Sing Chun Lee
Exploring Partial Intrinsic and Extrinsic Symmetry in 3D Medical Imaging
Mar 04, 2020
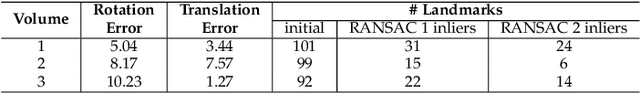


Abstract:We present a novel methodology to detect imperfect bilateral symmetry in CT of human anatomy. In this paper, the structurally symmetric nature of the pelvic bone is explored and is used to provide interventional image augmentation for treatment of unilateral fractures in patients with traumatic injuries. The mathematical basis of our solution is on the incorporation of attributes and characteristics that satisfy the properties of intrinsic and extrinsic symmetry and are robust to outliers. In the first step, feature points that satisfy intrinsic symmetry are automatically detected in the M\"obius space defined on the CT data. These features are then pruned via a two-stage RANSAC to attain correspondences that satisfy also the extrinsic symmetry. Then, a disparity function based on Tukey's biweight robust estimator is introduced and minimized to identify a symmetry plane parametrization that yields maximum contralateral similarity. Finally, a novel regularization term is introduced to enhance similarity between bone density histograms across the partial symmetry plane, relying on the important biological observation that, even if injured, the dislocated bone segments remain within the body. Our extensive evaluations on various cases of common fracture types demonstrate the validity of the novel concepts and the robustness and accuracy of the proposed method.
Pivot calibration concept for sensor attached mobile c-arms
Jan 09, 2020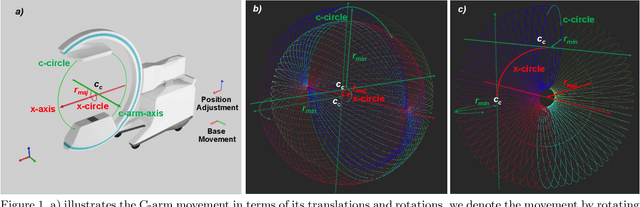
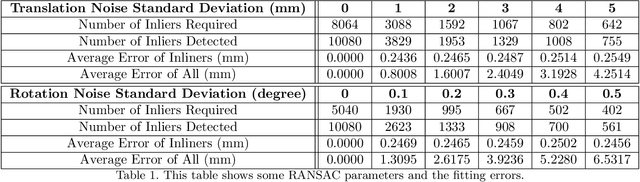


Abstract:Medical augmented reality has been actively studied for decades and many methods have been proposed torevolutionize clinical procedures. One example is the camera augmented mobile C-arm (CAMC), which providesa real-time video augmentation onto medical images by rigidly mounting and calibrating a camera to the imagingdevice. Since then, several CAMC variations have been suggested by calibrating 2D/3D cameras, trackers, andmore recently a Microsoft HoloLens to the C-arm. Different calibration methods have been applied to establishthe correspondence between the rigidly attached sensor and the imaging device. A crucial step for these methodsis the acquisition of X-Ray images or 3D reconstruction volumes; therefore, requiring the emission of ionizingradiation. In this work, we analyze the mechanical motion of the device and propose an alternatative methodto calibrate sensors to the C-arm without emitting any radiation. Given a sensor is rigidly attached to thedevice, we introduce an extended pivot calibration concept to compute the fixed translation from the sensor tothe C-arm rotation center. The fixed relationship between the sensor and rotation center can be formulated as apivot calibration problem with the pivot point moving on a locus. Our method exploits the rigid C-arm motiondescribing a Torus surface to solve this calibration problem. We explain the geometry of the C-arm motion andits relation to the attached sensor, propose a calibration algorithm and show its robustness against noise, as wellas trajectory and observed pose density by computer simulations. We discuss this geometric-based formulationand its potential extensions to different C-arm applications.
LumiPath - Towards Real-time Physically-based Rendering on Embedded Devices
Mar 09, 2019



Abstract:As the computational power of toady's devices increases, real-time physically-based rendering becomes possible, and is rapidly gaining attention across a variety of domains. These include gaming, where physically-based rendering enhances immersion and overall entertainment experience, all the way to medicine, where it constitutes a powerful tool for intuitive volumetric data visualization. However, leveraging the obvious benefits of physically-based rendering (also referred to as photo-realistic rendering) remains challenging on embedded devices such as optical see-through head-mounted displays because of their limited computational power, and restricted memory usage and power consumption. We propose methods that aim at overcoming these limitations, fueling the implementation of real-time physically-based rendering on embedded devices. We navigate the compromise between memory requirement, computational power, and image quality to achieve reasonable rendering results by introducing a flexible representation of plenoptic functions and adapting a fast approximation algorithm for image generation from our plenoptic functions. We conclude by discussing potential applications and limitations of the proposed method.
Closing the Calibration Loop: An Inside-out-tracking Paradigm for Augmented Reality in Orthopedic Surgery
Mar 22, 2018



Abstract:In percutaneous orthopedic interventions the surgeon attempts to reduce and fixate fractures in bony structures. The complexity of these interventions arises when the surgeon performs the challenging task of navigating surgical tools percutaneously only under the guidance of 2D interventional X-ray imaging. Moreover, the intra-operatively acquired data is only visualized indirectly on external displays. In this work, we propose a flexible Augmented Reality (AR) paradigm using optical see-through head mounted displays. The key technical contribution of this work includes the marker-less and dynamic tracking concept which closes the calibration loop between patient, C-arm and the surgeon. This calibration is enabled using Simultaneous Localization and Mapping of the environment of the operating theater. In return, the proposed solution provides in situ visualization of pre- and intra-operative 3D medical data directly at the surgical site. We demonstrate pre-clinical evaluation of a prototype system, and report errors for calibration and target registration. Finally, we demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed inside-out tracking system in achieving "bull's eye" view for C-arm-guided punctures. This AR solution provides an intuitive visualization of the anatomy and can simplify the hand-eye coordination for the orthopedic surgeon.
DeepDRR -- A Catalyst for Machine Learning in Fluoroscopy-guided Procedures
Mar 22, 2018


Abstract:Machine learning-based approaches outperform competing methods in most disciplines relevant to diagnostic radiology. Interventional radiology, however, has not yet benefited substantially from the advent of deep learning, in particular because of two reasons: 1) Most images acquired during the procedure are never archived and are thus not available for learning, and 2) even if they were available, annotations would be a severe challenge due to the vast amounts of data. When considering fluoroscopy-guided procedures, an interesting alternative to true interventional fluoroscopy is in silico simulation of the procedure from 3D diagnostic CT. In this case, labeling is comparably easy and potentially readily available, yet, the appropriateness of resulting synthetic data is dependent on the forward model. In this work, we propose DeepDRR, a framework for fast and realistic simulation of fluoroscopy and digital radiography from CT scans, tightly integrated with the software platforms native to deep learning. We use machine learning for material decomposition and scatter estimation in 3D and 2D, respectively, combined with analytic forward projection and noise injection to achieve the required performance. On the example of anatomical landmark detection in X-ray images of the pelvis, we demonstrate that machine learning models trained on DeepDRRs generalize to unseen clinically acquired data without the need for re-training or domain adaptation. Our results are promising and promote the establishment of machine learning in fluoroscopy-guided procedures.
Plan in 2D, execute in 3D: An augmented reality solution for cup placement in total hip arthroplasty
Jan 04, 2018Abstract:Reproducibly achieving proper implant alignment is a critical step in total hip arthroplasty (THA) procedures that has been shown to substantially affect patient outcome. In current practice, correct alignment of the acetabular cup is verified in C-arm X-ray images that are acquired in an anterior-posterior (AP) view. Favorable surgical outcome is, therefore, heavily dependent on the surgeon's experience in understanding the 3D orientation of a hemispheric implant from 2D AP projection images. This work proposes an easy to use intra-operative component planning system based on two C-arm X-ray images that is combined with 3D augmented reality (AR) visualization that simplifies impactor and cup placement according to the planning by providing a real-time RGBD data overlay. We evaluate the feasibility of our system in a user study comprising four orthopedic surgeons at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, and also report errors in translation, anteversion, and abduction as low as 1.98 mm, 1.10 degrees, and 0.53 degrees, respectively. The promising performance of this AR solution shows that deploying this system could eliminate the need for excessive radiation, simplify the intervention, and enable reproducibly accurate placement of acetabular implants.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge