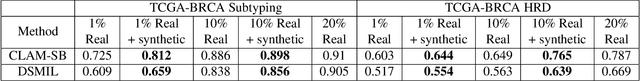
Abstract:To synthesize high-fidelity samples, diffusion models typically require auxiliary data to guide the generation process. However, it is impractical to procure the painstaking patch-level annotation effort required in specialized domains like histopathology and satellite imagery; it is often performed by domain experts and involves hundreds of millions of patches. Modern-day self-supervised learning (SSL) representations encode rich semantic and visual information. In this paper, we posit that such representations are expressive enough to act as proxies to fine-grained human labels. We introduce a novel approach that trains diffusion models conditioned on embeddings from SSL. Our diffusion models successfully project these features back to high-quality histopathology and remote sensing images. In addition, we construct larger images by assembling spatially consistent patches inferred from SSL embeddings, preserving long-range dependencies. Augmenting real data by generating variations of real images improves downstream classifier accuracy for patch-level and larger, image-scale classification tasks. Our models are effective even on datasets not encountered during training, demonstrating their robustness and generalizability. Generating images from learned embeddings is agnostic to the source of the embeddings. The SSL embeddings used to generate a large image can either be extracted from a reference image, or sampled from an auxiliary model conditioned on any related modality (e.g. class labels, text, genomic data). As proof of concept, we introduce the text-to-large image synthesis paradigm where we successfully synthesize large pathology and satellite images out of text descriptions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge